SBAS580D May 2013 – March 2018 ADS7250 , ADS7850 , ADS8350
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: All Devices
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: ADS7250
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: ADS7850
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: ADS8350
- 6.9 Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: ADS7250
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics: ADS7850
- 6.13 Typical Characteristics: ADS8350
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics: All Devices
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
9 Power Supply Recommendations
The devices have two separate power supplies: AVDD and DVDD. The ADC operates on AVDD; DVDD is used for the interface circuits. AVDD and DVDD can be independently set to any value within the permissible range.
The AVDD supply voltage value defines the permissible voltage swing on the analog input pins. To avoid saturation of output codes, the external reference voltages VREFIN_A and VREFIN_B should be as shown in Equation 10:
In other words, in order to use the VREFIN_x external reference voltage and use the full dynamic range on the analog input pins, AVDD must be set as shown in Equation 11, Equation 12, and Equation 13:
Decouple the AVDD and DVDD pins with the GND pin using individual 10-µF decoupling capacitors, as shown in Figure 62.
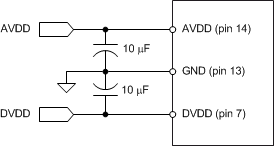 Figure 62. Power-Supply Decoupling
Figure 62. Power-Supply Decoupling