JAJSEG4C December 2013 – July 2018
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Details of a Qi Wireless Power System and bq51003 Power Transfer Flow Diagrams
- 8.3.2 Dynamic Rectifier Control
- 8.3.3 Dynamic Efficiency Scaling
- 8.3.4 RILIM Calculations
- 8.3.5 Input Overvoltage
- 8.3.6 Adapter Enable Functionality and EN1/EN2 Control
- 8.3.7 End Power Transfer Packet (WPC Header 0x02)
- 8.3.8 Status Outputs
- 8.3.9 WPC Communication Scheme
- 8.3.10 Communication Modulator
- 8.3.11 Adaptive Communication Limit
- 8.3.12 Synchronous Rectification
- 8.3.13 Temperature Sense Resistor Network (TS)
- 8.3.14 3-State Driver Recommendations for the TS-CTRL Pin
- 8.3.15 Thermal Protection
- 8.3.16 WPC v1.2 Compliance – Foreign Object Detection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
9.2.1.2.2 Series and Parallel Resonant Capacitor Selection
Shown in Figure 32, the capacitors C1 (series) and C2 (parallel) make up the dual resonant circuit with the receiver coil. These two capacitors must be sized correctly per the WPC v1.2 specification. Figure 33 illustrates the equivalent circuit of the dual resonant circuit:
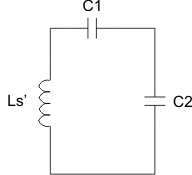 Figure 33. Dual Resonant Circuit With the Receiver Coil
Figure 33. Dual Resonant Circuit With the Receiver Coil Section 4.2 (Power Receiver Design Requirements) in Part 1 of the WPC v1.2 specification highlights in detail the sizing requirements. To summarize, the receiver designer will be required take inductance measurements with a fixed test fixture. Figure 34 shows the test fixture.
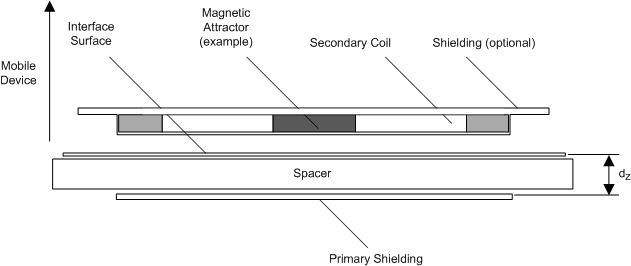 Figure 34. WPC v1.2 Receiver Coil Test Fixture for the Inductance Measurement Ls’ (Copied from System Description Wireless Power Transfer, Volume 1: Low Power, Part 1 Interface Definition,
Figure 34. WPC v1.2 Receiver Coil Test Fixture for the Inductance Measurement Ls’ (Copied from System Description Wireless Power Transfer, Volume 1: Low Power, Part 1 Interface Definition,
Version 1.2)
The primary shield is to be 50 mm x 50 mm x 1 mm of Ferrite material PC44 from TDK Corp. The gap dZ is to be 3.4 mm. The receiver coil, as it will be placed in the final system (that is, the back cover and battery must be included if the system calls for this), is to be placed on top of this surface and the inductance is to be measured at 1-V RMS and a frequency of 100 kHz. This measurement is termed Ls’. The same measurement is to be repeated without the test fixture shown in Figure 34. This measurement is termed Ls or the free-space inductance. Each capacitor can then be calculated using Equation 6:
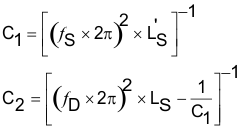
where
- fS is 100 kHz +5/-10%
- fD is 1 MHz ±10%.
C1 must be chosen first prior to calculating C2.
The quality factor must be greater than 77 and can be determined by Equation 7:
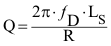
where
- R is the DC resistance of the receiver coil. All other constants are defined above.