SLVSBC6C March 2013 – December 2019 TPS84A20
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Ordering Information
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Device Information
- 8 Typical Characteristics (PVIN = VIN = 12 V)
- 9 Typical Characteristics (PVIN = VIN = 5 V)
- 10Typical Characteristics (PVIN = 3.3 V, VIN = 5 V)
-
11Application Information
- 11.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 11.2 Capacitor Recommendations for the TPS84A20 Power Supply
- 11.3 Transient Response
- 11.4 Transient Waveforms
- 11.5 Application Schematics
- 11.6 VIN and PVIN Input Voltage
- 11.7 3.3 V PVIN Operation
- 11.8 Power Good (PWRGD)
- 11.9 Light Load Efficiency (LLE)
- 11.10 SYNC_OUT
- 11.11 Parallel Operation
- 11.12 Power-Up Characteristics
- 11.13 Pre-Biased Start-Up
- 11.14 Remote Sense
- 11.15 Thermal Shutdown
- 11.16 Output On/Off Inhibit (INH)
- 11.17 Slow Start (SS/TR)
- 11.18 Overcurrent Protection
- 11.19 Synchronization (CLK)
- 11.20 Sequencing (SS/TR)
- 11.21 Programmable Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 11.22 Layout Considerations
- 11.23 EMI
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RVQ|42
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11.20 Sequencing (SS/TR)
Many of the common power supply sequencing methods can be implemented using the SS/TR, INH and PWRGD pins. The sequential method is illustrated in Figure 38 using two TPS84A20 devices. The PWRGD pin of the first device is coupled to the INH pin of the second device which enables the second power supply once the primary supply reaches regulation. Figure 39 shows sequential turnon waveforms of two TPS84A20 devices.
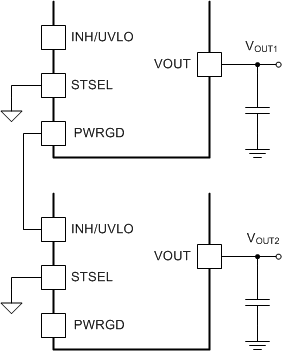 Figure 38. Sequencing Schematic
Figure 38. Sequencing Schematic 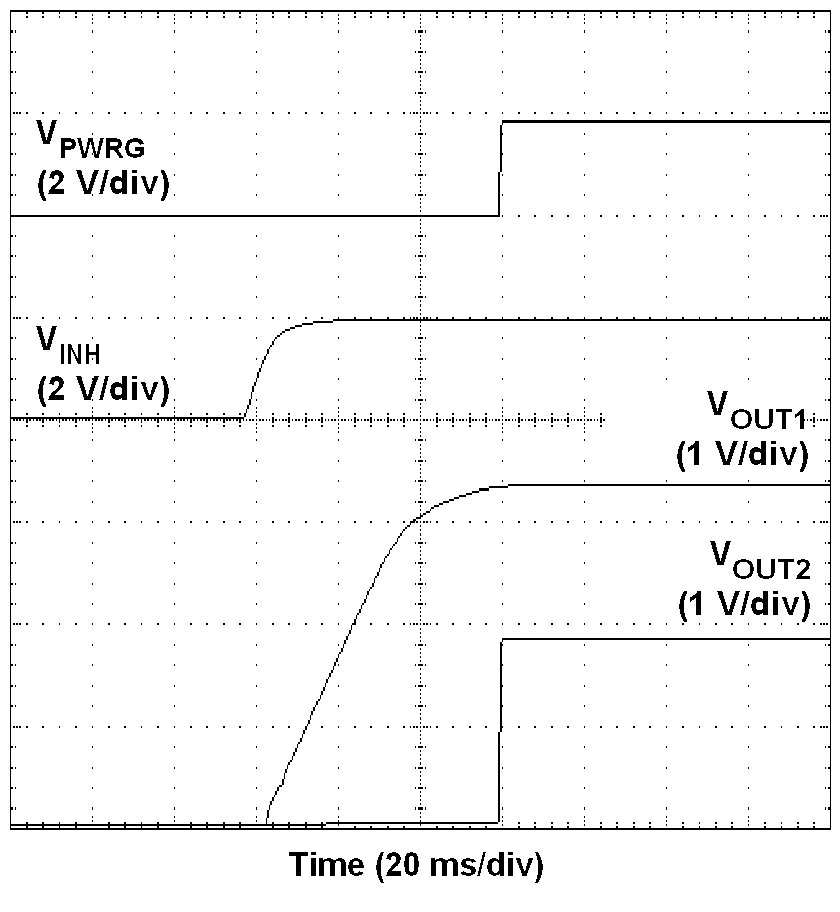 Figure 39. Sequencing Waveforms
Figure 39. Sequencing Waveforms Simultaneous power supply sequencing can be implemented by connecting the resistor network of R1 and R2 shown in Figure 40 to the output of the power supply that needs to be tracked or to another voltage reference source. The tracking voltage must exceed 750 mV before VOUT2 reaches its set-point voltage.Figure 41 shows simultaneous turnon waveforms of two TPS84A20 devices. Use and to calculate the values of R1 and R2.
