SLLSEV6C July 2017 – February 2021 TIOS101 , TIOS1013 , TIOS1015
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Current Limit Configuration
- 8.3.2 Current Fault Detection, Indication and Auto Recovery
- 8.3.3 Thermal Warning, Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.4 Fault Reporting (NFAULT)
- 8.3.5 Device Function Tables
- 8.3.6 The Integrated Voltage Regulator (LDO)
- 8.3.7 Reverse Polarity Protection
- 8.3.8 Integrated Surge Protection and Transient Waveform Tolerance
- 8.3.9 Power Up Sequence
- 8.3.10 Undervoltage Lock-Out (UVLO)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application Information Disclaimer
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
9.2.2.3 Driving Inductive Loads
The TIOS101(x) family is capable of magnetizing and demagnetizing inductive loads up to 1.5 H. These devices contain internal circuitry that enables fast demagnetization when configured as either P-switch or N-switch mode.
In P-switch configuration, the load inductor L is magnetized when the OUT pin is driven high. When the PNP is turned off, there is a significant amount of negative inductive kick back at the OUT pin. This voltage is clamped internally at about -75 V.
Similarly in N-switch configuration, the load inductor L is magnetized when the OUT pin is driven low. When the NPN is turned off, there is a significant amount of positive inductive kick back at the OUT pin. This voltage is clamped internally at about 75 V.
The equivalent protection circuits are shown in Figure 9-2 and Figure 9-3. The minimum value of the resistive load R can be calculated as:
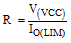
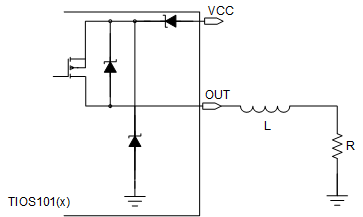 Figure 9-2 PNP Mode
Figure 9-2 PNP Mode Figure 9-3 NPN Mode
Figure 9-3 NPN Mode