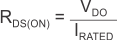SLVS561O December 2004 – June 2025 TLV1117
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.3.1 Dropout Voltage (Fixed Output, New Chip)
Dropout voltage (VDO) is defined as VIN – VOUT at the rated output current (IRATED), where the pass transistor is fully on. VIN is the input voltage, VOUT is the output voltage, and IRATED is the maximum IOUT listed in the Recommended Operating Conditions table. At this operating point, the pass transistor is driven fully on. Dropout voltage indirectly specifies a minimum input voltage greater than the nominal programmed output voltage where the output voltage is expected to stay in regulation. If the input voltage falls to less than the nominal output regulation, then the output voltage falls as well.
For a CMOS regulator, the dropout voltage is determined by the drain-source, on-state resistance (RDS(ON)) of the pass transistor. Therefore, if the linear regulator operates at less than the rated current, the dropout voltage for that current scales accordingly. The following equation calculates the RDS(ON) of the device.