SNAS333E August 2005 – December 2015 ADC128S052 , ADC128S052-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
Capacitive coupling between the noisy digital circuitry and the sensitive analog circuitry can lead to poor performance. The solution is to keep the analog circuitry separated from the digital circuitry and the clock line as short as possible.
Digital circuits create substantial supply and ground current transients. The logic noise generated could have significant impact upon system noise performance. To avoid performance degradation of the ADC128S052 due to supply noise, do not use the same supply for the ADC128S052 that is used for digital logic.
Generally, analog and digital lines must cross each other at 90° to avoid crosstalk. However, to maximize accuracy in high resolution systems, avoid crossing analog and digital lines altogether. It is important to keep clock lines as short as possible and isolated from ALL other lines, including other digital lines. In addition, the clock line must also be treated as a transmission line and be properly terminated.
The analog input must be isolated from noisy signal traces to avoid coupling of spurious signals into the input. Any external component (for example, a filter capacitor) connected between the input pins and ground of the converter or to the reference input pin and ground must be connected to a very clean point in the ground plane.
TI recommends the use of a single, uniform ground plane and the use of split power planes. The power planes must be located within the same board layer. All analog circuitry (input amplifiers, filters, reference components, and so forth) must be placed over the analog power plane. All digital circuitry and I/O lines must be placed over the digital power plane. Furthermore, all components in the reference circuitry and the input signal chain that are connected to ground must be connected together with short traces and enter the analog ground plane at a single, quiet point.
10.2 Layout Example
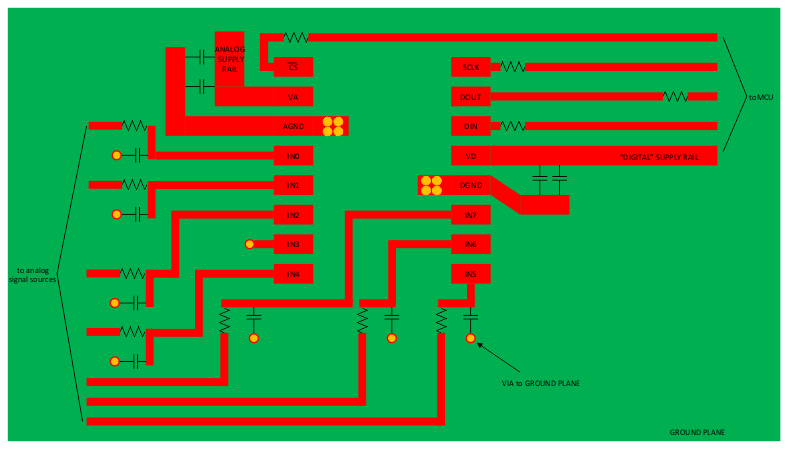 Figure 40. Layout Schematic
Figure 40. Layout Schematic