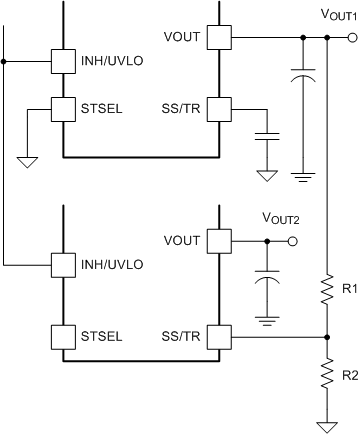 Figure 40. Simultaneous Tracking Schematic
Figure 40. Simultaneous Tracking Schematic 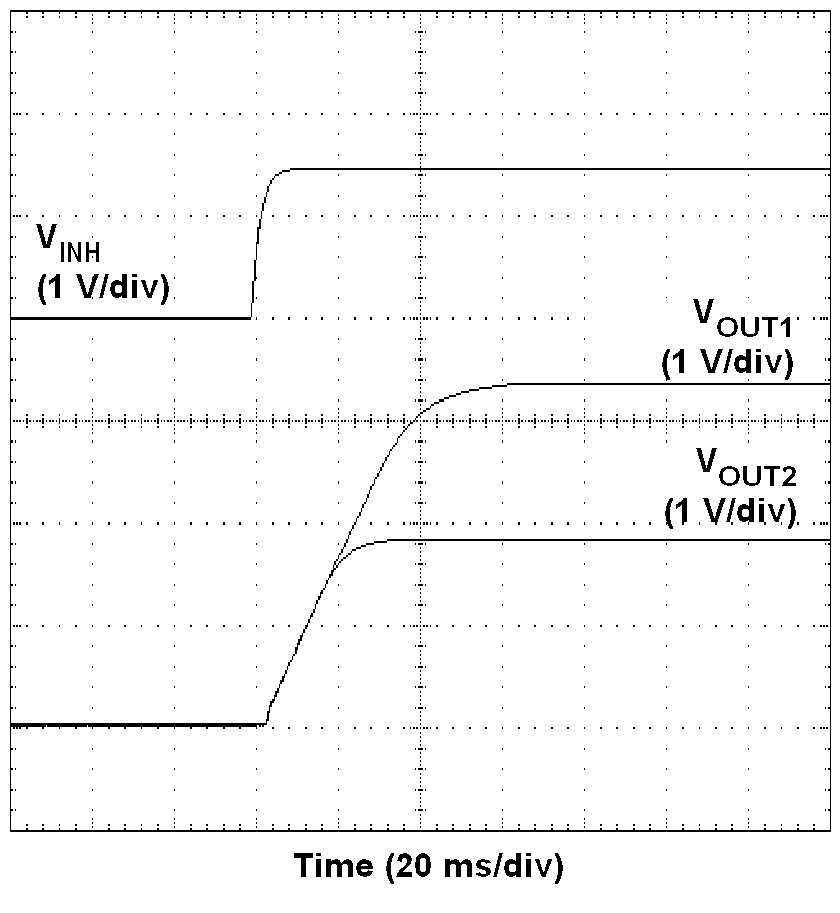 Figure 41. Simultaneous Tracking Waveforms
Figure 41. Simultaneous Tracking Waveforms