SLVAE87B December 2020 – June 2025 BQ79600-Q1 , BQ79612-Q1 , BQ79614-Q1 , BQ79616-Q1 , BQ79652-Q1 , BQ79654-Q1 , BQ79656-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 NPN LDO Supply
- 2 AVDD, CVDD Outputs and DVDD, NEG5, REFHP and REFHM
- 3 OTP Programming
- 4 Cell Voltage Sense (VCn) and Cell Balancing (CBn)
- 5 Bus Bar Support
- 6 TSREF
- 7 General Purpose Input-Output (GPIO) Configurations
- 8 Base and Bridge Device Configuration
- 9 Daisy-Chain Stack Configuration
- 10Multidrop Configuration
- 11Main ADC Digital LPF
- 12AUX Anti Aliasing Filter (AAF)
- 13Layout Guidelines
- 14BCI Performance
- 15Common and Differential Mode Noise
- 16Summary
- 17References
- 18Revision History
13.1 Ground Planes
Establish a clean grounding scheme to make sure of best performance of the device. There are three ground pins (AVSS, DVSS, CVSS) for the internal power supplies of the device and one ground reference (REFHM) for the precision reference. There are noisy grounds and quiet grounds that are separated in the layout initially and joint together in a lower PCB layer. The external components (for example, bypass capacitors) are tied to the proper grounding group if possible to keep the separation of noisy and quiet grounds apart.
- AVSS ground:
- Bypass capacitor for these pins: BAT, VC0, CB0, LDOIN, TSREF
- Package lower pad
- DVSS ground:
- Bypass capacitor for DVDD
- GPIO filter capacitor (if used). This can also connect to AVSS ground plane if needed
- CVSS ground:
- Bypass capacitor for CVDD
- The bypass capacitors for COMHP/N and COMLP/N
- REFHM ground:
- Bypass capacitor for REFHP
- If possible, then separate out REFHM from AVSS on the signal connection layer and reconnect REFHM to the AVSS ground plane on a lower layer
Even on a PCB layer that is mainly for signal routing, a best practice to have as small an island of ground pour as possible to provide a low impedance ground, rather than simply by down the ground trace to an lower ground plane.

There is a strong recommendation to have a minimum of four layers in the PCB, with one fully dedicated as an unbroken VSS plane (except thermal reliefs). Avoid placing tracks on this layer to maintain the unbroken integrity of the plane structure.
If multiple devices are placed on the same PCB, then each device has a ground plane with proper layout clearance.
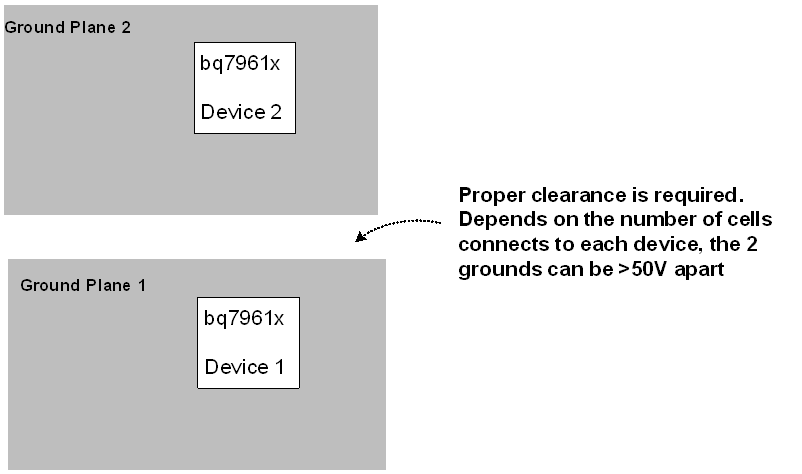 Figure 13-2 Separate Ground Plane per
Device on the Same PCB
Figure 13-2 Separate Ground Plane per
Device on the Same PCB