SNIS201A October 2017 – June 2022 LMT86-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.4.1 Mounting and Thermal Conductivity
The LMT86-Q1 can be applied easily in the same way as other integrated-circuit temperature sensors. It can be glued or cemented to a surface.
To ensure good thermal conductivity, the backside of the LMT86-Q1 die is directly attached to the GND pin. The temperatures of the lands and traces to the other leads of the LMT86-Q1 will also affect the temperature reading.
Alternatively, the LMT86-Q1 can be mounted inside a sealed-end metal tube, and can then be dipped into a bath or screwed into a threaded hole in a tank. As with any IC, the LMT86-Q1 and accompanying wiring and circuits must be kept insulated and dry, to avoid leakage and corrosion. This is especially true if the circuit may operate at cold temperatures where condensation can occur. If moisture creates a short circuit from the output to ground or VDD, the output from the LMT86-Q1 will not be correct. Printed-circuit coatings are often used to ensure that moisture cannot corrode the leads or circuit traces.
The thermal resistance junction to ambient (RθJA or θJA) is the parameter used to calculate the rise of a device junction temperature due to its power dissipation. Use Equation 7 to calculate the rise in the LMT86-Q1 die temperature:
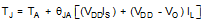
where
- TA is the ambient temperature,
- IS is the supply current,
- ILis the load current on the output,
- and VO is the output voltage.
For example, in an application where TA = 30°C, VDD = 5 V, IS = 5.4 µA, VO = 1777 mV junction temp 30.014°C self-heating error of 0.014°C. Because the junction temperature of the LMT86-Q1 is the actual temperature being measured, take care to minimize the load current that the LMT86-Q1 is required to drive. The Thermal Information table shows the thermal resistance of the LMT86-Q1.