JAJSCC1 June 2016 SM320C6748-HIREL
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1デバイスの概要
- 2改訂履歴
-
3Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 3.1 Pin Diagram
- 3.2
Pin Attributes
- 3.2.1 Device Reset, NMI and JTAG
- 3.2.2 High-Frequency Oscillator and PLL
- 3.2.3 Real-Time Clock and 32-kHz Oscillator
- 3.2.4 DEEPSLEEP Power Control
- 3.2.5 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 3.2.6 DDR2/mDDR Controller
- 3.2.7 Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (SPI)
- 3.2.8 Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU)
- 3.2.9 Enhanced Capture/Auxiliary PWM Modules (eCAP0)
- 3.2.10 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulators (eHRPWM)
- 3.2.11 Boot
- 3.2.12 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters (UART0, UART1, UART2)
- 3.2.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit Modules (I2C0, I2C1)
- 3.2.14 Timers
- 3.2.15 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP)
- 3.2.16 Multichannel Buffered Serial Ports (McBSP)
- 3.2.17 Universal Serial Bus Modules (USB0, USB1)
- 3.2.18 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 3.2.19 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD)
- 3.2.20 Liquid Crystal Display Controller (LCDC)
- 3.2.21 Serial ATA Controller (SATA)
- 3.2.22 Universal Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
- 3.2.23 Universal Parallel Port (uPP)
- 3.2.24 Video Port Interface (VPIF)
- 3.2.25 General Purpose Input Output
- 3.2.26 Reserved and No Connect
- 3.2.27 Supply and Ground
- 3.3 Pin Multiplexing
- 3.4 Connections for Unused Pins
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Power-On-Hours (POH) Limits
- 4.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.6 Thermal Data for GWT Package
- 4.7
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 4.7.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 4.7.2 Power Supply Sequencing
- 4.7.3 Reset Timing
- 4.7.4 Clock Specifications
- 4.7.5 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 4.7.6
Peripherals
- 4.7.6.1 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC)
- 4.7.6.2 Enhanced Direct Memory Access Controller (EDMA3)
- 4.7.6.3 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 4.7.6.4
DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller
- 4.7.6.4.1 DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller Electrical Data/Timing
- 4.7.6.4.2 DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller Register Description(s)
- 4.7.6.4.3
DDR2/mDDR Interface
- 4.7.6.4.3.1 DDR2/mDDR Interface Schematic
- 4.7.6.4.3.2 Compatible JEDEC DDR2/mDDR Devices
- 4.7.6.4.3.3 PCB Stackup
- 4.7.6.4.3.4 Placement
- 4.7.6.4.3.5 DDR2/mDDR Keep Out Region
- 4.7.6.4.3.6 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 4.7.6.4.3.7 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 4.7.6.4.3.8 Net Classes
- 4.7.6.4.3.9 DDR2/mDDR Signal Termination
- 4.7.6.4.3.10 VREF Routing
- 4.7.6.4.3.11 DDR2/mDDR CK and ADDR_CTRL Routing
- 4.7.6.4.3.12 DDR2/mDDR Boundary Scan Limitations
- 4.7.6.5 Memory Protection Units
- 4.7.6.6 MMC / SD / SDIO (MMCSD0, MMCSD1)
- 4.7.6.7 Serial ATA Controller (SATA)
- 4.7.6.8 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 4.7.6.9 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 4.7.6.10 Serial Peripheral Interface Ports (SPI0, SPI1)
- 4.7.6.11 Inter-Integrated Circuit Serial Ports (I2C)
- 4.7.6.12 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 4.7.6.13 Universal Serial Bus OTG Controller (USB0) [USB2.0 OTG]
- 4.7.6.14 Universal Serial Bus Host Controller (USB1) [USB1.1 OHCI]
- 4.7.6.15 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 4.7.6.16 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 4.7.6.17 LCD Controller (LCDC)
- 4.7.6.18 Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
- 4.7.6.19 Universal Parallel Port (uPP)
- 4.7.6.20 Video Port Interface (VPIF)
- 4.7.6.21 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Peripheral
- 4.7.6.22 Enhanced High-Resolution Pulse-Width Modulator (eHRPWM)
- 4.7.6.23 Timers
- 4.7.6.24 Real Time Clock (RTC)
- 4.7.6.25 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 4.7.6.26 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS)
- 4.7.7 Emulation and Debug
- 5Detailed Description
- 6デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 7メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
5 Detailed Description
5.1 Device Overview
Table 5-1 provides an overview of the device. The table shows significant features of the device, including the capacity of on-chip RAM, peripherals, and the package type with pin count.
Table 5-1 Characteristics of C6748
| HARDWARE FEATURES | C6748 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peripherals Not all peripherals pins are available at the same time (for more detail, see the Device Configurations section). |
DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller | DDR2, 16-bit bus width, up to 156 MHz Mobile DDR, 16-bit bus width, up to 150 MHz |
||
| EMIFA | Asynchronous (8/16-bit bus width) RAM, Flash, 16-bit SDRAM, NOR, NAND |
|||
| Flash Card Interface | 2 MMC and SD cards supported | |||
| EDMA3 | 64 independent channels, 16 QDMA channels, 2 channel controllers, 3 transfer controllers |
|||
| Timers | 4 64-Bit General Purpose (each configurable as 2 separate 32-bit timers, one configurable as Watch Dog) | |||
| UART | 3 (each with RTS and CTS flow control) | |||
| SPI | 2 (Each with one hardware chip select) | |||
| I2C | 2 (both Master/Slave) | |||
| Multichannel Audio Serial Port [McASP] | 1 (each with transmit/receive, FIFO buffer, 16 serializers) | |||
| Multichannel Buffered Serial Port [McBSP] | 2 (each with transmit/receive, FIFO buffer, 16) | |||
| 10/100 Ethernet MAC with Management Data I/O | 1 (MII or RMII Interface) | |||
| eHRPWM | 4 Single Edge, 4 Dual Edge Symmetric, or 2 Dual Edge Asymmetric Outputs |
|||
| eCAP | 3 32-bit capture inputs or 3 32-bit auxiliary PWM outputs | |||
| UHPI | 1 (16-bit multiplexed address/data) | |||
| USB 2.0 (USB0) | High-Speed OTG Controller with on-chip OTG PHY | |||
| USB 1.1 (USB1) | Full-Speed OHCI (as host) with on-chip PHY | |||
| General-Purpose Input/Output Port | 9 banks of 16-bit | |||
| LCD Controller | 1 | |||
| SATA Controller | 1 (Supports both SATA I and SATAII) | |||
| Universal Parallel Port (uPP) | 1 | |||
| Video Port Interface (VPIF) | 1 (video in and video out) | |||
| PRU Subsystem (PRUSS) | 2 Programmable PRU Cores | |||
| On-Chip Memory | Size (Bytes) | 448KB RAM | ||
| Organization | DSP
32KB L1 Program (L1P)/Cache (up to 32KB) 32KB L1 Data (L1D)/Cache (up to 32KB) 256KB Unified Mapped RAM/Cache (L2) DSP Memories can be made accessible to EDMA3 and other peripherals. ADDITIONAL MEMORY 128KB RAM |
|||
| Security | Secure Boot | TI Basic Secure Boot | ||
| C674x CPU ID + CPU Rev ID | Control Status Register (CSR.[31:16]) | 0x1400 | ||
| C674x Megamodule Revision | Revision ID Register (MM_REVID[15:0]) | 0x0000 | ||
| JTAG BSDL_ID | DEVIDR0 Register | see Section 4.7.7.4.1, JTAG Peripheral Register Description | ||
| CPU Frequency | MHz | 674x DSP 375 MHz (1.2 V) | ||
| Voltage | Core (V) | Variable (1.2 V - 1 V) for 375 MHz version | ||
| I/O (V) | 1.8 V or 3.3 V | |||
| Packages | 16 mm x 16 mm, 361-Ball 0.80 mm pitch, PBGA (GWT) | |||
| Product Status(1) | Product Preview (PP), Advance Information (AI), or Production Data (PD) |
375 MHz versions - PD | ||
5.2 Device Compatibility
The C674x DSP core is code-compatible with the C6000™ DSP platform and supports features of both the C64x+ and C67x+ DSP families.
