TIDUEO0C July 2019 – March 2021
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2 Design Considerations
- 2.3
Highlighted Products
- 2.3.1 TPS63900: 1.8V-5.5 VIN Buck-Boost Converter With 75-nA Ultra-low Quiescent Current and 400-mA Output Current
- 2.3.2 TPS610995: 0.7 VIN Synchronous Boost Converter With 400-nA Ultra-low Quiescent Current and 1-A Peak Current
- 2.3.3 TPS62840: 750-mA Synchronous Step-Down Converter With Ultra-low Quiescent Current Consumption
- 2.4 System Design Theory
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7Terminology
- 8About the Author
- 9Revision History
2.4.2.2 LPV521 Gain Calculation
The resistors R25 and R28 in the TIDA-01546 reference design are used to set the gain value of the LPV521 device:

The AVDD voltage of the ADS7142 device defines the full-scale input range of the device and for the TIDA-01546 design, it is set to 3.3 V and is the maximum input voltage. With this, and knowing the gain G, calculate the maximum VIN value for the input voltage of the LPV521 device:
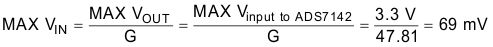
The 69 mV represents the full-scale voltage which can be applied to the input of the LPV521 device regardless of the current range used.
For these two current ranges, the maximum current value is one of the following:
- 69 mV / R32 = 6800 Ω =
- 10.47 µA for the low-current range
- 69 mV / 0.145 Ω = 475.86 mA for the high-current range
The minimal current values are enumerated in the following, since there are 4096 ADC steps:
- 10.47 µA / 4096 = 2.55 nA
- 475.86 mA / 4096 = 116 µA
The LPV521 and ADS7142 devices monitor the system current continuously with a minimum power consumption, since both devices draw about 1 µA when running from a 3.3-V supply.