SLVSCN0C june 2014 – may 2023 TPS65263
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 8.3.2 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
- 8.3.3 Soft-Start Time
- 8.3.4 Power-Up Sequencing
- 8.3.5 V7V Low Dropout Regulator and Bootstrap
- 8.3.6 Out-of-Phase Operation
- 8.3.7 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.8 Pulse Skipping Mode (PSM)
- 8.3.9 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.10 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.11 Power Good
- 8.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Register Maps
- 8.5.1 Register Description
- 8.5.2 VOUT1_SEL: Vout1 Voltage Selection Register (offset = 0x00H)
- 8.5.3 VOUT2_SEL: Vout2 Voltage Selection Register (offset = 0x01H)
- 8.5.4 VOUT3_SEL: Vout3 Voltage Selection Register (offset = 0x02H)
- 8.5.5 VOUT1_COM: Buck1 Command Register (offset = 0x03H)
- 8.5.6 VOUT2_COM: Buck2 Command Register (offset = 0x04H)
- 8.5.7 VOUT3_COM: Buck3 Command Register (offset = 0x05H)
- 8.5.8 SYS_STATUS: System Status Register (offset = 0x06H)
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
9.2.2.4 Loop Compensation
The TPS65263 incorporates a peak current mode control scheme. The error amplifier is a trans-conductance amplifier with a gain of 300 µS. A typical type II compensation circuit adequately delivers a phase margin between 60° and 90°. Cb adds a high frequency pole to attenuate high frequency noise when needed. To calculate the external compensation components, follow the following steps.
- Select switching frequency ƒSW that is appropriate for application depending on L and C sizes, output ripple, EMI, and etc. Switching frequency between 500 kHz to 1 MHz gives best trade-off between performance and cost. To optimize efficiency, lower switching frequency is desired.
- Set up cross over frequency, ƒc, which is typically between 1/5 and 1/20 of ƒSW.
- RC can be determined by
Equation 17.
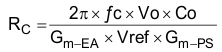
- Calculate CC by placing a compensation zero at or before the dominant pole
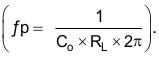 Equation 18.
Equation 18.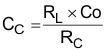
- Optional Cb can be used to cancel the zero from the ESR associated with CO.
Equation 19.
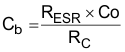
 Figure 9-1 DC/DC
Loop Compensation
Figure 9-1 DC/DC
Loop Compensation