5.3 DSP Subsystem
The DSP Subsystem includes the following features:
- C674x DSP CPU
- 32KB L1 Program (L1P)/Cache (up to 32KB)
- 32KB L1 Data (L1D)/Cache (up to 32KB)
- 256KB Unified Mapped RAM/Cache (L2)
- Boot ROM (cannot be used for application code)
- Little endian
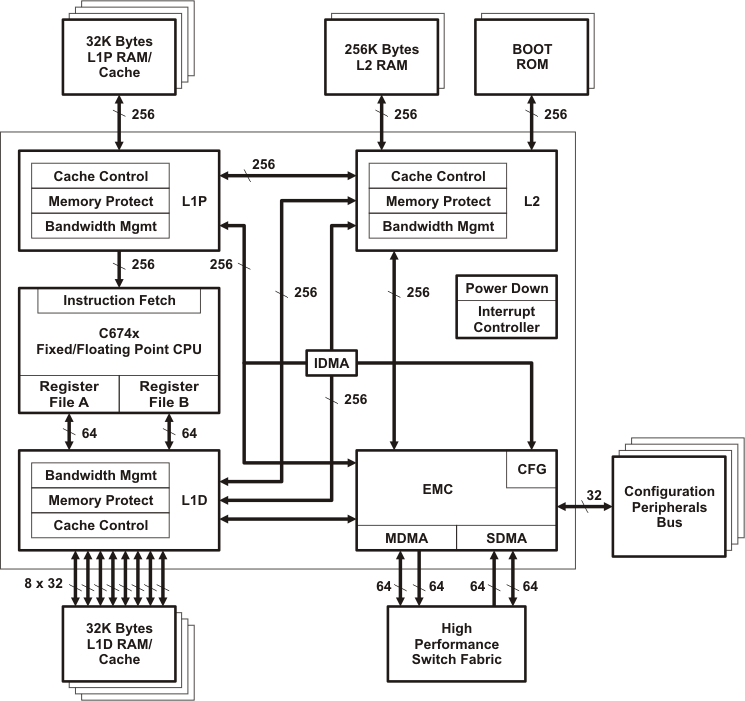 Figure 5-1 C674x Megamodule Block Diagram
Figure 5-1 C674x Megamodule Block Diagram
5.3.1 C674x DSP CPU Description
The C674x Central Processing Unit (CPU) consists of eight functional units, two register files, and two data paths as shown in Figure 5-2. The two general-purpose register files (A and B) each contain 32 32-bit registers for a total of 64 registers. The general-purpose registers can be used for data or can be data address pointers. The data types supported include packed 8-bit data, packed 16-bit data, 32-bit data, 40-bit data, and 64-bit data. Values larger than 32 bits, such as 40-bit-long or 64-bit-long values are stored in register pairs, with the 32 LSBs of data placed in an even register and the remaining 8 or 32 MSBs in the next upper register (which is always an odd-numbered register).
The eight functional units (.M1, .L1, .D1, .S1, .M2, .L2, .D2, and .S2) are each capable of executing one instruction every clock cycle. The .M functional units perform all multiply operations. The .S and .L units perform a general set of arithmetic, logical, and branch functions. The .D units primarily load data from memory to the register file and store results from the register file into memory.
The C674x CPU combines the performance of the C64x+ core with the floating-point capabilities of the C67x+ core.
Each C674x .M unit can perform one of the following each clock cycle: one 32 x 32 bit multiply, one 16 x 32 bit multiply, two 16 x 16 bit multiplies, two 16 x 32 bit multiplies, two 16 x 16 bit multiplies with add/subtract capabilities, four 8 x 8 bit multiplies, four 8 x 8 bit multiplies with add operations, and four 16 x 16 multiplies with add/subtract capabilities (including a complex multiply). There is also support for Galois field multiplication for 8-bit and 32-bit data. Many communications algorithms such as FFTs and modems require complex multiplication. The complex multiply (CMPY) instruction takes for 16-bit inputs and produces a 32-bit real and a 32-bit imaginary output. There are also complex multiplies with rounding capability that produces one 32-bit packed output that contain 16-bit real and 16-bit imaginary values. The 32 x 32 bit multiply instructions provide the extended precision necessary for high-precision algorithms on a variety of signed and unsigned 32-bit data types.
The .L or (Arithmetic Logic Unit) now incorporates the ability to do parallel add/subtract operations on a pair of common inputs. Versions of this instruction exist to work on 32-bit data or on pairs of 16-bit data performing dual 16-bit add and subtracts in parallel. There are also saturated forms of these instructions.
The C674x core enhances the .S unit in several ways. On the previous cores, dual 16-bit MIN2 and MAX2 comparisons were only available on the .L units. On the C674x core they are also available on the .S unit which increases the performance of algorithms that do searching and sorting. Finally, to increase data packing and unpacking throughput, the .S unit allows sustained high performance for the quad 8-bit/16-bit and dual 16-bit instructions. Unpack instructions prepare 8-bit data for parallel 16-bit operations. Pack instructions return parallel results to output precision including saturation support.
Other new features include:
- SPLOOP - A small instruction buffer in the CPU that aids in creation of software pipelining loops where multiple iterations of a loop are executed in parallel. The SPLOOP buffer reduces the code size associated with software pipelining. Furthermore, loops in the SPLOOP buffer are fully interruptible.
- Compact Instructions - The native instruction size for the C6000 devices is 32 bits. Many common instructions such as MPY, AND, OR, ADD, and SUB can be expressed as 16 bits if the C674x compiler can restrict the code to use certain registers in the register file. This compression is performed by the code generation tools.
- Instruction Set Enhancement - As noted above, there are new instructions such as 32-bit multiplications, complex multiplications, packing, sorting, bit manipulation, and 32-bit Galois field multiplication.
