SBAS794E november 2018 – august 2023 DAC60501 , DAC70501 , DAC80501
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Timing Requirements: SPI Mode
- 7.7 Timing Requirements: I2C Standard Mode
- 7.8 Timing Requirements: I2C Fast Mode
- 7.9 Timing Requirements: I2C Fast-Mode Plus
- 7.10 Timing Diagrams
- 7.11 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2 Typical Application
End equipment, such as oscilloscopes, battery test equipment, and other lab instruments require precision calibration and control signals to tune the system accuracy. Precision DACs are typically used to generate these signals. The complexity and accuracy of these systems are driving the need for multiple precision signals to be generated in the system. The common approach for generating these signal is by using a multichannel DAC. An alternative way to generate these signal is to use a single-channel DAC with a sample-and-hold circuit to produce multichannel output. Using this approach, users can generate a customized number of channels instead of using a fixed number of channels available in multichannel DACs.
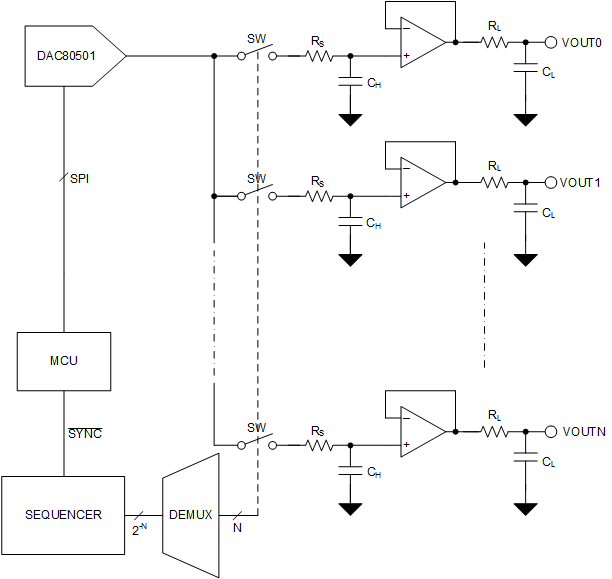 Figure 9-1 Multichannel Sample-and-Hold Circuit
Figure 9-1 Multichannel Sample-and-Hold Circuit