SNAS474H April 2009 – March 2015 LM98725
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Modes of Operation Introduction
- 7.3.2 Mode 3 - Three Channel Input/Synchronous Pixel Sampling
- 7.3.3 Mode 2 - Two Channel Input/Synchronous Pixel Sampling
- 7.3.4 Mode 1 - One Channel Input
- 7.3.5 CIS Lamp and Coefficient Modes
- 7.3.6 Clock Sources
- 7.3.7 Clock Sources - Additional Settings and Flexibility
- 7.3.8 Spread Spectrum Clock Generation (SSCG)
- 7.3.9 Typical EMI Cases and Recommended SSCG Settings
- 7.3.10 Recommended Master/Slave, Clock Source and SSCG Combinations and Settings
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Mode 3 - Three Channel Input/Synchronous Pixel Sampling
- 7.4.2 Mode 2 - Two Channel Input/Synchronous Pixel Sampling
- 7.4.3 Mode 1 - One Channel Input
- 7.4.4 Input Bias and Clamping
- 7.4.5 Sample/Hold Mode
- 7.4.6 DC Coupled Applications
- 7.4.7 Input Source Follower Buffers
- 7.4.8 CDS Mode
- 7.4.9 VCLP DAC
- 7.4.10 Gain and Offset Correction
- 7.4.11 LM98725 Typical Line Timing and Pixel Gain Regions
- 7.4.12
Automatic Black and White Level Calibration Loops
- 7.4.12.1 Calibration Overview
- 7.4.12.2 Different Modes for Different Needs
- 7.4.12.3 Calibration Initiation
- 7.4.12.4 Key Calibration Settings
- 7.4.12.5 General Black Loop Operation
- 7.4.12.6 ADAC/DDAC Convergence
- 7.4.12.7 General White Loop Operation
- 7.4.12.8 White Loop Modes
- 7.4.12.9 Bimodal (Automatic) Correction
- 7.4.13 Coarse Pixel Phase Alignment
- 7.4.14 Internal Sample Timing
- 7.4.15 CCD Timing Generator Master/Slave Modes
- 7.4.16 LVDS Control Bit Coding - LM98714 Mode
- 7.4.17 Flexible LVDS Formatting Mode: Mapping
- 7.4.18 LVDS Data Randomization for EMI Reduction
- 7.4.19 LVDS Drive Strength Adjust
- 7.4.20 LVDS Output Timing Details
- 7.4.21 LVDS Data Latency Diagrams
- 7.4.22 Data Test Patterns
- 7.4.23 CMOS Output Format
- 7.4.24 CMOS Output Data Latency Diagrams
- 7.4.25 Serial Interface
- 7.5 Register Maps
- 8 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(2)(3)(1)
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any Positive Supply Voltage (VA, VR, VD, VC) | 4.2 | V | ||
| Voltage on Any Input or Output Pin (except DVB) (Not to exceed 4.2V) | −0.3 | 4.2 | V | |
| DVB Output Voltage | 2.0 | V | ||
| Input Current at any pin(4) | ±25 | mA | ||
| Package Input Current(4) | ±50 | mA | ||
| Package Dissipation at TA = 25°C(7) | 1.9 | W | ||
| Soldering Temperature, Infrared, 10 seconds(8) | 235 | °C | ||
(1) If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the Texas Instruments Sales Office/ Distributors for availability and specifications.
(2) Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is functional, but do not ensure specific performance limits. For ensured specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The ensured specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test conditions. Operation of the device beyond the Operating Ratings is not recommended.
(3) All voltages are measured with respect to AGND = DGND = 0V, unless otherwise specified.
(4) When the input voltage (VIN) at any pin exceeds the power supplies (VIN < GND or VIN > VA or VD), the current at that pin should be limited to 25 mA. The 50 mA maximum package input current rating limits the number of pins that can simultaneously safely exceed the power supplies with an input current of 25 mA to two.
(5) Human body model is 100 pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5-kΩ resistor. Machine model is 220-pF discharged through 0Ω.
(6) Reflow temperature profiles are different for lead-free and non-lead-free packages.
(7) The absolute maximum junction temperature (TJMAX) for this device is 150°C. The maximum allowable power dissipation is dictated by TJMAX, the junction to ambient thermal resistance (RθJA), and the ambient temperature (TA), and can be calculated using the formula PDMAX = (TJMAX - TA)/RθJA. The values for maximum power dissipation listed will be reached only when the LM98725 is operated in a severe faulty condition.