- Exceptions Handling - Intended to aid the programmer in isolating bugs. The C674x CPU is able to detect and respond to exceptions, both from internally detected sources (such as illegal op-codes) and from system events (such as a watchdog time expiration).
- Privilege - Defines user and supervisor modes of operation, allowing the operating system to give a basic level of protection to sensitive resources. Local memory is divided into multiple pages, each with read, write, and execute permissions.
- Time-Stamp Counter - Primarily targeted for Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) robustness, a free-running time-stamp counter is implemented in the CPU which is not sensitive to system stalls.
For more details on the C674x CPU and its enhancements over the C64x architecture, see the following documents:
- TMS320C64x/C64x+ DSP CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (literature number SPRUFE8)
- TMS320C64x Technical Overview (literature number SPRU395)
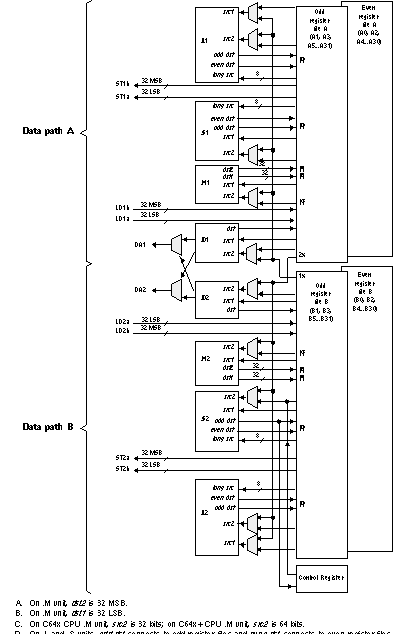 Figure 5-2 TMS320C674x CPU (DSP Core) Data Paths
Figure 5-2 TMS320C674x CPU (DSP Core) Data Paths
5.3.2 DSP Memory Mapping
The DSP memory map is shown in Section 5.4.
By default the DSP also has access to most on and off chip memory areas.
Additionally, the DSP megamodule includes the capability to limit access to its internal memories through its SDMA port; without needing an external MPU unit.
5.3.2.1 External Memories
The DSP has access to the following External memories:
- Asynchronous EMIF / SDRAM / NAND / NOR Flash (EMIFA)
- SDRAM (DDR2)
5.3.2.2 DSP Internal Memories
The DSP has access to the following DSP memories:
- L2 RAM
- L1P RAM
- L1D RAM
5.3.2.3 C674x CPU
The C674x core uses a two-level cache-based architecture. The Level 1 Program cache (L1P) is 32 KB direct mapped cache and the Level 1 Data cache (L1D) is 32 KB 2-way set associated cache. The Level 2 memory/cache (L2) consists of a 256 KB memory space that is shared between program and data space. L2 memory can be configured as mapped memory, cache, or a combination of both.
Table 5-2 shows a memory map of the C674x CPU cache registers for the device.
Table 5-2 C674x Cache Registers
| Byte Address | Register Name | Register Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0184 0000 | L2CFG | L2 Cache configuration register |
| 0x0184 0020 | L1PCFG | L1P Size Cache configuration register |
| 0x0184 0024 | L1PCC | L1P Freeze Mode Cache configuration register |
| 0x0184 0040 | L1DCFG | L1D Size Cache configuration register |
| 0x0184 0044 | L1DCC | L1D Freeze Mode Cache configuration register |
| 0x0184 0048 - 0x0184 0FFC | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 1000 | EDMAWEIGHT | L2 EDMA access control register |
| 0x0184 1004 - 0x0184 1FFC | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 2000 | L2ALLOC0 | L2 allocation register 0 |
| 0x0184 2004 | L2ALLOC1 | L2 allocation register 1 |
| 0x0184 2008 | L2ALLOC2 | L2 allocation register 2 |
| 0x0184 200C | L2ALLOC3 | L2 allocation register 3 |
| 0x0184 2010 - 0x0184 3FFF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 4000 | L2WBAR | L2 writeback base address register |
| 0x0184 4004 | L2WWC | L2 writeback word count register |
| 0x0184 4010 | L2WIBAR | L2 writeback invalidate base address register |
| 0x0184 4014 | L2WIWC | L2 writeback invalidate word count register |
| 0x0184 4018 | L2IBAR | L2 invalidate base address register |
| 0x0184 401C | L2IWC | L2 invalidate word count register |
| 0x0184 4020 | L1PIBAR | L1P invalidate base address register |
| 0x0184 4024 | L1PIWC | L1P invalidate word count register |
| 0x0184 4030 | L1DWIBAR | L1D writeback invalidate base address register |
| 0x0184 4034 | L1DWIWC | L1D writeback invalidate word count register |
| 0x0184 4038 | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 4040 | L1DWBAR | L1D Block Writeback |
| 0x0184 4044 | L1DWWC | L1D Block Writeback |
| 0x0184 4048 | L1DIBAR | L1D invalidate base address register |
| 0x0184 404C | L1DIWC | L1D invalidate word count register |
| 0x0184 4050 - 0x0184 4FFF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 5000 | L2WB | L2 writeback all register |
| 0x0184 5004 | L2WBINV | L2 writeback invalidate all register |
| 0x0184 5008 | L2INV | L2 Global Invalidate without writeback |
| 0x0184 500C - 0x0184 5027 | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 5028 | L1PINV | L1P Global Invalidate |
| 0x0184 502C - 0x0184 5039 | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 5040 | L1DWB | L1D Global Writeback |
| 0x0184 5044 | L1DWBINV | L1D Global Writeback with Invalidate |
| 0x0184 5048 | L1DINV | L1D Global Invalidate without writeback |
| 0x0184 8000 – 0x0184 80FF | MAR0 - MAR63 | Reserved 0x0000 0000 – 0x3FFF FFFF |
| 0x0184 8100 – 0x0184 817F | MAR64 – MAR95 | Memory Attribute Registers for EMIFA SDRAM Data (CS0) External memory addresses 0x4000 0000 – 0x5FFF FFFF |
| 0x0184 8180 – 0x0184 8187 | MAR96 - MAR97 | Memory Attribute Registers for EMIFA Async Data (CS2) External memory addresses 0x6000 0000 – 0x61FF FFFF |
| 0x0184 8188 – 0x0184 818F | MAR98 – MAR99 | Memory Attribute Registers for EMIFA Async Data (CS3) External memory addresses 0x6200 0000 – 0x63FF FFFF |
| 0x0184 8190 – 0x0184 8197 | MAR100 – MAR101 | Memory Attribute Registers for EMIFA Async Data (CS4) External memory addresses 0x6400 0000 – 0x65FF FFFF |
| 0x0184 8198 – 0x0184 819F | MAR102 – MAR103 | Memory Attribute Registers for EMIFA Async Data (CS5) External memory addresses 0x6600 0000 – 0x67FF FFFF |
| 0x0184 81A0 – 0x0184 81FF | MAR104 – MAR127 | Reserved 0x6800 0000 – 0x7FFF FFFF |
| 0x0184 8200 | MAR128 | Memory Attribute Register for RAM External memory addresses 0x8000 0000 – 0x8001 FFFF |
| Reserved 0x8002 0000 – 0x81FF FFFF | ||
| 0x0184 8204 – 0x0184 82FF | MAR129 – MAR191 | Reserved 0x8200 0000 – 0xBFFF FFFF |
| 0x0184 8300 – 0x0184 837F | MAR192 – MAR223 | Memory Attribute Registers for DDR2 Data (CS2) External memory addresses 0xC000 0000 – 0xDFFF FFFF |
| 0x0184 8380 – 0x0184 83FF | MAR224 – MAR255 | Reserved 0xE000 0000 – 0xFFFF FFFF |
Table 5-3 C674x L1/L2 Memory Protection Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | REGISTER ACRONYM | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0184 A000 | L2MPFAR | L2 memory protection fault address register |
| 0x0184 A004 | L2MPFSR | L2 memory protection fault status register |
| 0x0184 A008 | L2MPFCR | L2 memory protection fault command register |
| 0x0184 A00C - 0x0184 A0FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 A100 | L2MPLK0 | L2 memory protection lock key bits [31:0] |
| 0x0184 A104 | L2MPLK1 | L2 memory protection lock key bits [63:32] |
| 0x0184 A108 | L2MPLK2 | L2 memory protection lock key bits [95:64] |
| 0x0184 A10C | L2MPLK3 | L2 memory protection lock key bits [127:96] |
| 0x0184 A110 | L2MPLKCMD | L2 memory protection lock key command register |
| 0x0184 A114 | L2MPLKSTAT | L2 memory protection lock key status register |
| 0x0184 A118 - 0x0184 A1FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 A200 | L2MPPA0 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 0 (controls memory address 0x0080 0000 - 0x0080 1FFF) |
| 0x0184 A204 | L2MPPA1 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 1 (controls memory address 0x0080 2000 - 0x0080 3FFF) |
| 0x0184 A208 | L2MPPA2 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 2 (controls memory address 0x0080 4000 - 0x0080 5FFF) |
| 0x0184 A20C | L2MPPA3 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 3 (controls memory address 0x0080 6000 - 0x0080 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A210 | L2MPPA4 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 4 (controls memory address 0x0080 8000 - 0x0080 9FFF) |
| 0x0184 A214 | L2MPPA5 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 5 (controls memory address 0x0080 A000 - 0x0080 BFFF) |
