SLOS490C July 2006 – November 2015
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
ZQV Package
8-Pin BGA MICROSTAR JUNIOR
Top View
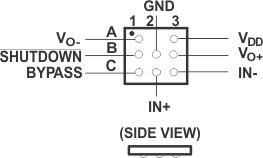
DRB Package
8-Pin SON
Top View
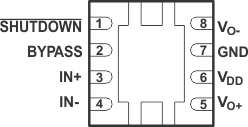
DGN Package
8-Pin MSOP-PowerPAD
Top View
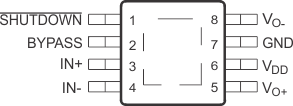
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | BGA MICROSTAR JUNIOR | SON, MSOP-PowerPAD |
||
| BYPASS | C1 | 2 | I | Mid-supply voltage. Adding a bypass capacitor improves PSRR. |
| GND | B2 | 7 | I | High-current ground |
| IN– | C3 | 4 | I | Negative differential input |
| IN+ | C2 | 3 | I | Positive differential input |
| SHUTDOWN | B1 | 1 | I | Shutdown terminal (active low logic) |
| VDD | A3 | 6 | I | Supply voltage terminal |
| VO+ | B3 | 5 | O | Positive BTL output |
| VO– | A1 | 8 | O | Negative BTL output |
| Thermal Pad | N/A | — | — | Connect to ground. Thermal pad must be soldered down in all applications to properly secure device on the PCB. |