(8) See AN450, “Surface Mounting Methods and Their Effect on Product Reliability”, or the section entitled “Surface Mount” found in any post 1986 Texas Instruments Semiconductor Linear Data Book, for other methods of soldering surface mount devices.
6.2 Handling Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | −65 | +150 | °C | |
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge(5) | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | 2500 | V | |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | 250 | ||||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 2500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions(1)(2)
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature Range | 0 ≤ TA ≤ +70 | °C | |
| All Supply Voltage | +3.0 | +3.6 | V |
(1) Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is functional, but do not ensure specific performance limits. For ensured specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The ensured specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test conditions. Operation of the device beyond the Operating Ratings is not recommended.
(2) All voltages are measured with respect to AGND = DGND = 0V, unless otherwise specified.
6.4 Electrical Characteristics
The following specifications apply for VA = VD = VR = VC = 3.3 V, CL = 10 pF, and fINCLK = 27 MHz unless otherwise specified. all other limits TA = 25°C.(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(2) | TYP(3) | MAX(2) | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMOS DIGITAL INPUT DC SPECIFICATIONS (RESETb, SH_R, SCLK, SENb) | |||||||
| VIH | Logical “1” Input Voltage | 2.0 | V | ||||
| VIL | Logical “0” Input Voltage | 0.8 | V | ||||
| VIHYST | Logic Input Hysteresis | 0.6 | V | ||||
| IIH | Logical “1” Input Current | VIH = VD: | |||||
| RESET, SEN | 100 | nA | |||||
| SH_R, SCLK, SDI, CAL | 65 | μA | |||||
| CE | 30 | ||||||
| IIL | Logical “0” Input Current | VIL = DGND: | |||||
| RESET, SEN | –65 | μA | |||||
| SH_R, SCLK, SDI, CAL | –100 | nA | |||||
| CE | –30 | μA | |||||
| CMOS DIGITAL OUTPUT DC SPECIFICATIONS (SH1 to SH5, RS, CP, PHIA, PHIB, PHIC) | |||||||
| VOH | Logical “1” Output Voltage | IOUT = -0.5 mA | 3.0 | V | |||
| VOL | Logical “0” Output Voltage | IOUT = 1.6 mA | 0.21 | V | |||
| IOS | Output Short Circuit Current | VOUT = DGND | 18 | mA | |||
| VOUT= VD | –25 | ||||||
| IOZ | CMOS Output TRI-STATE Current | VOUT = DGND | 20 | nA | |||
| VOUT = VD | –25 | ||||||
| CMOS DIGITAL OUTPUT DC SPECIFICATIONS (CMOS DATA OUTPUTS) | |||||||
| VOH | Logical “1” Output Voltage | IOUT = -0.5 mA | 2.3 | V | |||
| VOL | Logical “0” Output Voltage | IOUT = 1.6 mA | 0.12 | V | |||
| IOS | Output Short Circuit Current | VOUT = DGND | 12 | mA | |||
| VOUT= VD | –14 | ||||||
| IOZ | CMOS Output TRI-STATE Current | VOUT = DGND | 20 | nA | |||
| VOUT = VD | –25 | ||||||
| LVDS/CMOS CLOCK RECEIVER DC SPECIFICATIONS (INCLK+ and INCLK-PINS) | |||||||
| VIHL | Differential LVDS Clock | RL = 100 Ω VCM (LVDS Input Common Mode Voltage)= 1.25 V |
200 | mV | |||
| High Threshold Voltage | |||||||
| VILL | Differential LVDS Clock | –200 | mV | ||||
| Low Threshold Voltage | |||||||
| VIHC | CMOS Clock | INCLK- = DGND | 2.0 | V | |||
| High Threshold Voltage | |||||||
