SBASA35A June 2020 – October 2020 AMC3330-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Ratings
- 6.6 Insulation Specifications
- 6.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 6.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Timing Diagram
- 6.12 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 6.13 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.2 Isolation Channel Signal Transmission
The AMC3330-Q1 uses an on-off keying (OOK) modulation scheme to transmit the modulator output-bitstream across the capacitive SiO2-based isolation barrier. Figure 7-1 shows the block diagram of an isolation channel. The transmitter modulates the bitstream at TX IN with an internally generated, 480-MHz carrier and sends a burst across the isolation barrier to represent a digital one and sends a no signal to represent the digital zero. The receiver demodulates the signal after advanced signal conditioning and produces the output. The symmetrical design of each isolation channel improves the common-mode transient immunity (CMTI) performance and reduces the radiated emissions caused by the high-frequency carrier.
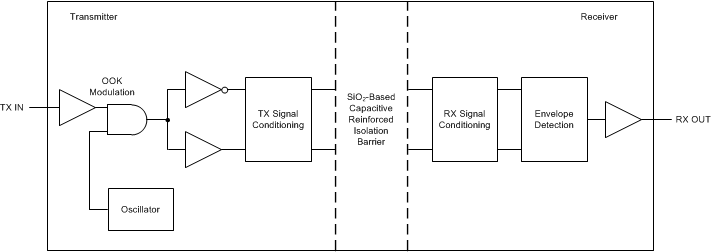 Figure 7-1 Block Diagram of an Isolation Channel
Figure 7-1 Block Diagram of an Isolation ChannelFigure 7-2 shows the concept of the on-off keying scheme.
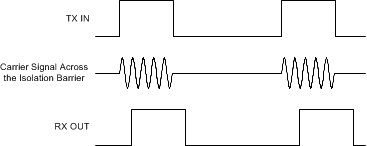 Figure 7-2 OOK-Based Modulation Scheme
Figure 7-2 OOK-Based Modulation Scheme