SCDS375A September 2017 – September 2017 TS5USBC402
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFP|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
There are many USB applications in which the USB hubs or controllers have a limited number of USB I/Os or need to route signals from a single USB connector. The TS5USBC402 solution can effectively expand the limited USB I/Os by switching between multiple USB buses to interface them to a single USB hub or controller or route signals from on connector to two different locations. With independent control of the two switches using SEL1 and SEL2, TS5USBC402 can be used to cross switch single ended signals.
9.2 Typical Application
TS5USBC402 USB/UART switch. The TS5USBC402 is used to switch signals between the USB path, which goes to the baseband or application processor, or the UART path, which goes to debug port. The TS5USBC402 has internal 6-MΩ pull-down resistors on SEL1, SEL2, and OE. The pull-down on SEL1 and SEL2 pins ensure the D1+/D1- channel is selected by default. The pull-down on OE enables the switch when power is applied.
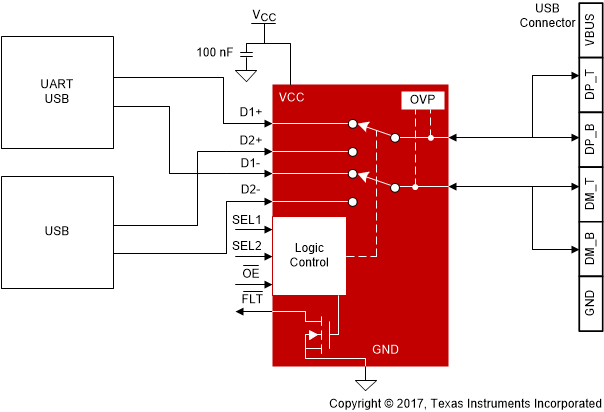 Figure 17. Typical TS5USBC402 Application
Figure 17. Typical TS5USBC402 Application
9.2.1 Design Requirements
Design requirements of USB 1.0,1.1, and 2.0 standards must be followed. The TS5USBC402 has internal 6-MΩ pulldown resistors on SEL1, SEL2, and OE, so no external resistors are required on the logic pins. The internal pull-down resistor on SEL1 and SEL2 pins ensures the D1+ and D1- channels are selected by default. The internal pull-down resistor on OE enables the switch when power is applied to VCC.
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The TS5USBC402can be properly operated without any external components. However, TI recommends that unused pins must be connected to ground through a 50-Ω resistor to prevent signal reflections back into the device. TI does recommend a 100nF bypass capacitor placed close to TS5USBC402 VCC pin.
9.2.3 Application Curves
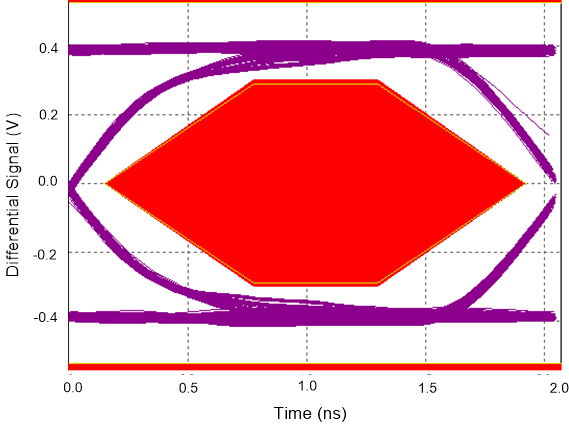 Figure 18. High Speed Eye Diagram With TS5USBC402
Figure 18. High Speed Eye Diagram With TS5USBC402
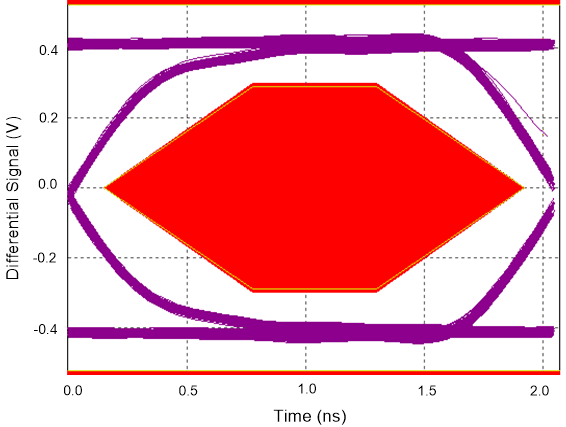 Figure 19. High Speed Eye Diagram Without TS5USBC402
Figure 19. High Speed Eye Diagram Without TS5USBC402