| VILC | CMOS Clock | 0.8 | V | ||||
| Low Threshold Voltage | |||||||
| IIHL | CMOS Clock | 230 | 260 | μA | |||
| Input High Current | |||||||
| IILC | CMOS Clock | –135 | –120 | μA | |||
| Input Low Current | |||||||
| LVDS OUTPUT DC SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| VOD | Differential Output Voltage | RL = 100 Ω | 280 | 390 | 490 | mV | |
| VOS | LVDS Output Offset Voltage | 1.08 | 1.20 | 1.33 | V | ||
| IOS | Output Short Circuit Current | VOUT = 0 V, RL = 100 Ω | 8.5 | mA | |||
| POWER SUPPLY SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| IA | VA Analog Supply Current | LVDS Output Data Format | 152 | 180 | mA | ||
| LVDS Output Data Format (Powerdown) |
3.6 | 6 | mA | ||||
| CMOS Output Data Format (40 MHz) |
136 | 168 | mA | ||||
| ID | VD Digital Output Driver Supply Current | LVDS Output Data Format | 76 | 94 | mA | ||
| LVDS Output Data Format (Powerdown) |
8.5 | 17 | mA | ||||
| CMOS Output Data Format (ATE Loading of CMOS Outputs > 50 pF) (40 MHz) |
46 | 68 | mA | ||||
| IC | VC CCD Timing Generator Output Driver Supply Current | Typical sensor outputs: SH1-SH5, PHIA, PHIB, PHIC, RS, CP (ATE Loading of CMOS Outputs > 50 pF) | 1 | 4 | mA | ||
| PWR | Average Power Dissipation | LVDS Output Data Format | 755 | 885 | mW | ||
| LVDS Output Data Format (Powerdown) |
40 | 70 | mW | ||||
| CMOS Output Data Format (ATE Loading of CMOS Outputs > 50 pF) (40 MHz) |
600 | 740 | mW | ||||
| INPUT SAMPLING CIRCUIT SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| VIN | Input Voltage Level | CDS Gain=1x, PGA Gain=1x | 2.3 | Vp-p | |||
| CDS Gain=2x, PGA Gain= 1x | 1.22 | ||||||
| IIN_SH | Sample and Hold Mode Input Leakage Current (Vclamp = Default = 2.6 V) |
Source Followers Off CDS/SH Gain = 1x OSX = VA (OSX = AGND) |
(–200) | 32 (-165) |
50 | μA | |
| Source Followers Off CDS/SH Gain = 2x OSX = VA (OSX = AGND) |
(–290) | 55 (–240) |
70 | μA | |||
| Source Followers On CDS/SH Gain = 2x OSX = VA (OSX = AGND) |
(–250) | 20 (–50) |
250 | nA | |||
| CSH | Sample/Hold Mode Equivalent Input Capacitance (see Figure 12) |
CDS Gain = 1x | 2.5 | pF | |||
| CDS Gain = 2x | 4 | pF | |||||
| IIN_CDS | CDS Mode Input Leakage Current |
Source Followers Off OSX = VA (OSX = AGND) |
(–250) | 10 (–50) |
250 | nA | |
| RCLPIN | CLPIN Switch Resistance (OSX to VCLP Node in Figure 9) |
16 | 55 | Ω | |||
| VCLP REFERENCE CIRCUIT SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| VVCLP | VCLP Voltage 000 | VCLP Voltage Setting = 000 | 0.85VA | V | |||
| VCLP Voltage 001 | VCLP Voltage Setting = 001 | 0.9VA | V | ||||
| VCLP Voltage 010 | VCLP Voltage Setting = 010 | 0.95VA | V | ||||
| VCLP Voltage 011 | VCLP Voltage Setting = 011 | 0.6VA | V | ||||
| VCLP Voltage 100 | VCLP Voltage Setting = 100 | 0.55VA | V | ||||
| VCLP Voltage 101 | VCLP Voltage Setting = 101 | 0.4VA | V | ||||
| VCLP Voltage 110 | VCLP Voltage Setting = 110 | 0.35VA | V | ||||
| VCLP Voltage 111 | VCLP Voltage Setting = 111 | 0.15VA | V | ||||
| ISC | VCLP DAC Short Circuit Output Current | 30 | mA | ||||
| BLACK LEVEL OFFSET DAC SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| Resolution | 10 | Bits | |||||
| Monotonicity | Ensured by characterization | ||||||
| Offset Adjustment Range Referred to AFE Input |
