SBOU211A October 2018 – July 2025 INA105 , INA106 , INA132 , INA134 , INA137 , INA143 , INA152 , INA154 , INA157 , INA333 , INA592 , INA600
2.6.3.2 AC Coupled Output
It is possible to generate an ac coupled output by feeding the output of the diff-amp through an integrator and back to the reference pin. The output of the integrator drives the reference such that the dc voltage at the output of the diff-amp matches the voltage applied to the non-inverting terminal of the reference amplifier. R5 can be removed if the user desires to ground the input of the amplifier in dual supply operation. The cutoff frequency is set by the RC time constant of the integrator. This is sometimes preferable to using ac coupling capacitors at the input because capacitors tend to have wide tolerance ranges and mismatch in these capacitors can degrade the common-mode rejection of the amplifier. This can be implemented by placing a jumper on J7, removing R3, and populating R4 and C9 as shown in Figure 2-3.
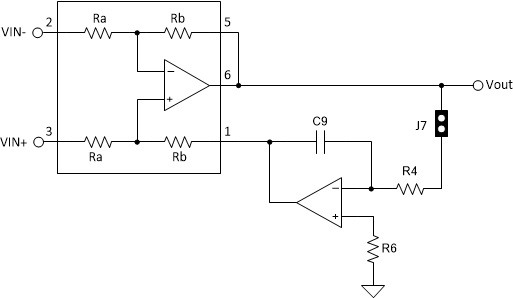 Figure 2-3 AC Coupling with Output Integrator
Figure 2-3 AC Coupling with Output Integrator