SBOS410K june 2007 – june 2023 REF5010 , REF5020 , REF5025 , REF5030 , REF5040 , REF5045 , REF5050
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGK|8
Orderable Information
9.3.4 Noise Performance
Typical 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz voltage noise for each member of the REF50xx family is specified in Section 7.5 table. The noise voltage increases with output voltage and operating temperature. Additional filtering can be used to improve output noise levels, although take care to ensure the output impedance does not degrade performance.
For additional information about how to minimize noise and maximize performance in mixed-signal applications such as data converters, refer to the How a Voltage Reference Affects ADC Performance Part 1, How a Voltage Reference Affects ADC Performance Part 2, and How a Voltage Reference Affects ADC Performance Part 3 analog design journals.
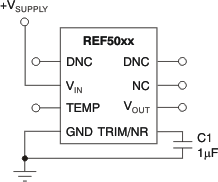 Figure 9-2 Noise Reduction Using the TRIM/NR Pin
Figure 9-2 Noise Reduction Using the TRIM/NR Pin