CDS Gain = 1x | mV | |||||
| Minimum DAC Code = 0x000 | –614 | ||||||
| Maximum DAC Code = 0x3FF | 614 | ||||||
| CDS Gain = 2x | mV | ||||||
| Minimum DAC Code = 0x000 | –307 | ||||||
| Maximum DAC Code = 0x3FF | 307 | ||||||
| Offset Adjustment Range Referred to AFE Output |
Minimum DAC Code = 0x000 | –17500 | –16130 | LSB | |||
| Maximum DAC Code = 0x3FF | +16130 | +17500 | |||||
| DAC LSB Step Size | CDS Gain = 1x Referred to AFE Output |
1.2 | mV | ||||
| (32) | (LSB) | ||||||
| DNL | Differential Non-Linearity | –0.84 | +0.74/ –0.37 |
+2.4 | LSB | ||
| INL | Integral Non-Linearity | –2.5 | +0.72/ –0.56 |
+2.5 | LSB | ||
| PGA SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| Gain Resolution | 8 | Bits | |||||
| Monotonicity | Ensured by characterization | ||||||
| Maximum Gain | CDS Gain = 1x | 7.7 | 8.3 | 8.8 | V/V | ||
| CDS Gain = 1x | 17.7 | 18.4 | 18.9 | dB | |||
| Minimum Gain | CDS Gain = 1x | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.67 | V/V | ||
| CDS Gain = 1x | –4.7 | –4.2 | –3.5 | dB | |||
| PGA Function | Gain (V/V) = (180/(277-PGA Code)) Gain (dB) = 20LOG10(180/(277-PGA Code)) |
||||||
| Channel Matching | Minimum PGA Gain | 3% | |||||
| Maximum PGA Gain | 12.7% | ||||||
| ADC SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| VREFT | Top of Reference | 2.07 | V | ||||
| VREFB | Bottom of Reference | 0.89 | V | ||||
| VREFT - VREFB | Differential Reference Voltage | 1.06 | 1.18 | 1.30 | V | ||
| Over range Output Code | 65535 | ||||||
| Under range Output Code | 0 | ||||||
| DIGITAL OFFSET “DAC” SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| Resolution | 7 | Bits | |||||
| Digital Offset DAC LSB Step Size | Referred to AFE Output | 32 | LSB | ||||
| Offset Adjustment Range Referred to AFE Output | Min DAC Code =7'b0000000 | –2048 | LSB | ||||
| Mid DAC Code =7'b1000000 | 0 | ||||||
| Max DAC Code = 7'b1111111 | +2016 | ||||||
| FULL CHANNEL PERFORMANCE SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| DNL | Differential Non-Linearity | See (1) | -0.999 | +0.8/ –0.7 |
2.5 | LSB | |
| INL | Integral Non-Linearity | See (1) | –75 | +18/ –25 |
75 | LSB | |
| SNR | Total Output Noise | Minimum PGA Gain(1) | –76 | dB | |||
| 10 | 26 | LSB RMS | |||||
| Maximum PGA Gain(1) | –56 | dB | |||||
| 96 | LSB RMS | ||||||
| Channel to Channel Crosstalk | Mode 3 | 26 | LSB | ||||
| Mode 2 | 17 | ||||||
(1) This parameter ensured by design and characterization.
(2) Test limits are specified to Texas Instruments' AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
(3) Typical figures are at TA = 25°C, and represent most likely parametric norms at the time of product characterization. The typical specifications are not ensured.
6.5 AC Timing Specifications
The following specifications apply for VA = VD = VR = VC = 3.3 V, CL = 10 pF, and fINCLK = 27 MHz unless otherwise specified. All other limits TA = 25°C.(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(1) | TYP(2) | MAX(1) | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT CLOCK TIMING SPECIFICATIONS | ||||||
| fINCLK | Input Clock Frequency | INCLK = PIXCLK (Pixel Rate Clock) | 0.66 | 27 (Mode 3) | MHz | |
| 1 | 30 (Mode 2) | |||||
| 1 | 30 (Mode 1) | |||||