| 0x0184 A218 | L2MPPA6 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 6 (controls memory address 0x0080 C000 - 0x0080 DFFF) |
| 0x0184 A21C | L2MPPA7 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 7 (controls memory address 0x0080 E000 - 0x0080 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A220 | L2MPPA8 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 8 (controls memory address 0x0081 0000 - 0x0081 1FFF) |
| 0x0184 A224 | L2MPPA9 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 9 (controls memory address 0x0081 2000 - 0x0081 3FFF) |
| 0x0184 A228 | L2MPPA10 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 10 (controls memory address 0x0081 4000 - 0x0081 5FFF) |
| 0x0184 A22C | L2MPPA11 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 11 (controls memory address 0x0081 6000 - 0x0081 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A230 | L2MPPA12 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 12 (controls memory address 0x0081 8000 - 0x0081 9FFF) |
| 0x0184 A234 | L2MPPA13 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 13 (controls memory address 0x0081 A000 - 0x0081 BFFF) |
| 0x0184 A238 | L2MPPA14 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 14 (controls memory address 0x0081 C000 - 0x0081 DFFF) |
| 0x0184 A23C | L2MPPA15 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 15 (controls memory address 0x0081 E000 - 0x0081 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A240 | L2MPPA16 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 16 (controls memory address 0x0082 0000 - 0x0082 1FFF) |
| 0x0184 A244 | L2MPPA17 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 17 (controls memory address 0x0082 2000 - 0x0082 3FFF) |
| 0x0184 A248 | L2MPPA18 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 18 (controls memory address 0x0082 4000 - 0x0082 5FFF) |
| 0x0184 A24C | L2MPPA19 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 19 (controls memory address 0x0082 6000 - 0x0082 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A250 | L2MPPA20 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 20 (controls memory address 0x0082 8000 - 0x0082 9FFF) |
| 0x0184 A254 | L2MPPA21 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 21 (controls memory address 0x0082 A000 - 0x0082 BFFF) |
| 0x0184 A258 | L2MPPA22 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 22 (controls memory address 0x0082 C000 - 0x0082 DFFF) |
| 0x0184 A25C | L2MPPA23 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 23 (controls memory address 0x0082 E000 - 0x0082 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A260 | L2MPPA24 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 24 (controls memory address 0x0083 0000 - 0x0083 1FFF) |
| 0x0184 A264 | L2MPPA25 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 25 (controls memory address 0x0083 2000 - 0x0083 3FFF) |
| 0x0184 A268 | L2MPPA26 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 26 (controls memory address 0x0083 4000 - 0x0083 5FFF) |
| 0x0184 A26C | L2MPPA27 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 27 (controls memory address 0x0083 6000 - 0x0083 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A270 | L2MPPA28 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 28 (controls memory address 0x0083 8000 - 0x0083 9FFF) |
| 0x0184 A274 | L2MPPA29 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 29 (controls memory address 0x0083 A000 - 0x0083 BFFF) |
| 0x0184 A278 | L2MPPA30 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 30 (controls memory address 0x0083 C000 - 0x0083 DFFF) |
| 0x0184 A27C | L2MPPA31 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 31 (controls memory address 0x0083 E000 - 0x0083 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A280 | L2MPPA32 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 32 (controls memory address 0x0070 0000 - 0x0070 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A284 | L2MPPA33 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 33 (controls memory address 0x0070 8000 - 0x0070 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A288 | L2MPPA34 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 34 (controls memory address 0x0071 0000 - 0x0071 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A28C | L2MPPA35 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 35 (controls memory address 0x0071 8000 - 0x0071 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A290 | L2MPPA36 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 36 (controls memory address 0x0072 0000 - 0x0072 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A294 | L2MPPA37 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 37 (controls memory address 0x0072 8000 - 0x0072 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A298 | L2MPPA38 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 38 (controls memory address 0x0073 0000 - 0x0073 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A29C | L2MPPA39 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 39 (controls memory address 0x0073 8000 - 0x0073 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2A0 | L2MPPA40 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 40 (controls memory address 0x0074 0000 - 0x0074 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2A4 | L2MPPA41 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 41 (controls memory address 0x0074 8000 - 0x0074 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2A8 | L2MPPA42 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 42 (controls memory address 0x0075 0000 - 0x0075 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2AC | L2MPPA43 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 43 (controls memory address 0x0075 8000 - 0x0075 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2B0 | L2MPPA44 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 44 (controls memory address 0x0076 0000 - 0x0076 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2B4 | L2MPPA45 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 45 (controls memory address 0x0076 8000 - 0x0076 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2B8 | L2MPPA46 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 46 (controls memory address 0x0077 0000 - 0x0077 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2BC | L2MPPA47 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 47 (controls memory address 0x0077 8000 - 0x0077 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2C0 | L2MPPA48 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 48 (controls memory address 0x0078 0000 - 0x0078 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2C4 | L2MPPA49 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 49 (controls memory address 0x0078 8000 - 0x0078 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2C8 | L2MPPA50 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 50 (controls memory address 0x0079 0000 - 0x0079 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2CC | L2MPPA51 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 51 (controls memory address 0x0079 8000 - 0x0079 FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2D0 | L2MPPA52 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 52 (controls memory address 0x007A 0000 - 0x007A 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2D4 | L2MPPA53 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 53 (controls memory address 0x007A 8000 - 0x007A FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2D8 | L2MPPA54 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 54 (controls memory address 0x007B 0000 - 0x007B 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2DC | L2MPPA55 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 