SCEU021A November 2019 – August 2021 TXB0101 , TXB0102 , TXB0104 , TXB0108-Q1
1.1.1 TXB Family
The TXB family uses two separate configurable power supply rails VCCA and VCCB with A ports tracking the VCCA supply and B ports tracking the VCCB supply. These devices are fully specified for partial-power-down applications using IOFF. The IOFF circuitry (SCEA026) disables the outputs, preventing damaging current backflow through the device when it is powered down. The VCC isolation feature ensures that if either VCC supply is powered down (0V), then the I/O ports are in a high-impedance state. Refer to the application note A guide to voltage translation with the TXB family for more on TXB family characteristics.
Weak driving capability is characteristic of auto-bidirectional translators, allowing the device output to be overridden by the external driver during a direction change, without the need for a separate DIR control pin. TXB devices are designed with buffered I/O architecture suitable for light load push-pull applications. During an edge transition, the One-shot (O.S) circuitry becomes active and lowers the effective output impedance. Once the transition is complete, the weak 4-kΩ buffer drives the output. During a DC state, only the series resistor drives the output, thus allowing the port to be overridden externally. Consequently, external pull-up or pull-down resistor values must be larger than 50-kΩ to avoid affecting VOH or VOL. Refer to the application note Effects of pull-up and pull-down resistors on TXB devices for further information.
Table 1-1 shows the comparison between the TXB, TXS and LSF Auto-Bidirectional families of TI.
| Metrics | TXB | TXS | LSF |
| Translation mechanism | Weak buffered translation | Passive translation with NMOS and internal pull-up resistors | Passive translation with NMOS and external pull-up resistors |
| Drive strength | Very low drive of 20ua due to 4K limiting buffer | No DC drive | No DC drive |
| Applications/ Interface | Push-pull applications | Open-drain applications | Push-pull and open-drain applications |
| Speed | Up to 140Mbps | Up to 24Mbps | High speed up to 200Mbps |
| Translation flexibility | Buffered and fixed translation on A and B ports | Integrated pull-up resistors-reduces BOM cost of the system; Fixed translation on A and B ports | Flexible translation due to external pull-up resistors |
| Frequency vs load balance trade-off | |||
| I/O ports | A ports referenced to Vcca and B ports referenced to Vccb | A ports referenced to Vcca and B ports referenced to Vccb | A ports not referenced to Vcca, B ports not referenced to Vccb; allows multi-voltage translation |
| Edge- acceleration | Integrated one-shot edge acceleration circuitry | Integrated one-shot edge acceleration circuitry | No integrated one-shot acceleration circuitry |
| Vih/Vil requirements | Datasheet spec has Vih/Vil specifications | Has Vih /Vil spec but no RON for the FET | No Vih / Vil conditions, has RON specifications |
| Additional care-about | VCCA<=VCCB | VCCA<=VCCB | VCCB>VCCA+0.8 V |
TXB-EVM is shown in Figure 1-1. Table 1-2 shows the packages supported by the TXB-EVM.
| Device | Package | Pins | Device Populated |
| TXB0101 | DCK (SC-70) | 6 | Yes |
| TXB0102 | DCU (VSSOP) | 8 | Yes |
| TXB0104 (TXB0104-Q1*)(1) | PW (TSSOP) | 14 | No |
| RUT (UQFN) | 12 | Yes | |
| TXB0108 | PW (TSSOP) | 20 | No |
| RGY (VQFN) | 20 | Yes |
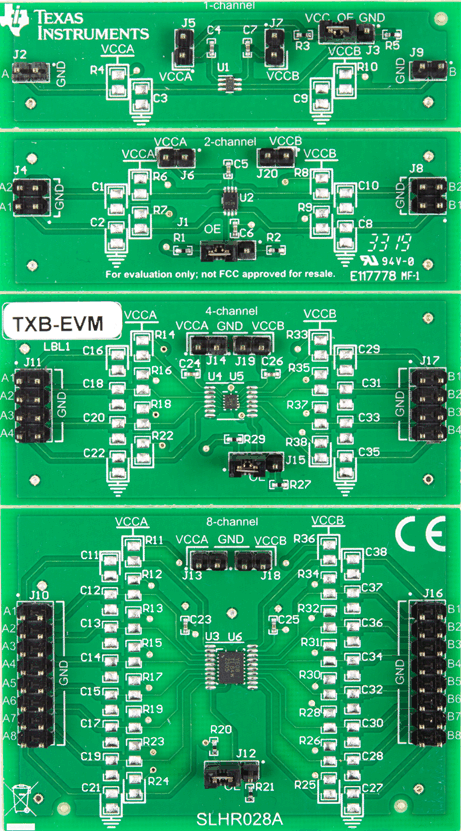 Figure 1-1 TXB-EVM
Figure 1-1 TXB-EVM