SBVS240C November 2014 – February 2019 TPS3701
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDC|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.1.2 Input and Output Configurations
Figure 21 to Figure 24 show examples of the various input and output configurations.
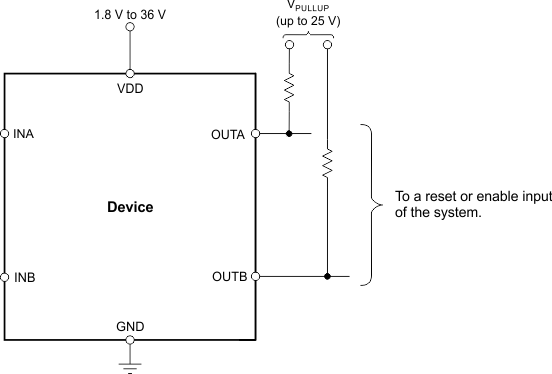 Figure 21. Interfacing to Voltages Other than VDD
Figure 21. Interfacing to Voltages Other than VDD 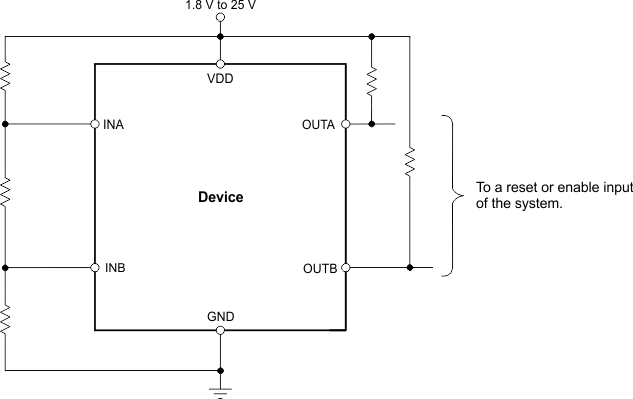 Figure 22. Monitoring the Same Voltage as VDD
Figure 22. Monitoring the Same Voltage as VDD 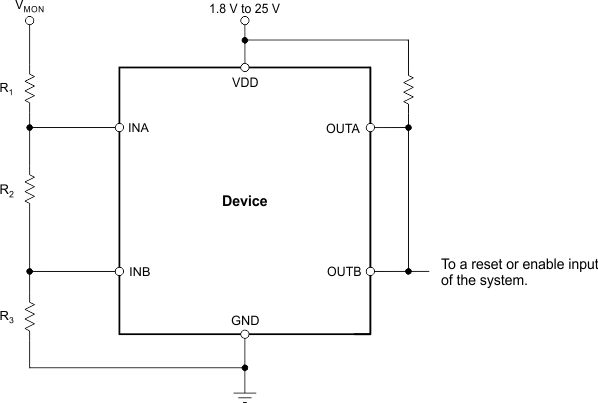
NOINDENT:
NOTE: The inputs can monitor a voltage higher than VDD (max) with the use of an external resistor divider network.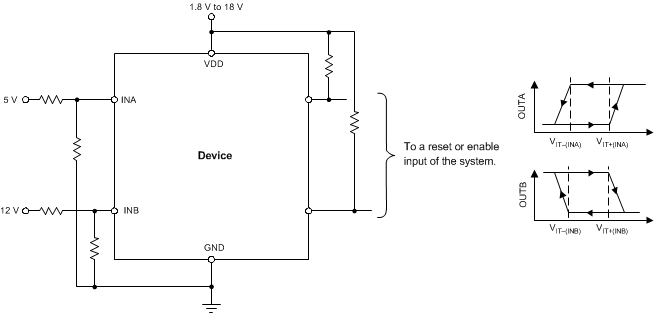
NOINDENT:
NOTE: In this case, OUTA is driven low when an undervoltage condition is detected at the 5-V rail and OUTB is driven low when an overvoltage condition is detected at the 12-V rail.