JAJSFX6C August 2018 – July 2019 INA821
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DRG|8
発注情報
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
There are two modes of operation for the circuit shown in Figure 69: current input and voltage input. This design requires R1 >> R2 >> R3. Given this relationship, Equation 3 calculates the current input mode transfer function.
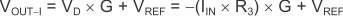
where
- G represents the gain of the instrumentation amplifier.
- VD represents the differential voltage at the INA821 inputs.
- VREF is the voltage at the INA821 REF pin.
- IIN is the input current.
Equation 4 shows the transfer function for the voltage input mode.
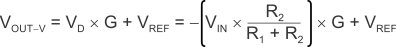
where
- VIN is the input voltage
R1 sets the input impedance of the voltage input mode. The minimum typical input impedance is 100 kΩ. The R1 value is 100 kΩ because increasing the R1 value also increases noise. The value of R3 must be extremely small compared to R1 and R2. The value of R3 is 20 Ω because that resistance value is smaller than R1 and yields an input voltage of ±400 mV when operating in current mode (±20 mA).
Use Equation 5 to calculate R2 if VD = ±400 mV, VIN = ±10 V, and R1 = 100 kΩ.
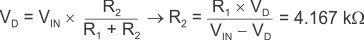
The value obtained from Equation 5 is not a standard 0.1% value, so 4.17 kΩ is selected. R1 and R2 use 0.1% tolerance resistors to minimize error.
Use Equation 6 to calculate the gain of the instrumentation amplifier.
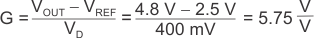
Equation 7 calculates the gain-setting resistor value using the INA821 gain equation (Equation 1).
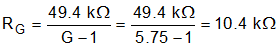
Use a standard 0.1% resistor value of 10.5 kΩ for this design.