SWRU423A July 2015 – May 2016 WL1801MOD , WL1805MOD , WL1807MOD , WL1831MOD , WL1835MOD , WL1837MOD
-
WiLink 8 WLAN Features Guide
- Trademarks
- 1 Introducion
- 2
General Features
- 2.1 Supported Rates
- 2.2 High-Throughput (HT) Features
- 2.3 Quality of Service (QoS)
- 2.4 Protection Types
- 2.5 Suspend and Resume
- 2.6 WoW (Wake on WLAN)
- 2.7 Set TX Power
- 2.8 5-GHz Antenna Diversity
- 2.9 Wi-Fi – Bluetooth/Bluetooth Smart Coexistence
- 2.10 Wi-Fi – ZigBee Coexistence
- 2.11 Accurate Synchronization Over Wi-Fi
- 3
Single Role: Station
- 3.1 Scanning
- 3.2 Connection
- 3.3 Disconnection
- 3.4 DHCP Client
- 3.5 Security
- 3.6 Filtering
- 3.7 Auto ARP
- 3.8 Preferred Networks (Profiles)
- 3.9 Power-Save Mode
- 3.10 Power-Save Delivery Protocols
- 3.11 Keep-Alive Mechanism
- 3.12 Smart Config
- 3.13 Regulatory Domain
- 3.14 DFS Slave (Channel Switch)
- 3.15 Roaming
- 4 Single Role: AP
- 5 Single Role: P2P
- 6 Single Role: Mesh
- 7 Multi-Role
- 8 Performance
- Revision History
2.8 5-GHz Antenna Diversity
WiLink8.0 supports two-antenna diversity on the 5-GHz band, using an external double pole, double throw (DPDT) switch. This switch can be found on TI MOD1837.
The WiLink8.0 algorithm studies and analyzes the best signal path considering the reasons mentioned earlier, choosing the better of the two paths for transmitting and/or receiving an RF signal to maximize the likelihood that a packet will be correctly received, and increase throughput. The decision mechanism is based on RSSI level. 5-GHz antenna diversity is mostly relevant for the following use-cases:
- In urban and indoor environments, there is no clear line of sight between the transmitter and receiver. Instead, the signal is reflected along multiple paths before finally being received. Each of these bounces can introduce phase shifts, time delays, attenuations, and distortions that can destructively interfere with one another at the aperture of the receiving antenna.
- The antenna radiation pattern defines the variation of the power radiated by an antenna as a function of the direction away from the antenna. This power variation as a function of the arrival angle is observed at the antenna far field. Diversity between two antennas with different patterns can overcome nulls.
- Improves performance for Airplay compliance (audio customers)
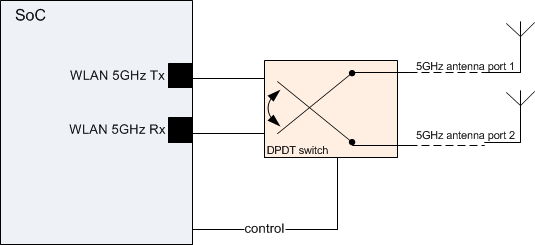 Figure 3. 5-GHz Antenna Diversity
Figure 3. 5-GHz Antenna Diversity