SWRS223D February 2020 – February 2024 AWR2243
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Functional Block Diagram
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Power Supply Specifications
- 7.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.7 RF Specification
- 7.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for FCBGA Package [ABL0161]
- 7.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.1 Power Supply Sequencing and Reset Timing
- 7.9.2 Synchronized Frame Triggering
- 7.9.3 Input Clocks and Oscillators
- 7.9.4 Multibuffered / Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (MibSPI)
- 7.9.5 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 7.9.6 LVDS Interface Configuration
- 7.9.7 General-Purpose Input/Output
- 7.9.8 Camera Serial Interface (CSI)
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Monitoring and Diagnostic Mechanisms
- 10Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ABL|161
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.1.3 Receive Subsystem
The AWR2243 receive subsystem consists of four parallel channels. A single receive channel consists of an LNA, mixer, IF filtering, ADC conversion, and decimation. All four receive channels can be operational at the same time an individual power-down option is also available for system optimization.
Unlike conventional real-only receivers, the AWR2243 device supports a complex baseband architecture, which uses quadrature mixer and dual IF and ADC chains to provide complex I and Q outputs for each receiver channel. The AWR2243 is targeted for fast chirp systems. The band-pass IF chain has configurable lower cutoff frequencies above 175 kHz and can support bandwidths up to 20 MHz.
Figure 8-3 describes the receive subsystem.
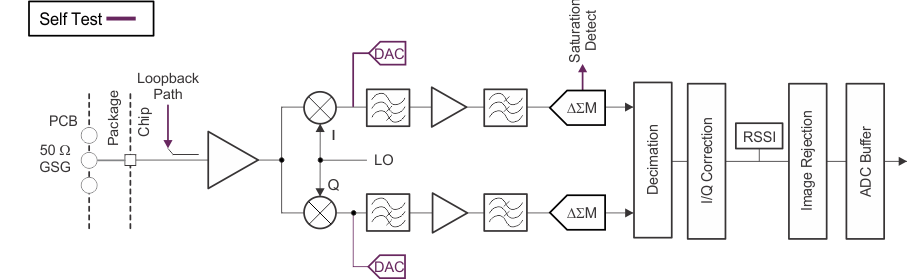 Figure 8-3 Receive Subsystem (Per Channel)
Figure 8-3 Receive Subsystem (Per Channel)