SLOS913A October 2015 – February 2017 SN55HVD75-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRB|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRB|8
Orderable Information
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The SN55HVD75-EP is a low-power, half-duplex RS-485 transceiver available in a speed grade suitable for data transmission up to 20 Mbps.
This device has active-high driver enables and active-low receiver enables. A standby current of less than 2 µA can be achieved by disabling both driver and receiver.
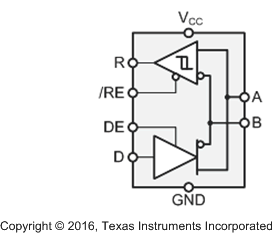
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
8.3 Feature Description
Internal ESD protection circuits protect the transceiver against electrostatic discharges (ESD) according to IEC 61000-4-2 of up to ±12 kV, and against electrical fast transients (EFT) according to IEC 61000-4-4 of up to
±4 kV.
The SN55HVD75-EP half-duplex family provides internal biasing of the receiver input thresholds in combination with large input threshold hysteresis. At a positive input threshold of VIT+ = –20 mV and an input hysteresis of
VHYS = 50 mV, the receiver output remains logic high under a bus-idle or bus-short condition even in the presence of 140-mVPP differential noise without the need for external failsafe biasing resistors.
Device operation is specified over a wide ambient temperature range from –55°C to 125°C.
8.4 Device Functional Modes
When the driver enable pin, DE, is logic high, the differential outputs A and B follow the logic states at data input D. A logic high at D causes A to turn high and B to turn low. In this case the differential output voltage defined as VOD = VA – VB is positive. When D is low, the output states reverse, B turns high, A becomes low, and VOD is negative.
When DE is low, both outputs turn high-impedance. In this condition the logic state at D is irrelevant. The DE pin has an internal pulldown resistor to ground; thus, when left open, the driver is disabled (high-impedance) by default. The D pin has an internal pullup resistor to VCC; thus, when left open while the driver is enabled, output A turns high and B turns low.
Table 1. Driver Function Table
| INPUT | ENABLE | OUTPUTS | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | DE | A | B | |
| H | H | H | L | Actively drive bus high. |
| L | H | L | H | Actively drive bus low. |
| X | L | Z | Z | Driver disabled. |
| X | OPEN | Z | Z | Driver disabled by default. |
| OPEN | H | H | L | Actively drive bus high by default. |
When the receiver enable pin, RE, is logic low, the receiver is enabled. When the differential input voltage defined as VID = VA – VB is positive and higher than the positive input threshold, VIT+, the receiver output, R, turns high. When VID is negative and lower than the negative input threshold, VIT–, the receiver output turns low. If VID is between VIT+ and VIT–, the output is indeterminate.
When RE is logic high or left open, the receiver output is high-impedance and the magnitude and polarity of VID are irrelevant. Internal biasing of the receiver inputs causes the output to go failsafe-high when the transceiver is disconnected from the bus (open-circuit), the bus lines are shorted (short-circuit), or the bus is not actively driven (idle bus).
Table 2. Receiver Function Table
| DIFFERENTIAL INPUT | ENABLE | OUTPUT | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| VID = VA – VB | RE | R | |
| VIT+ < VID | L | H | Receive valid bus high. |
| VIT– < VID < VIT+ | L | ? | Indeterminate bus state. |
| VID < VIT– | L | L | Receive valid bus low. |
| X | H | Z | Receiver disabled. |
| X | OPEN | Z | Receiver disabled by default. |
| Open-circuit bus | L | H | Failsafe high output. |
| Short-circuit bus | L | H | Failsafe high output. |
| Idle (terminated) bus | L | H | Failsafe high output. |
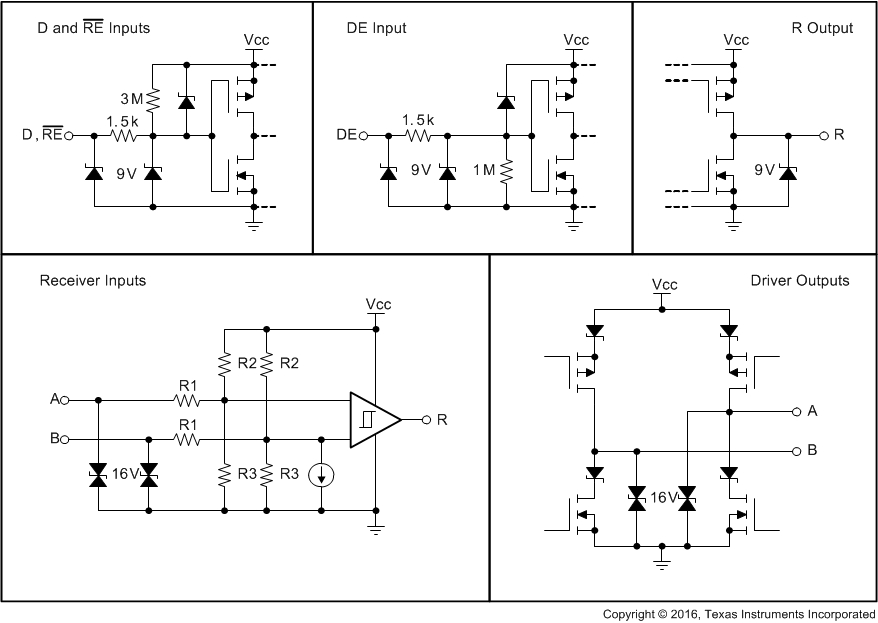 Figure 14. Equivalent Input and Output Circuit Diagrams
Figure 14. Equivalent Input and Output Circuit Diagrams