SLOS739A July 2012 – March 2016 TAS5721
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics - I/O Pin Characteristics
- 7.6 Master Clock Characteristics
- 7.7 Speaker Amplifier Characteristics
- 7.8 Headphone Amplifier and Line Driver Characteristics
- 7.9 Protection Characteristics
- 7.10 I2C Serial Control Port Requirements and Specifications
- 7.11 Serial Audio Port Timing
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Power Supply
- 9.3.2 I2C Address Selection and Fault Output
- 9.3.3 Device Protection System
- 9.3.4 Clock, Auto Detection, and PLL
- 9.3.5 PWM Section
- 9.3.6 SSTIMER Functionality
- 9.3.7 2.1-Mode Support
- 9.3.8 PBTL-Mode Support
- 9.3.9 I2C Serial Control Interface
- 9.3.10 Dynamic Range Control (DRC)
- 9.3.11 Bank Switching
- 9.3.12 Serial Data Interface
- 9.3.13 DirectPath Headphone/Line Driver
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 Clock Control Register (0x00)
- 9.6.2 Device ID Register (0x01)
- 9.6.3 Error Status Register (0x02)
- 9.6.4 System Control Register 1 (0x03)
- 9.6.5 Serial Data Interface Register (0x04)
- 9.6.6 System Control Register 2 (0x05)
- 9.6.7 Soft Mute Register (0x06)
- 9.6.8 Volume Registers (0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A)
- 9.6.9 Volume Configuration Register (0x0E)
- 9.6.10 Modulation Limit Register (0x10)
- 9.6.11 Interchannel Delay Registers (0x11, 0x12, 0x13, and 0x14)
- 9.6.12 Pwm Shutdown Group Register (0x19)
- 9.6.13 Start/stop Period Register (0x1A)
- 9.6.14 Oscillator Trim Register (0x1B)
- 9.6.15 BKND_ERR Register (0x1C)
- 9.6.16 Input Multiplexer Register (0x20)
- 9.6.17 Channel 4 Source Select Register (0x21)
- 9.6.18 PWM Output MUX Register (0x25)
- 9.6.19 DRC Control (0x46)
- 9.6.20 Bank Switch and EQ Control (0x50)
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2 Typical Application
- 10.3 System Examples
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DCA|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DCA|48
Orderable Information
12 Layout
12.1 Layout Guidelines
Class-D switching edges are fast and switched currents are high so it is necessary to take care when planning the layout of the printed circuit board. The following suggestions will help to meet audio, thermal and EMC requirements.
- uses the PCB for heat sinking therefore the powerPad needs to be soldered to the PCB and adequate copper area and copper vias connecting the top, bottom and internal layers should be used.
- Decoupling capacitors: the high-frequency decoupling capacitors should be placed as close to the supply pins as possible; on the a 1-µF high-quality ceramic capacitor is used. Large (10μ-F or greater) bulk power supply decoupling capacitors should be placed near the on the PVDD supplies.
- Keep the current loop from each of the outputs through the output inductor and the small filter cap and back to GND as small and tight as possible. The size of this current loop determines its effectiveness as an antenna.
- To avoid crosstalk issues on the headphone/line driver output, it is recommended to have a wide space between the traces of the outputs.
- Grounding: A big common GND plane is recommended. The PVDD decoupling capacitors should connect to GND. The TAS5721 PowerPAD should be connected to GND.
- Output filter: remember to select inductors that can handle the high short circuit current of the device. The LC filter should be placed close to the outputs.
The EVM product folder (http://www.ti.com/tool/tas5721evm) and User’s Guide available on www.ti.com shows schematic, bill of material, gerber files and more detailed layout plots.
12.2 Layout Example
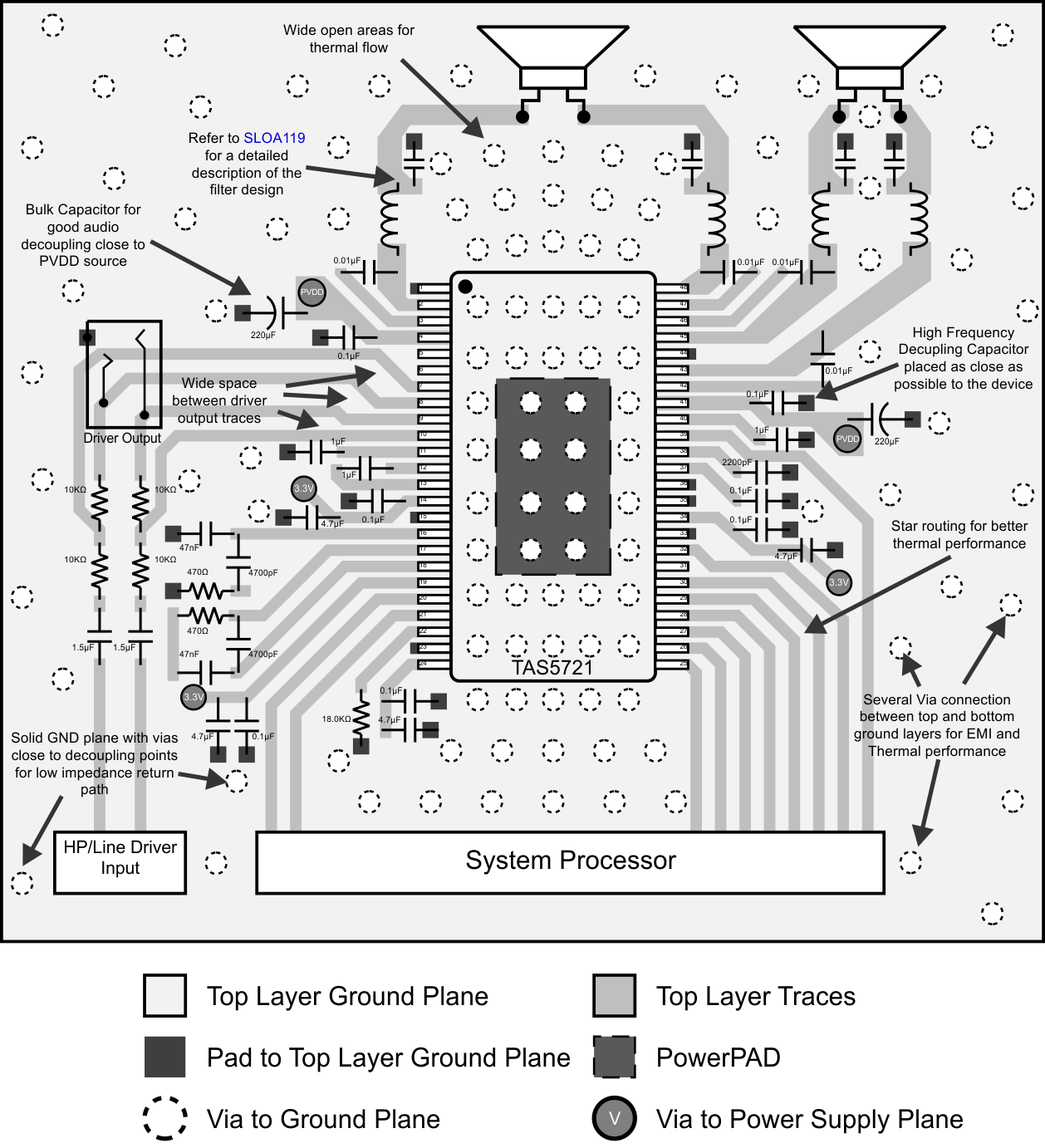 Figure 82. Layout Recommendation
Figure 82. Layout Recommendation