SCDA036 May 2022 TMUX8212
7 On-Resistance and Flatness
One disadvantage many multiplexer devices have is On-Resistance. Because of the architecture of many multiplexer devices, the On-Resistance can vary significantly across bias voltage. This can result in large distortions on the output. However, TI’s Flat On-Resistance family of multiplexers address this issue. These devices keep the On-Resistance flat across a wide bias range. As a result, the performance is more comparable to a Photorelay or mechanical relay. This Flat On-Resistance has significant benefits to system performance, reducing THD and ensuring signal integrity. These Flat On-Resistance multiplexers have extremely low distortion and bridge the performance gap to photorelays. An example of one of these TI multiplexers is the TMUX821x.
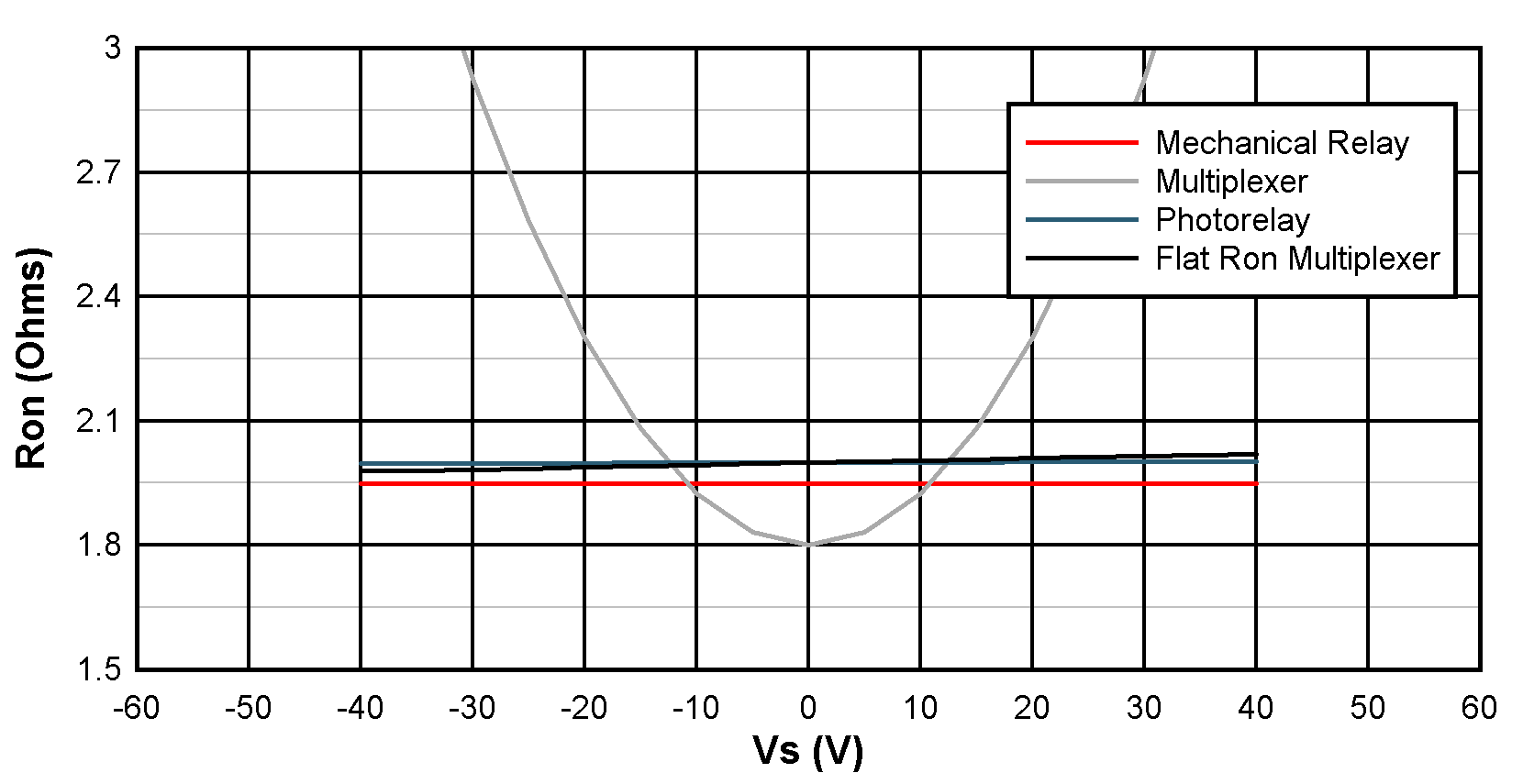 Figure 7-1 On-Resistance of a Mechanical
Relay, Photorelay, conventional Multiplexer, and TI’s Flat Ron Multiplexer
Figure 7-1 On-Resistance of a Mechanical
Relay, Photorelay, conventional Multiplexer, and TI’s Flat Ron Multiplexer