SNOI146C September 2011 – December 2017 ADC141S628-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGS|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Device and Documentation Support
11.1 Device Support
11.1.1 Device Nomenclature
11.1.1.1 Specification Definitions
APERTURE DELAY is the time between the first falling edge of SCLK and the time when the input signal is sampled for conversion.
COMMON-MODE REJECTION RATIO (CMRR) is a measure of how well in-phase signals common to both input pins are rejected.
To calculate CMRR, the change in output offset is measured while the common mode input voltage is changed from 2 V to 3 V.
CONVERSION TIME is the time required, after the input voltage is acquired, for the ADC to convert the input voltage to a digital word.
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY (DNL) is the measure of the maximum deviation from the ideal step size of 1 LSB.
DUTY CYCLE is the ratio of the time that a repetitive digital waveform is high to the total time of one period. The specification here refers to the SCLK.
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS (ENOB, or EFFECTIVE BITS) is another method of specifying signal-to-noise and distortion or SINAD. ENOB is defined as (SINAD − 1.76) / 6.02 and says that the converter is equivalent to a perfect ADC of this (ENOB) number of bits.
FULL POWER BANDWIDTH is a measure of the frequency at which the reconstructed output fundamental drops 3 dB below its low frequency value for a full-scale input.
FULL-SCALE ERROR is the difference between the input voltage at which the output code transitions to positive full-scale and VREF minus 1 LSB.
GAIN ERROR is the deviation from the ideal slope of the transfer function. Gain error is the difference between positive full-scale error and negative full-scale error and can be calculated as:
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY (INL) is a measure of the deviation of each individual code from a line drawn from ½ LSB below the first code transition through ½ LSB above the last code transition. The deviation of any given code from this straight line is measured from the center of that code value.
MISSING CODES are those output codes that will never appear at the ADC outputs. The ADC141S628-Q1 is specified not to have any missing codes.
OFFSET ERROR is the difference between the input voltage at which the output code transitions from code 0000h to 0001h and 1 LSB.
POST CALIBRATION TOTAL UNADJUSTED ERROR is the total unadjusted error over the temperature range after system calibration to remove gain and offset errors at 25°C.
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO (PSRR) is a measure of how well a change in the analog supply voltage is rejected. PSRR is calculated from the ratio of the change in offset error for a given change in supply voltage, expressed in dB. For the ADC141S628-Q1, VA is changed from 4.5 V to 5.5 V.
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO (SNR) is the ratio, expressed in dB, of the rms value of the input signal to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components below one-half the sampling frequency, not including harmonics or DC.
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE AND DISTORTION (S/N+D or SINAD) Is the ratio, expressed in dB, of the rms value of the input signal to the rms value of all of the other spectral components below one-half the sampling frequency, including harmonics but excluding DC.
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR) is the difference, expressed in dB, between the desired signal amplitude to the amplitude of the peak spurious spectral component below one-half the sampling frequency, where a spurious spectral component is any signal present in the output spectrum that is not present at the input and may or may not be a harmonic.
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION (THD) is the ratio of the rms total of the first five harmonic components at the output to the rms level of the input signal frequency as seen at the output, expressed in dB. THD is calculated as:
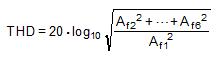
where
- Af1 is the RMS power of the input frequency at the output
- Af2 through Af6 are the RMS power in the first five harmonic frequencies
TOTAL UNADJUSTED ERROR is the difference between the parts transfer function and the ideal transfer function.
THROUGHPUT TIME is the minimum time required between the start of two successive conversion.
11.2 Documentation Support
11.2.1 Related Documentation
For related documentation see the following:
11.3 Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates
To receive notification of documentation updates, navigate to the device product folder on ti.com. In the upper right corner, click on Alert me to register and receive a weekly digest of any product information that has changed. For change details, review the revision history included in any revised document.
11.4 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI E2E™ Online Community TI's Engineer-to-Engineer (E2E) Community. Created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
-
Design Support TI's Design Support Quickly find helpful E2E forums along with design support tools and contact information for technical support.
11.5 Trademarks
E2E is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
SPI, QSPI are trademarks of Motorola Mobility LLC.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
11.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution

This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications.
11.7 Glossary
SLYZ022 — TI Glossary.
This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.