SLLSEK9B January 2015 – April 2015 ISO7330C , ISO7330FC , ISO7331C , ISO7331FC
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Applications and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DW|16
Orderable Information
9 Applications and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
ISO733x utilize single-ended TTL-logic switching technology. Its supply voltage range is from 3 V to 5.5 V for both supplies, VCC1 and VCC2. When designing with digital isolators, it is important to keep in mind that due to the single-ended design structure, digital isolators do not conform to any specific interface standard and are only intended for isolating single-ended CMOS or TTL digital signal lines. The isolator is typically placed between the data controller (that is, μC or UART), and a data converter or a line transceiver, regardless of the interface type or standard.
9.2 Typical Application
ISO7331C combined with Texas Instruments' mixed signal micro-controller, RS-485 transceiver, transformer driver, and voltage regulator can create an isolated RS-485 system as shown in Figure 18.
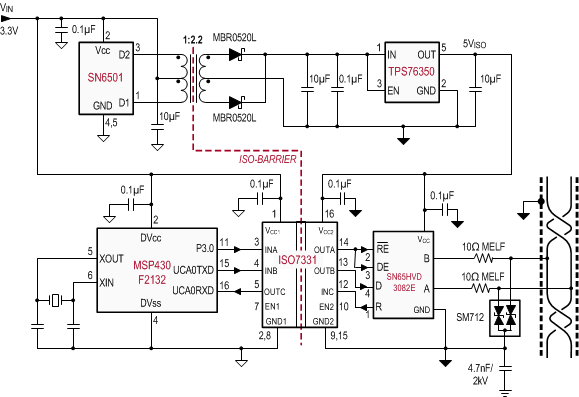 Figure 18. Typical ISO7331 Application Circuit
Figure 18. Typical ISO7331 Application Circuit
9.2.1 Design Requirements
9.2.1.1 Typical Supply Current Equations
| ISO7330: | ISO7331: | ||
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 5 V
|
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 5 V
|
||
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 3.3 V
|
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 3.3 V
|
ICC1 and ICC2 are typical supply currents measured in mA, f is data rate measured in Mbps, CL is the capacitive load measured in pF.
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
9.2.2.1 Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Considerations
Many applications in harsh industrial environment are sensitive to disturbances such as electrostatic discharge (ESD), electrical fast transient (EFT), surge and electromagnetic emissions. These electromagnetic disturbances are regulated by international standards such as IEC 61000-4-x and CISPR 22. Although system-level performance and reliability depends, to a large extent, on the application board design and layout, the ISO733x incorporate many chip-level design improvements for overall system robustness. Some of these improvements include:
- Robust ESD protection cells for input and output signal pins and inter-chip bond pads.
- Low-resistance connectivity of ESD cells to supply and ground pins.
- Enhanced performance of high voltage isolation capacitor for better tolerance of ESD, EFT and surge events.
- Bigger on-chip decoupling capacitors to bypass undesirable high energy signals through a low impedance path.
- PMOS and NMOS devices isolated from each other by using guard rings to avoid triggering of parasitic SCRs.
- Reduced common mode currents across the isolation barrier by ensuring purely differential internal operation.
9.2.3 Application Performance Curves
Typical eye diagrams of ISO733x below indicate low jitter and wide open eye at the maximum data rate of 25 Mbps.
