SLVAFF1 January 2023 DRV8452 , DRV8462
PRODUCTION DATA
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Power Efficiency of Stepper Motor Drivers
-
2Auto-Torque
- 2.1 Auto-Torque: Learning Principle
- 2.2 Current Control
- 2.3 PD Control Loop
- 2.4
Impact of Auto-Torque Tuning
Parameters
- 2.4.1 Impact of Learning Parameters on Load Transient Response
- 2.4.2 Impact of ATQ_UL, ATQ_LL Hysteresis
- 2.4.3 Impact of Load Profile on Power Saving
- 2.4.4 Adaptive ATQ_UL, ATQ_LL
- 2.4.5 PD Parameter Dependency Curves
- 2.4.6 ATQ_CNT at Different Motor Speeds
- 2.4.7 ATQ_CNT at Different Supply Voltages
- 2.4.8 Motor Temperature Estimation
- 2.5 Efficiency Improvement With Auto-Torque
- 3Case Studies
- 4Summary
- 5References
3.3.1 Printer Motor With Auto-Torque
In this application, a 1.5 A rated stepper motor used in printers was subjected to load torque transients and the motor speed was simultaneously changed, to mimic the conditions for a typical printer.
Figure 3-11 and Figure 3-12 showcase the output current and supply current waveforms with and without auto-torque.
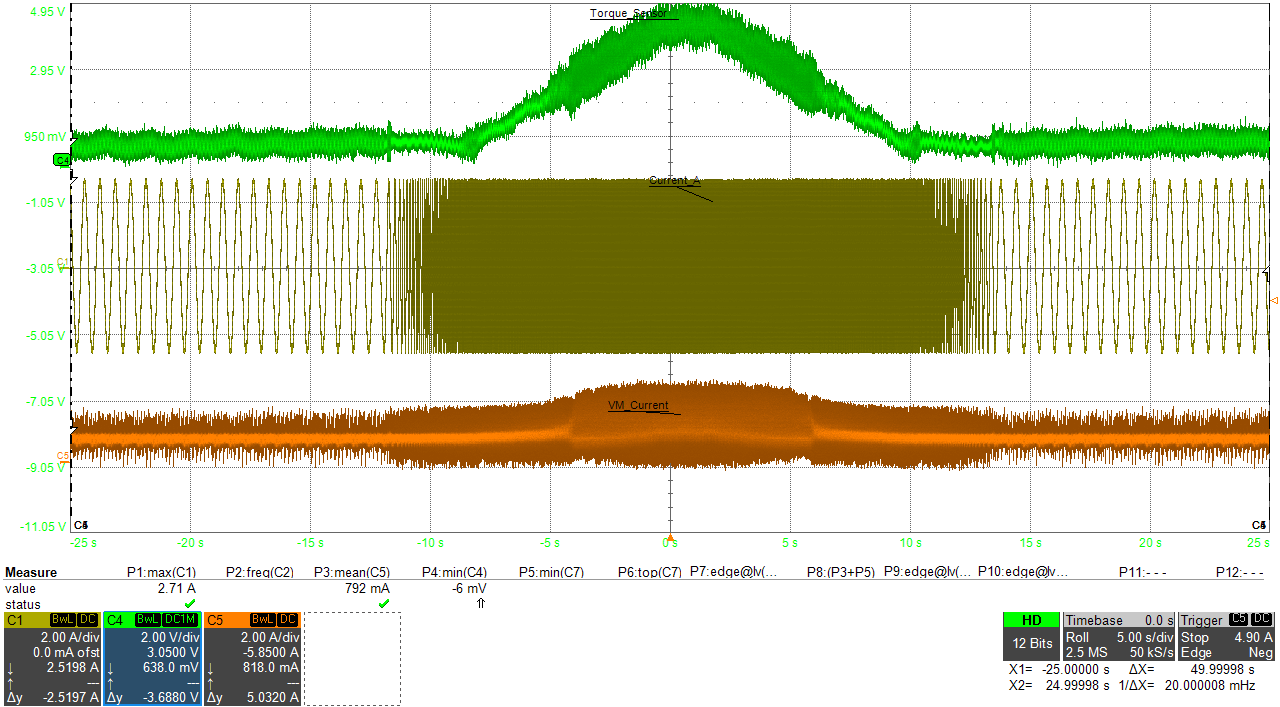 Figure 3-11 Printer Motor Loading/Unloading Without Auto-Torque
Figure 3-11 Printer Motor Loading/Unloading Without Auto-Torque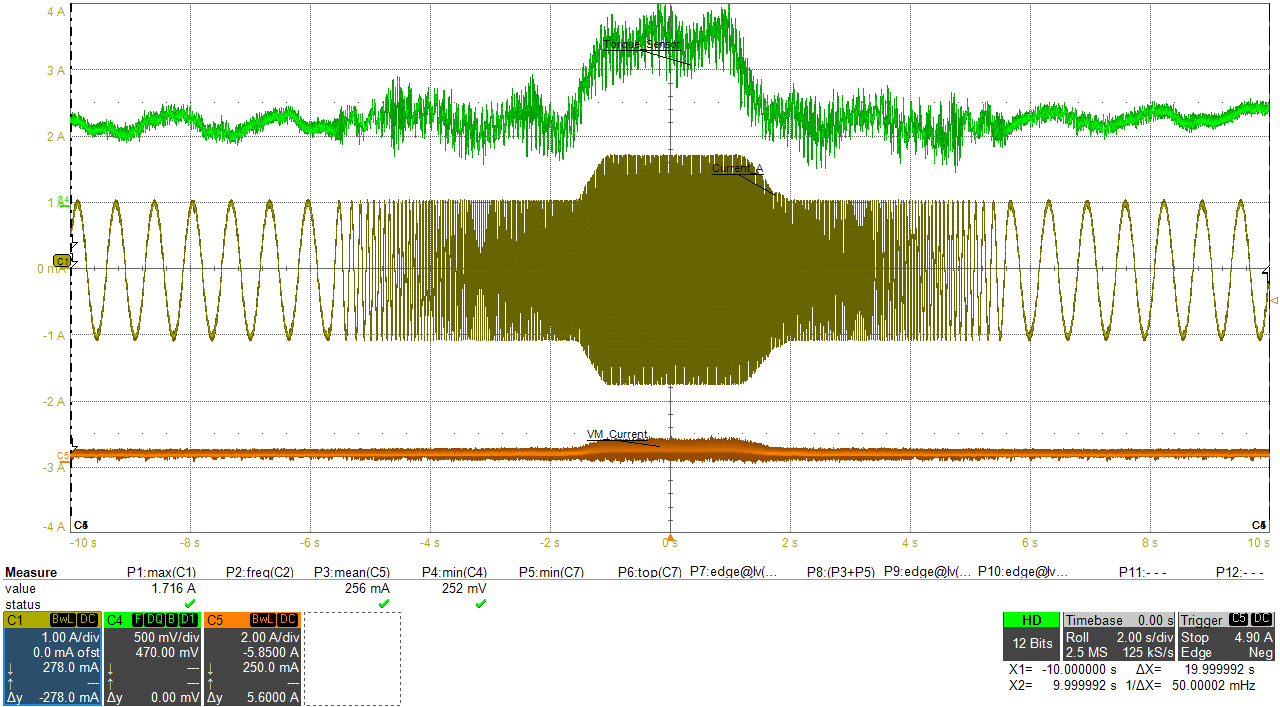 Figure 3-12 Printer Motor Loading/Unloading With Auto-Torque
Figure 3-12 Printer Motor Loading/Unloading With Auto-Torque