SLVS834B July 2008 – June 2019 TPS5450-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Oscillator Frequency
- 7.3.2 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.3 Enable (ENA) and Internal Slow Start
- 7.3.4 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.5 Output Feedback (VSENSE) and Internal Compensation
- 7.3.6 Voltage Feedforward
- 7.3.7 Pulse-Width-Modulation (PWM) Control
- 7.3.8 Overcurrent Limiting
- 7.3.9 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
-
8 Application Information
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Boost Capacitor (BOOT)
- 8.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.4 Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.5 Output Filter Components
- 8.2.2.6 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 8.2.2.7 Boot Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 Catch Diode
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage Limitations
- 8.2.2.10 Internal Compensation Network
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
8.2.2.5.2 Capacitor Selection
The important design factors for the output capacitor are dc voltage rating, ripple current rating, and equivalent series resistance (ESR). The dc voltage and ripple current ratings cannot be exceeded. The ESR is important because, along with the inductor ripple current, it determines the amount of output ripple voltage. The actual value of the output capacitor is not critical, but some practical limits do exist. Consider the relationship between the desired closed loop crossover frequency of the design and LC corner frequency of the output filter. Due to the design of the internal compensation, it is desirable to keep the closed loop crossover frequency in the range 3 kHz to 30 kHz, as this frequency range has adequate phase boost to allow for stable operation. For this design example, it is assumed that the intended closed loop crossover frequency is between 2590 Hz and 24 kHz and also below the ESR zero of the output capacitor. Under these conditions the closed loop crossover frequency is related to the LC corner frequency by:
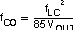
And the desired output capacitor value for the output filter to:
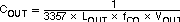
For a desired crossover of 12 kHz and a 15-μH inductor, the calculated value for the output capacitor is 330 μF. The capacitor type should be chosen so that the ESR zero is above the loop crossover. The maximum ESR should be:
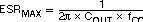
The maximum ESR of the output capacitor also determines the amount of output ripple as specified in the initial design parameters. The output ripple voltage is the inductor ripple current times the ESR of the output filter. Check that the maximum specified ESR as listed in the capacitor data sheet results in an acceptable output ripple voltage:
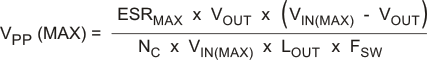
where
- ΔVPP is the desired peak-to-peak output ripple
- NC is the number of parallel output capacitors
- FSW is the switching frequency
For this design example, a single 330-μF output capacitor is chosen for C3. The calculated RMS ripple current is 143 mA and the maximum ESR required is 40 mΩ. A capacitor that meets these requirements is a Sanyo Poscap 10TPB330M, rated at 10 V with a maximum ESR of 35 mΩ and a ripple current rating of 3 A. An additional small 0.1-μF ceramic bypass capacitor, C6 is also used in this design.
The minimum ESR of the output capacitor should also be considered. For good phase margin, the ESR zero when the ESR is at a minimum should not be too far above the internal compensation poles at 24 kHz and 54 kHz.
The selected output capacitor must also be rated for a voltage greater than the desired output voltage plus one half the ripple voltage. Any derating amount must also be included. The maximum RMS ripple current in the output capacitor is given by Equation 11:
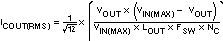
where
- NC is the number of output capacitors in parallel
- FSW is the switching frequency
Other capacitor types can be used with the TPS5450-Q1, depending on the needs of the application.