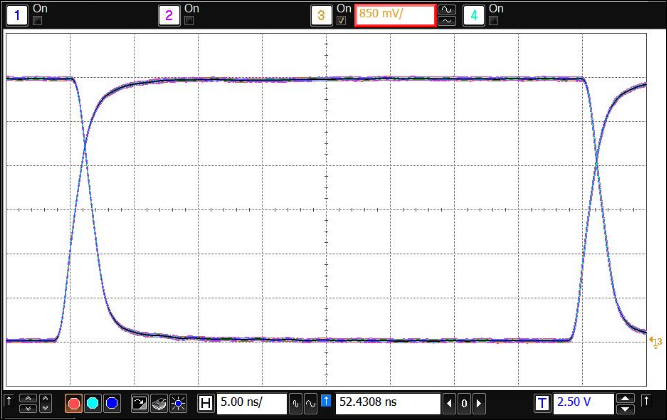 Figure 19. Eye Diagram at 25 Mbps, 5 V and 25°C
Figure 19. Eye Diagram at 25 Mbps, 5 V and 25°C
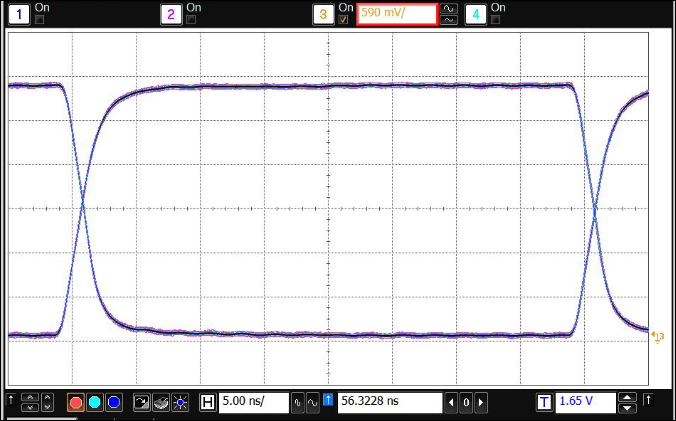 Figure 20. Eye Diagram at 25 Mbps, 3.3 V and 25°C
Figure 20. Eye Diagram at 25 Mbps, 3.3 V and 25°C
9.2.4 Systems Examples
Unlike Optocouplers, which need external components to improve performance, provide bias, or limit current, ISO733x only needs two external bypass capacitors to operate.
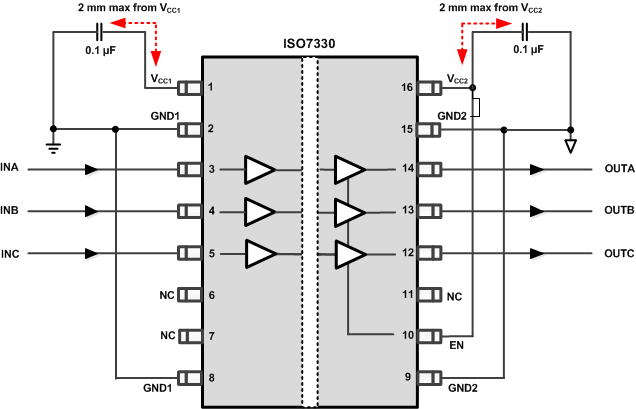 Figure 21. Typical ISO7330 Circuit Hook-up
Figure 21. Typical ISO7330 Circuit Hook-up
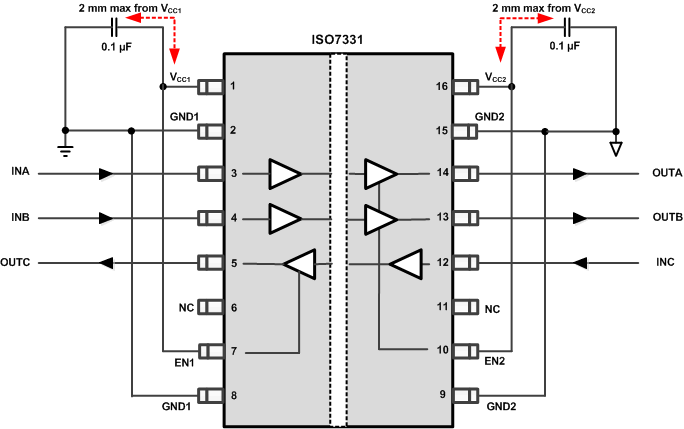 Figure 22. Typical ISO7331 Circuit Hook-up
Figure 22. Typical ISO7331 Circuit Hook-up