SLVSDR8B April 2018 – February 2023 TPS62147 , TPS62148
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Operation
- 9.4.2 Power Save Mode Operation (PWM/PFM)
- 9.4.3 100% Duty-Cycle Operation
- 9.4.4 Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection (for TPS62148)
- 9.4.5 HICCUP Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection (for TPS62147)
- 9.4.6 Soft Start / Tracking (SS/TR)
- 9.4.7 Output Discharge Function (TPS62148 only)
- 9.4.8 Starting into a Pre-Biased Load
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.4.4 Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection (for TPS62148)
The TPS62148 is protected against overload and short circuit events. If the inductor current exceeds the current limit I(LIMF), the high side switch is turned off and the low side switch is turned on to ramp down the inductor current. This allows it to provide the maximum current, for example, charging a large output capacitance without the must increase the soft-start time.
Due to internal propagation delay, the actual current can exceed the static current limit during that time. The dynamic current limit is given as:
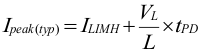
where
- ILIMF is the static current limit as specified in the electrical characteristics
- L is the effective inductance at the peak current
- VL is the voltage across the inductor (VIN - VOUT) and
- tPD is the internal propagation delay of typically 50 ns.
The current limit can exceed static values, especially if the input voltage is high and very small inductances are used. The dynamic high side switch peak current can be calculated as follows: