SBOU024C august 2004 – july 2023 PGA309
- 1
- Read This First
-
1Introduction
- 1.1 PGA309 Functional Description
- 1.2 Sensor Error Adjustment Range
- 1.3 Gain Scaling
- 1.4 Offset Adjustment
- 1.5 Voltage Reference
- 1.6 Sensor Excitation and Linearization
- 1.7 ADC for Temperature Sensing
- 1.8 External EEPROM and Temperature Coefficients
- 1.9 Fault Monitor
- 1.10 Over-Scale and Under-Scale Limits
- 1.11 Power-Up and Normal Operation
- 1.12 Digital Interface
- 1.13 Pin Configuration
- 2Detailed Description
- 3Operating Modes
-
4Digital Interface
- 4.1 Description
- 4.2 Two-Wire Interface
- 4.3 One-Wire Interface
- 4.4 One-Wire Interface Timeout
- 4.5 One-Wire Interface Timing Considerations
- 4.6 Two-Wire Access to External EEPROM
- 4.7 One-Wire Interface Initiated Two-Wire EEPROM Transactions
- 4.8 PGA309 Stand-Alone Mode and Two-Wire Transactions
- 4.9 PGA309 Two-Wire Bus Master Operation and Bus Sharing Considerations
- 4.10 One-Wire Operation with PRG Connected to VOUT
- 4.11 Four-Wire Modules and One-Wire Interface (PRG)
- 5Application Background
-
6Register Descriptions
- 6.1 Internal Register Overview
- 6.2
Internal Register Map
- 6.2.1 Register 0: Temp ADC Output Register (Read Only, Address Pointer = 00000)
- 6.2.2 Register 1: Fine Offset Adjust (Zero DAC) Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00001)
- 6.2.3 Register 2: Fine Gain Adjust (Gain DAC) Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00010)
- 6.2.4 Register 3: Reference Control and Linearization Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00011)
- 6.2.5 Register 4: PGA Coarse Offset Adjust and Gain Select/Output Amplifier Gain Select Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00100)
- 6.2.6 Register 5: PGA Configuration and Over/Under-Scale Limit Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00101)
- 6.2.7 Register 6: Temp ADC Control Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00110)
- 6.2.8 Register 7: Output Enable Counter Control Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00111)
- 6.2.9 Register 8: Alarm Status Register (Read Only, Address Pointer = 01000)
- A External EEPROM Example
- B Detailed Block Diagram
- C Glossary
- Revision History
5.1 Bridge Sensors
A typical bridge pressure sensor is shown in Figure 5-1. For a given bridge excitation voltage (VEXC), the output voltage of the bridge (VP − VN) is a voltage proportional to the pressure applied to the sensor.
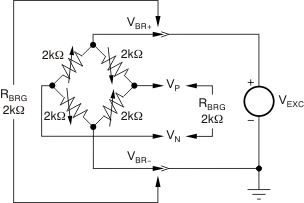 Figure 5-1 Typical Bridge Sensor
Figure 5-1 Typical Bridge SensorSpan is the scale factor for VP − VN at full-scale pressure input relative to the bridge excitation (VBR+ − VBR−). Span is also called FSO (Full-Scale Output), FSS (Full-Scale Sensitivity), Sensitivity, or Gain. For example, with a bridge excitation voltage of 5V, a 2mV/V FSS implies that the bridge output will be 10mV at full-scale pressure.
Offset, also known as Zero, is the output of the bridge (VP − VN) with zero pressure applied. Often a bridge sensor’s Zero may be equal to or greater than its FSS for a given excitation voltage. Figure 5-2 graphically illustrates the definition of Span and Offset.
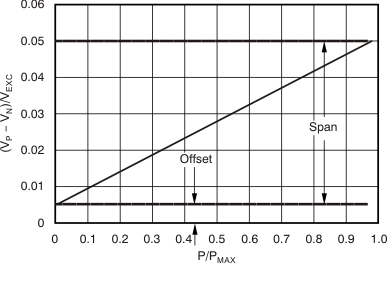 Figure 5-2 Example of Span and Offset
Figure 5-2 Example of Span and OffsetAn ideal sensor would have span and offset curves over temperature, as shown in Figure 5-3. Real-world sensors have span and offset changes that change over temperature. Both span and offset have variations at +25°C, linear changes with temperature, and nonlinear changes with temperature. Figure 5-4 and Figure 5-5 illustrate span and offset changes over temperature for a bridge sensor with second-order nonlinearities. TC1 coefficients represent a linear change with temperature, and TC2 a second-order change with temperature.
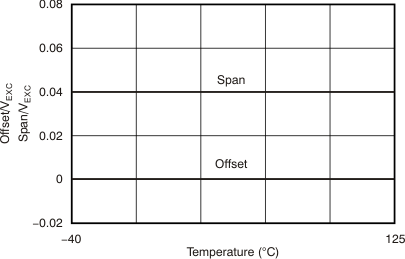 Figure 5-3 Ideal Span and Offset vs Temperature
Figure 5-3 Ideal Span and Offset vs Temperature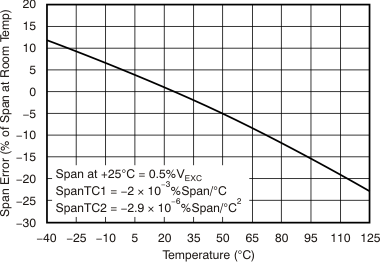 Figure 5-4 Effect of Nonlinearity on Bridge Sensor Span Over Temperature
Figure 5-4 Effect of Nonlinearity on Bridge Sensor Span Over Temperature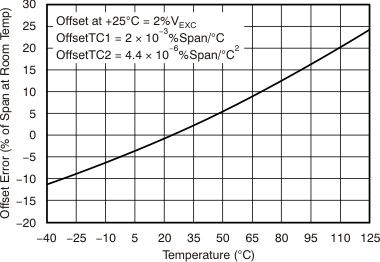 Figure 5-5 Effect of Nonlinearity on Bridge Sensor Offset Over Temperature
Figure 5-5 Effect of Nonlinearity on Bridge Sensor Offset Over TemperatureMany bridge sensors have a nonlinear output with applied pressure. Figure 5-6 shows the non-ideal curves for both a positive and negative nonlinear bridge sensor output with applied pressure. The PGA309 provides calibration over temperature for both span and offset, and has dedicated linearization circuitry to linearize many types of bridge sensors whose outputs are not linear with applied pressure.
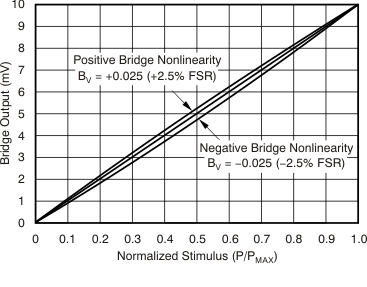 Figure 5-6 Non-Ideal Curves for Both a Positive and Negative Nonlinear Bridge Sensor Output with Applied Pressure
Figure 5-6 Non-Ideal Curves for Both a Positive and Negative Nonlinear Bridge Sensor Output with Applied Pressure