SBOS122E December 1999 – December 2017 INA138 , INA168
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The INA138 and INA168 devices (INA1x8) are comprised of a high voltage, precision operational amplifier, precision thin film resistors trimmed in production to an absolute tolerance and a low noise output transistor. The INA1x8 devices can be powered from a single power supply and their input voltages can exceed the power supply voltage. The INA1x8 devices are ideal for measuring small differential voltages, such as those generated across a shunt resistor, in the presence of large common-mode voltages. Refer to Functional Block Diagram which illustrates the functional components within both INA1x8 devices.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
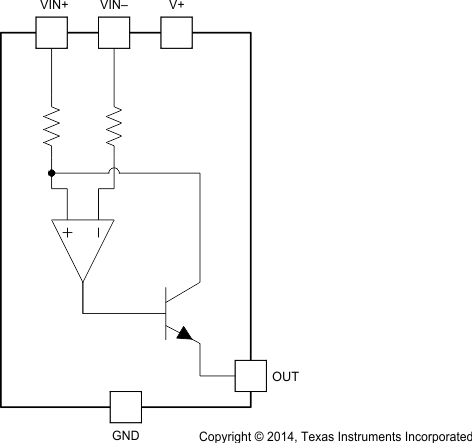
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Output Voltage Range
The output of the INA1x8 device is a current that is converted to a voltage by the load resistor, RL. The output current remains accurate within the compliance voltage range of the output circuitry. The shunt voltage and the input common-mode and power-supply voltages limit the maximum possible output swing. The maximum output voltage (Vout max) compliance is limited by either Equation 1 or Equation 2, whichever is lower:
or
7.3.2 Bandwidth
Measurement bandwidth is affected by the value of the load resistor, RL. High gain produced by high values of RL will yield a narrower measurement bandwidth (see Typical Characteristics). For widest possible bandwidth, keep the capacitive load on the output to a minimum. Reduction in bandwidth due to capacitive load is shown in the Typical Characteristics.
If bandwidth limiting (filtering) is desired, a capacitor can be added to the output (see Figure 12). This will not cause instability.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
For proper operation the INA1x8 devices must operate within their specified limits. Operating either device outside of their specified power supply voltage range or their specified common-mode range will result in unexpected behavior and is not recommended. Additionally operating the output beyond their specified limits with respect to power supply voltage and input common-mode voltage will also produce unexpected results. Refer to Electrical Characteristics for the device specifications.