55 (controls memory address 0x007B 8000 - 0x007B FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2E0 | L2MPPA56 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 56 (controls memory address 0x007C 0000 - 0x007C 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2E4 | L2MPPA57 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 57 (controls memory address 0x007C 8000 - 0x007C FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2E8 | L2MPPA58 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 58 (controls memory address 0x007D 0000 - 0x007D 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2EC | L2MPPA59 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 59 (controls memory address 0x007D 8000 - 0x007D FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2F0 | L2MPPA60 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 60 (controls memory address 0x007E 0000 - 0x007E 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2F4 | L2MPPA61 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 61 (controls memory address 0x007E 8000 - 0x007E FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A2F8 | L2MPPA62 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 62 (controls memory address 0x007F 0000 - 0x007F 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A2FC | L2MPPA63 | L2 memory protection page attribute register 63 (controls memory address 0x007F 8000 - 0x007F FFFF) |
| 0x0184 A300 - 0x0184 A3FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 A400 | L1PMPFAR | L1P memory protection fault address register |
| 0x0184 A404 | L1PMPFSR | L1P memory protection fault status register |
| 0x0184 A408 | L1PMPFCR | L1P memory protection fault command register |
| 0x0184 A40C - 0x0184 A4FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 A500 | L1PMPLK0 | L1P memory protection lock key bits [31:0] |
| 0x0184 A504 | L1PMPLK1 | L1P memory protection lock key bits [63:32] |
| 0x0184 A508 | L1PMPLK2 | L1P memory protection lock key bits [95:64] |
| 0x0184 A50C | L1PMPLK3 | L1P memory protection lock key bits [127:96] |
| 0x0184 A510 | L1PMPLKCMD | L1P memory protection lock key command register |
| 0x0184 A514 | L1PMPLKSTAT | L1P memory protection lock key status register |
| 0x0184 A518 - 0x0184 A5FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 A600 - 0x0184 A63F | - | Reserved (1) |
| 0x0184 A640 | L1PMPPA16 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 16 (controls memory address 0x00E0 0000 - 0x00E0 07FF) |
| 0x0184 A644 | L1PMPPA17 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 17 (controls memory address 0x00E0 0800 - 0x00E0 0FFF) |
| 0x0184 A648 | L1PMPPA18 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 18 (controls memory address 0x00E0 1000 - 0x00E0 17FF) |
| 0x0184 A64C | L1PMPPA19 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 19 (controls memory address 0x00E0 1800 - 0x00E0 1FFF) |
| 0x0184 A650 | L1PMPPA20 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 20 (controls memory address 0x00E0 2000 - 0x00E0 27FF) |
| 0x0184 A654 | L1PMPPA21 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 21 (controls memory address 0x00E0 2800 - 0x00E0 2FFF) |
| 0x0184 A658 | L1PMPPA22 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 22 (controls memory address 0x00E0 3000 - 0x00E0 37FF) |
| 0x0184 A65C | L1PMPPA23 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 23 (controls memory address 0x00E0 3800 - 0x00E0 3FFF) |
| 0x0184 A660 | L1PMPPA24 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 24 (controls memory address 0x00E0 4000 - 0x00E0 47FF) |
| 0x0184 A664 | L1PMPPA25 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 25 (controls memory address 0x00E0 4800 - 0x00E0 4FFF) |
| 0x0184 A668 | L1PMPPA26 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 26 (controls memory address 0x00E0 5000 - 0x00E0 57FF) |
| 0x0184 A66C | L1PMPPA27 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 27 (controls memory address 0x00E0 5800 - 0x00E0 5FFF) |
| 0x0184 A670 | L1PMPPA28 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 28 (controls memory address 0x00E0 6000 - 0x00E0 67FF) |
| 0x0184 A674 | L1PMPPA29 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 29 (controls memory address 0x00E0 6800 - 0x00E0 6FFF) |
| 0x0184 A678 | L1PMPPA30 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 30 (controls memory address 0x00E0 7000 - 0x00E0 77FF) |
| 0x0184 A67C | L1PMPPA31 | L1P memory protection page attribute register 31 (controls memory address 0x00E0 7800 - 0x00E0 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 A67F – 0x0184 ABFF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 AC00 | L1DMPFAR | L1D memory protection fault address register |
| 0x0184 AC04 | L1DMPFSR | L1D memory protection fault status register |
| 0x0184 AC08 | L1DMPFCR | L1D memory protection fault command register |
| 0x0184 AC0C - 0x0184 ACFF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 AD00 | L1DMPLK0 | L1D memory protection lock key bits [31:0] |
| 0x0184 AD04 | L1DMPLK1 | L1D memory protection lock key bits [63:32] |
| 0x0184 AD08 | L1DMPLK2 | L1D memory protection lock key bits [95:64] |
| 0x0184 AD0C | L1DMPLK3 | L1D memory protection lock key bits [127:96] |
| 0x0184 AD10 | L1DMPLKCMD | L1D memory protection lock key command register |
| 0x0184 AD14 | L1DMPLKSTAT | L1D memory protection lock key status register |
| 0x0184 AD18 - 0x0184 ADFF | - | Reserved |
| 0x0184 AE00 - 0x0184 AE3F | - | Reserved (2) |
| 0x0184 AE40 | L1DMPPA16 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 16 (controls memory address 0x00F0 0000 - 0x00F0 07FF) |
| 0x0184 AE44 | L1DMPPA17 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 17 (controls memory address 0x00F0 0800 - 0x00F0 0FFF) |
| 0x0184 AE48 | L1DMPPA18 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 18 (controls memory address 0x00F0 1000 - 0x00F0 17FF) |
| 0x0184 AE4C | L1DMPPA19 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 19 (controls memory address 0x00F0 1800 - 0x00F0 1FFF) |
| 0x0184 AE50 | L1DMPPA20 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 20 (controls memory address 0x00F0 2000 - 0x00F0 27FF) |
| 0x0184 AE54 | L1DMPPA21 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 21 (controls memory address 0x00F0 2800 - 0x00F0 2FFF) |
| 0x0184 AE58 | L1DMPPA22 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 22 (controls memory address 0x00F0 3000 - 0x00F0 37FF) |
| 0x0184 AE5C | L1DMPPA23 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 23 (controls memory address 0x00F0 3800 - 0x00F0 3FFF) |
| 0x0184 AE60 | L1DMPPA24 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 24 (controls memory address 0x00F0 4000 - 0x00F0 47FF) |
| 0x0184 AE64 | L1DMPPA25 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 25 (controls memory address 0x00F0 4800 - 0x00F0 4FFF) |
| 0x0184 AE68 | L1DMPPA26 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 26 (controls memory address 0x00F0 5000 - 0x00F0 57FF) |
| 0x0184 AE6C | L1DMPPA27 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 27 (controls memory address 0x00F0 5800 - 0x00F0 5FFF) |
| 0x0184 AE70 | L1DMPPA28 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 28 (controls memory address 0x00F0 6000 - 0x00F0 67FF) |
| 0x0184 AE74 | L1DMPPA29 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 29 (controls memory address 0x00F0 6800 - 0x00F0 6FFF) |
| 0x0184 AE78 | L1DMPPA30 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 30 (controls memory address 0x00F0 7000 - 0x00F0 77FF) |
| 0x0184 AE7C | L1DMPPA31 | L1D memory protection page attribute register 31 (controls memory address 0x00F0 7800 - 0x00F0 7FFF) |
| 0x0184 AE80 – 0x0185 FFFF | - | Reserved |
5.4 Memory Map Summary
Note: Read/Write accesses to illegal or reserved addresses in the memory map may cause undefined behavior.
