SBOS623 October 2020 OPA856
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Orderable Information
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
The OPA856 is a classic voltage feedback operational amplifier (op amp) with two high-impedance inputs and a low-impedance output. Standard application circuits are supported, like the two basic options shown in Figure 8-1 and Figure 8-2. The resistor on the noninverting pin is used for bias current cancellation to minimize the output offset voltage. In a noninverting configuration the additional resistors on the noninverting pin add noise to the system so if SNR is critical, the resistor can be eliminated. In an inverting configuration the noninverting node is typically connected to a DC voltage, so the high-frequency noise contribution from the bias cancellation resistor can be bypassed by adding a large 1-µF capacitor in parallel to the resistor to shunt the noise. The DC operating point for each configuration is level-shifted by the reference voltage (VREF), which is typically set to midsupply in single-supply operation. VREF is typically connected to ground in split-supply applications.
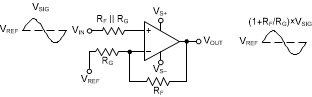 Figure 8-1 Noninverting Amplifier
Figure 8-1 Noninverting Amplifier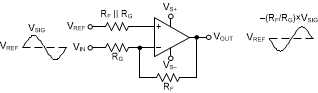 Figure 8-2 Inverting Amplifier
Figure 8-2 Inverting Amplifier