| INCLK = ADCCLK (ADC Rate Clock) | 2 | 81 (Mode 3) | MHz | |||
| 2 | 60 (Mode 2) | |||||
| 2 | 30 (Mode 1) | |||||
| Tdc | Input Clock Duty Cycle | 40/60% | 50/50% | 60/40% | ||
| FULL CHANNEL LATENCY SPECIFICATIONS | ||||||
| tLAT3 | 3 Channel Mode Pipeline Delay | PIXPHASE0 | 24 | TADC | ||
| Figure 53 (LVDS) | PIXPHASE1 | 23.5 | ||||
| Figure 58 (CMOS) | PIXPHASE2 | 23 | ||||
| PIXPHASE3 | 22.5 | |||||
| tLAT2 | 2 Channel Mode Pipeline Delay | PIXPHASE0 | 21 | TADC | ||
| Figure 54 (LVDS) | PIXPHASE1 | 20.5 | ||||
| Figure 59 (CMOS) | PIXPHASE2 | 20 | ||||
| PIXPHASE3 | 19.5 | |||||
| tLAT1 | 1 Channel Mode Pipeline Delay | PIXPHASE0 | 19 | TADC | ||
| Figure 55 (LVDS) | PIXPHASE1 | 18.5 | ||||
| Figure 60 (CMOS) | PIXPHASE2 | 18 | ||||
| PIXPHASE3 | 17.5 | |||||
| SH_R TIMING SPECIFICATIONS (Figure 43) | ||||||
| tSHR_S | SH_R Setup Time | 2 | ns | |||
| tSHR_H | SH_R Hold Time | 2 | ns | |||
| LVDS OUTPUT TIMING SPECIFICATIONS (Figure 52) | ||||||
| TXpp0 | TXCLK to Pulse Position 0 | -0.26 | 0 | 0.26 | ns | |
| TXpp1 | TXCLK to Pulse Position 1 | 1.50 | 1.76 | 2.02 | ns | |
| TXpp2 | TXCLK to Pulse Position 2 | 3.26 | 3.53 | 3.79 | ns | |
| TXpp3 | TXCLK to Pulse Position 3 | 5.03 | 5.29 | 5.55 | ns | |
| TXpp4 | TXCLK to Pulse Position 4 | 6.80 | 7.06 | 7.32 | ns | |
| TXpp5 | TXCLK to Pulse Position 5 | 8.56 | 8.82 | 9.08 | ns | |
| TXpp6 | TXCLK to Pulse Position 6 | 10.32 | 10.58 | 10.84 | ns | |
| CMOS OUTPUT TIMING SPECIFICATIONS | ||||||
| tCRDO | CLKOUT Rising Edge to CMOS Output Data Transition | fINCLK = 40 MHz, INCLK = ADCCLK (ADC Rate Clock) |
2 | 4.5 | 9 | ns |
| SERIAL INTERFACE TIMING SPECIFICATIONS | ||||||
| fSCLK | Input Clock Frequency | fSCLK <= fINCLK,
INCLK = PIXCLK (Pixel Rate Clock) Mode 3/2/1 |
27/30/30 | MHz | ||
| fSCLK <= fINCLK,
INCLK = ADCCLK (ADC Rate Clock) Mode 3/2/1 |
81/60/30 | MHz | ||||
| SCLK Duty Cycle | 50/50 | ns | ||||
| tIH | Input Hold Time | 1.5 | ns | |||
| tIS | Input Setup Time | 2.5 | ns | |||
| tSENSC | SCLK Start Time after SEN Low | 1.5 | ns | |||
| tSCSEN | SEN High after last SCLK Rising Edge | 2.5 | ns | |||
| tSENW | SEN Pulse Width | INCLK present(4)(5) | 6 | TINCLK | ||
| INCLK stopped(4)(5) | 50 | ns | ||||
| tOD | Output Delay Time | 11 | 14 | ns | ||
| tHZ | Data Output to High Z | 0.5 | TSCLK | |||
(1) Test limits are specified to AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
(2) Typical figures are at TA = 25°C, and represent most likely parametric norms at the time of product characterization. The typical specifications are not ensured.
(3) The analog inputs are protected as shown in Figure 2. Input voltage magnitudes beyond the supply rails will not damage the device, provided the current is limited per Note 4 under the Absolute Maximum Ratings Table. However, input errors will be generated If the input goes above VA and below AGND.
(4) If the input INCLK is divided down to a lower internal clock rate via the PLL, the parameter tSENW will be increased by the same factor.
(5) When the Spread Spectrum Clock Generation feature is enabled, tSENW should be increased by 1.
6.6 Serial Interface Timing Details
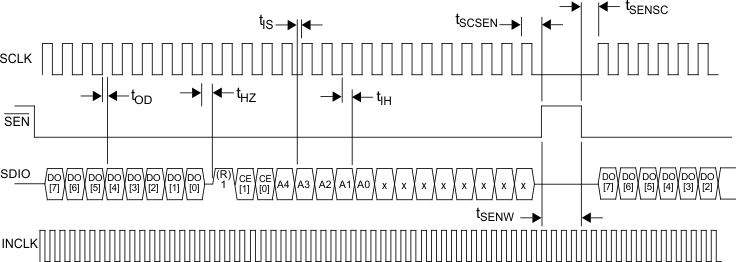 Figure 1. Serial Interface Specification Diagram
Figure 1. Serial Interface Specification Diagram