Table 5-4 C6748 Top Level Memory Map
| Start Address | End Address | Size | DSP Mem Map | EDMA Mem Map | PRUSS Mem Map | Master Peripheral Mem Map | LCDC Mem Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0000 0000 | 0x0000 0FFF | 4K | PRUSS Local Address Space | ||||
| 0x0000 1000 | 0x006F FFFF | ||||||
| 0x0070 0000 | 0x007F FFFF | 1024K | DSP L2 ROM (1) | ||||
| 0x0080 0000 | 0x0083 FFFF | 256K | DSP L2 RAM | ||||
| 0x0084 0000 | 0x00DF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x00E0 0000 | 0x00E0 7FFF | 32K | DSP L1P RAM | ||||
| 0x00E0 8000 | 0x00EF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x00F0 0000 | 0x00F0 7FFF | 32K | DSP L1D RAM | ||||
| 0x00F0 8000 | 0x017F FFFF | ||||||
| 0x0180 0000 | 0x0180 FFFF | 64K | DSP Interrupt Controller | ||||
| 0x0181 0000 | 0x0181 0FFF | 4K | DSP Powerdown Controller | ||||
| 0x0181 1000 | 0x0181 1FFF | 4K | DSP Security ID | ||||
| 0x0181 2000 | 0x0181 2FFF | 4K | DSP Revision ID | ||||
| 0x0181 3000 | 0x0181 FFFF | 52K | |||||
| 0x0182 0000 | 0x0182 FFFF | 64K | DSP EMC | ||||
| 0x0183 0000 | 0x0183 FFFF | 64K | DSP Internal Reserved | ||||
| 0x0184 0000 | 0x0184 FFFF | 64K | DSP Memory System | ||||
| 0x0185 0000 | 0x01BF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01C0 0000 | 0x01C0 7FFF | 32K | EDMA3 CC | ||||
| 0x01C0 8000 | 0x01C0 83FF | 1K | EDMA3 TC0 | ||||
| 0x01C0 8400 | 0x01C0 87FF | 1K | EDMA3 TC1 | ||||
| 0x01C0 8800 | 0x01C0 FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01C1 0000 | 0x01C1 0FFF | 4K | PSC 0 | ||||
| 0x01C1 1000 | 0x01C1 1FFF | 4K | PLL Controller 0 | ||||
| 0x01C1 2000 | 0x01C1 3FFF | ||||||
| 0x01C1 4000 | 0x01C1 4FFF | 4K | SYSCFG0 | ||||
| 0x01C1 5000 | 0x01C1 FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01C2 0000 | 0x01C2 0FFF | 4K | Timer0 | ||||
| 0x01C2 1000 | 0x01C2 1FFF | 4K | Timer1 | ||||
| 0x01C2 2000 | 0x01C2 2FFF | 4K | I2C 0 | ||||
| 0x01C2 3000 | 0x01C2 3FFF | 4K | RTC | ||||
| 0x01C2 4000 | 0x01C3 FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01C4 0000 | 0x01C4 0FFF | 4K | MMC/SD 0 | ||||
| 0x01C4 1000 | 0x01C4 1FFF | 4K | SPI 0 | ||||
| 0x01C4 2000 | 0x01C4 2FFF | 4K | UART 0 | ||||
| 0x01C4 3000 | 0x01CF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01D0 0000 | 0x01D0 0FFF | 4K | McASP 0 Control | ||||
| 0x01D0 1000 | 0x01D0 1FFF | 4K | McASP 0 AFIFO Ctrl | ||||
| 0x01D0 2000 | 0x01D0 2FFF | 4K | McASP 0 Data | ||||
| 0x01D0 3000 | 0x01D0 BFFF | ||||||
| 0x01D0 C000 | 0x01D0 CFFF | 4K | UART 1 | ||||
| 0x01D0 D000 | 0x01D0 DFFF | 4K | UART 2 | ||||
| 0x01D0 E000 | 0x01D0 FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01D1 0000 | 0x01D1 07FF | 2K | McBSP0 | ||||
| 0x01D1 0800 | 0x01D1 0FFF | 2K | McBSP0 FIFO Ctrl | ||||
| 0x01D1 1000 | 0x01D1 17FF | 2K | McBSP1 | ||||
| 0x01D1 1800 | 0x01D1 1FFF | 2K | McBSP1 FIFO Ctrl | ||||
| 0x01D1 2000 | 0x01DF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01E0 0000 | 0x01E0 FFFF | 64K | USB0 | ||||
| 0x01E1 0000 | 0x01E1 0FFF | 4K | UHPI | ||||
| 0x01E1 1000 | 0x01E1 2FFF | ||||||
| 0x01E1 3000 | 0x01E1 3FFF | 4K | LCD Controller | ||||
| 0x01E1 4000 | 0x01E1 4FFF | 4K | Memory Protection Unit 1 (MPU 1) | ||||
| 0x01E1 5000 | 0x01E1 5FFF | 4K | Memory Protection Unit 2 (MPU 2) | ||||
| 0x01E1 6000 | 0x01E1 6FFF | 4K | UPP | ||||
| 0x01E1 7000 | 0x01E1 7FFF | 4K | VPIF | ||||
| 0x01E1 8000 | 0x01E1 9FFF | 8K | SATA | ||||
| 0x01E1 A000 | 0x01E1 AFFF | 4K | PLL Controller 1 | ||||
| 0x01E1 B000 | 0x01E1 BFFF | 4K | MMCSD1 | ||||
| 0x01E1 C000 | 0x01E1 FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01E2 0000 | 0x01E2 1FFF | 8K | EMAC Control Module RAM | ||||
| 0x01E2 2000 | 0x01E2 2FFF | 4K | EMAC Control Module Registers | ||||
| 0x01E2 3000 | 0x01E2 3FFF | 4K | EMAC Control Registers | ||||
| 0x01E2 4000 | 0x01E2 4FFF | 4K | EMAC MDIO port | ||||
| 0x01E2 5000 | 0x01E2 5FFF | 4K | USB1 | ||||
| 0x01E2 6000 | 0x01E2 6FFF | 4K | GPIO | ||||
| 0x01E2 7000 | 0x01E2 7FFF | 4K | PSC 1 | ||||
| 0x01E2 8000 | 0x01E2 8FFF | 4K | I2C 1 | ||||
| 0x01E2 9000 | 0x01E2 BFFF | ||||||
| 0x01E2 C000 | 0x01E2 CFFF | 4K | SYSCFG1 | ||||
| 0x01E2 D000 | 0x01E2 FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01E3 0000 | 0x01E3 7FFF | 32K | EDMA3 CC1 | ||||
| 0x01E3 8000 | 0x01E3 83FF | 1K | EDMA3 TC2 | ||||
| 0x01E3 8400 | 0x01EF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01F0 0000 | 0x01F0 0FFF | 4K | eHRPWM 0 | ||||
| 0x01F0 1000 | 0x01F0 1FFF | 4K | HRPWM 0 | ||||
| 0x01F0 2000 | 0x01F0 2FFF | 4K | eHRPWM 1 | ||||
| 0x01F0 3000 | 0x01F0 3FFF | 4K | HRPWM 1 | ||||
| 0x01F0 4000 | 0x01F0 5FFF | ||||||
| 0x01F0 6000 | 0x01F0 6FFF | 4K | ECAP 0 | ||||
| 0x01F0 7000 | 0x01F0 7FFF | 4K | ECAP 1 | ||||
| 0x01F0 8000 | 0x01F0 8FFF | 4K | ECAP 2 | ||||
| 0x01F0 9000 | 0x01F0 BFFF | ||||||
| 0x01F0 C000 | 0x01F0 CFFF | 4K | Timer2 | ||||
| 0x01F0 D000 | 0x01F0 DFFF | 4K | Timer3 | ||||
| 0x01F0 E000 | 0x01F0 EFFF | 4K | SPI1 | ||||
| 0x01F0 F000 | 0x01F0 FFFF | ||||||
| 0x01F1 0000 | 0x01F1 0FFF | 4K | McBSP0 FIFO Data | ||||
| 0x01F1 1000 | 0x01F1 1FFF | 4K | McBSP1 FIFO Data | ||||
| 0x01F1 2000 | 0x116F FFFF | ||||||
| 0x1170 0000 | 0x117F FFFF | 1024K | DSP L2 ROM (1) | ||||
| 0x1180 0000 | 0x1183 FFFF | 256K | DSP L2 RAM | ||||
| 0x1184 0000 | 0x11DF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x11E0 0000 | 0x11E0 7FFF | 32K | DSP L1P RAM | ||||
| 0x11E0 8000 | 0x11EF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x11F0 0000 | 0x11F0 7FFF | 32K | DSP L1D RAM | ||||
| 0x11F0 8000 | 0x3FFF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x4000 0000 | 0x5FFF FFFF | 512M | EMIFA SDRAM data (CS0) | ||||
| 0x6000 0000 | 0x61FF FFFF | 32M | EMIFA async data (CS2) | ||||
| 0x6200 0000 | 0x63FF FFFF | 32M | EMIFA async data (CS3) | ||||
| 0x6400 0000 | 0x65FF FFFF | 32M | EMIFA async data (CS4) | ||||
| 0x6600 0000 | 0x67FF FFFF | 32M | EMIFA async data (CS5) | ||||
| 0x6800 0000 | 0x6800 7FFF | 32K | EMIFA Control Regs | ||||
| 0x6800 8000 | 0x7FFF FFFF | ||||||
| 0x8000 0000 | 0x8001 FFFF | 128K | On-chip RAM | ||||
| 0x8002 0000 | 0xAFFF FFFF | ||||||
| 0xB000 0000 | 0xB000 7FFF | 32K | DDR2/mDDR Control Regs | ||||
| 0xB000 8000 | 0xBFFF FFFF | ||||||
| 0xC000 0000 | 0xCFFF FFFF | 256M | DDR2/mDDR Data | ||||
| 0xD000 0000 | 0xFFFF FFFF | ||||||
5.5 Boot Modes
This device supports a variety of boot modes through an internal DSP ROM bootloader. This device does not support dedicated hardware boot modes; therefore, all boot modes utilize the internal DSP ROM. The input states of the BOOT pins are sampled and latched into the BOOTCFG register, which is part of the system configuration (SYSCFG) module, when device reset is deasserted. Boot mode selection is determined by the values of the BOOT pins.
See Using the SM320C6748-HIREL/C6746/C6742 Bootloader (SPRAAT2) for more details on the ROM Boot Loader.
The following boot modes are supported:
- NAND Flash boot
- 8-bit NAND
- 16-bit NAND (supported on ROM revisions after d800k002 -- see the bootloader documents mentioned above to determine the ROM revision)
- NOR Flash boot
- NOR Direct boot (8-bit or 16-bit)
- NOR Legacy boot (8-bit or 16-bit)
- NOR AIS boot (8-bit or 16-bit)
- HPI Boot
- I2C0/I2C1 Boot
- EEPROM (Master Mode)
- External Host (Slave Mode)
-
SPI0/SPI1 Boot
- Serial Flash (Master Mode)
- SERIAL EEPROM (Master Mode)
- External Host (Slave Mode)
- UART0/UART1/UART2 Boot
- External Host
- MMC/SD0 Boot
5.6 SYSCFG Module
The following system level features of the chip are controlled by the SYSCFG peripheral:
- Readable Device, Die, and Chip Revision ID
- Control of Pin Multiplexing
- Priority of bus accesses different bus masters in the system
- Capture at power on reset the chip BOOT pin values and make them available to software
- Control of the DeepSleep power management function
- Enable and selection of the programmable pin pullups and pulldowns
- Special case settings for peripherals:
- Locking of PLL controller settings
- Default burst sizes for EDMA3 transfer controllers
- Selection of the source for the eCAP module input capture (including on chip sources)
- McASP AMUTEIN selection and clearing of AMUTE status for the McASP
- Control of the reference clock source and other side-band signals for both of the integrated USB PHYs
- Clock source selection for EMIFA
- DDR2 Controller PHY settings
- SATA PHY power management controls
- Selects the source of emulation suspend signal (from DSP) of peripherals supporting this function.
Many registers are accessible only by a host (DSP) when it is operating in its privileged mode (ex. from the kernel, but not from user space code).
Table 5-5 System Configuration (SYSCFG) Module Register Access
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION | REGISTER ACCESS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01C1 4000 | REVID | Revision Identification Register | — |
| 0x01C1 4008 | DIEIDR0 | Device Identification Register 0 | — |
| 0x01C1 400C | DIEIDR1 | Device Identification Register 1 | — |
| 0x01C1 4010 | DIEIDR2 | Device Identification Register 2 | — |
| 0x01C1 4014 | DIEIDR3 | Device Identification Register 3 | — |
| 0x01C1 4020 | BOOTCFG | Boot Configuration Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4038 | KICK0R | Kick 0 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 403C | KICK1R | Kick 1 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4044 | HOST1CFG | Host 1 Configuration Register | — |
| 0x01C1 40E0 | IRAWSTAT | Interrupt Raw Status/Set Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 40E4 | IENSTAT | Interrupt Enable Status/Clear Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 40E8 | IENSET | Interrupt Enable Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 40EC | IENCLR | Interrupt Enable Clear Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 40F0 | EOI | End of Interrupt Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 40F4 | FLTADDRR | Fault Address Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 40F8 | FLTSTAT | Fault Status Register | — |
| 0x01C1 4110 | MSTPRI0 | Master Priority 0 Registers | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4114 | MSTPRI1 | Master Priority 1 Registers | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4118 | MSTPRI2 | Master Priority 2 Registers | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4120 | PINMUX0 | Pin Multiplexing Control 0 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4124 | PINMUX1 | Pin Multiplexing Control 1 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4128 | PINMUX2 | Pin Multiplexing Control 2 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 412C | PINMUX3 | Pin Multiplexing Control 3 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4130 | PINMUX4 | Pin Multiplexing Control 4 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4134 | PINMUX5 | Pin Multiplexing Control 5 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4138 | PINMUX6 | Pin Multiplexing Control 6 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 413C | PINMUX7 | Pin Multiplexing Control 7 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4140 | PINMUX8 | Pin Multiplexing Control 8 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4144 | PINMUX9 | Pin Multiplexing Control 9 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4148 | PINMUX10 | Pin Multiplexing Control 10 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 414C | PINMUX11 | Pin Multiplexing Control 11 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4150 | PINMUX12 | Pin Multiplexing Control 12 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4154 | PINMUX13 | Pin Multiplexing Control 13 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4158 | PINMUX14 | Pin Multiplexing Control 14 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 415C | PINMUX15 | Pin Multiplexing Control 15 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4160 | PINMUX16 | Pin Multiplexing Control 16 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4164 | PINMUX17 | Pin Multiplexing Control 17 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4168 | PINMUX18 | Pin Multiplexing Control 18 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 416C | PINMUX19 | Pin Multiplexing Control 19 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4170 | SUSPSRC | Suspend Source Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4174 | CHIPSIG | Chip Signal Register | — |
| 0x01C1 4178 | CHIPSIG_CLR | Chip Signal Clear Register | — |
| 0x01C1 417C | CFGCHIP0 | Chip Configuration 0 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4180 | CFGCHIP1 | Chip Configuration 1 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4184 | CFGCHIP2 | Chip Configuration 2 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 4188 | CFGCHIP3 | Chip Configuration 3 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01C1 418C | CFGCHIP4 | Chip Configuration 4 Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01E2 C000 | VTPIO_CTL | VTPIO COntrol Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01E2 C004 | DDR_SLEW | DDR Slew Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01E2 C008 | DeepSleep | DeepSleep Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01E2 C00C | PUPD_ENA | Pullup / Pulldown Enable Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01E2 C010 | PUPD_SEL | Pullup / Pulldown Selection Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01E2 C014 | RXACTIVE | RXACTIVE Control Register | Privileged mode |
| 0x01E2 C018 | PWRDN | PWRDN Control Register | Privileged mode |
5.7 Pullup/Pulldown Resistors
Proper board design should ensure that input pins to the device always be at a valid logic level and not floating. This may be achieved via pullup/pulldown resistors. The device features internal pullup (IPU) and internal pulldown (IPD) resistors on most pins to eliminate the need, unless otherwise noted, for external pullup/pulldown resistors.
An external pullup/pulldown resistor needs to be used in the following situations:
- Boot and Configuration Pins: If the pin is both routed out and 3-stated (not driven), an external pullup/pulldown resistor is strongly recommended, even if the IPU/IPD matches the desired value/state.
- Other Input Pins: If the IPU/IPD does not match the desired value/state, use an external pullup/pulldown resistor to pull the signal to the opposite rail.
For the boot and configuration pins, if they are both routed out and 3-stated (not driven), it is strongly recommended that an external pullup/pulldown resistor be implemented. Although, internal pullup/pulldown resistors exist on these pins and they may match the desired configuration value, providing external connectivity can help ensure that valid logic levels are latched on these device boot and configuration pins. In addition, applying external pullup/pulldown resistors on the boot and configuration pins adds convenience to the user in debugging and flexibility in switching operating modes.
Tips for choosing an external pullup/pulldown resistor:
- Consider the total amount of current that may pass through the pullup or pulldown resistor. Make sure to include the leakage currents of all the devices connected to the net, as well as any internal pullup or pulldown resistors.
- Decide a target value for the net. For a pulldown resistor, this should be below the lowest VIL level of all inputs connected to the net. For a pullup resistor, this should be above the highest VIH level of all inputs on the net. A reasonable choice would be to target the VOL or VOH levels for the logic family of the limiting device; which, by definition, have margin to the VIL and VIH levels.
- Select a pullup/pulldown resistor with the largest possible value; but, which can still ensure that the net will reach the target pulled value when maximum current from all devices on the net is flowing through the resistor. The current to be considered includes leakage current plus, any other internal and external pullup/pulldown resistors on the net.
- For bidirectional nets, there is an additional consideration which sets a lower limit on the resistance value of the external resistor. Verify that the resistance is small enough that the weakest output buffer can drive the net to the opposite logic level (including margin).
- Remember to include tolerances when selecting the resistor value.
- For pullup resistors, also remember to include tolerances on the IO supply rail.
- For most systems, a 1-kΩ resistor can be used to oppose the IPU/IPD while meeting the above criteria. Users should confirm this resistor value is correct for their specific application.
- For most systems, a 20-kΩ resistor can be used to compliment the IPU/IPD on the boot and configuration pins while meeting the above criteria. Users should confirm this resistor value is correct for their specific application.
- For more detailed information on input current (II), and the low-/high-level input voltages (VIL and VIH) for the device, see Section 4.4, Recommended Operating Conditions.
- For the internal pullup/pulldown resistors for all device pins, see the peripheral/system-specific terminal functions table.
5.8 Reset
5.8.1 Power-On Reset (POR)
A power-on reset (POR) is required to place the device in a known good state after power-up. Power-On Reset is initiated by bringing RESET and TRST low at the same time. POR sets all of the device internal logic to its default state. All pins are tri-stated with the exception of RESETOUT which remains active through the reset sequence, and RTCK/GP8[0]. During reset, GP8[0] is configured as a reserved function, and its behavior is not deterministic; the user should be aware that this pin will drive a level, and fact may toggle, during reset. RESETOUT in an output for use by other controllers in the system that indicates the device is currently in reset.
While both TRST and RESET need to be asserted upon power up, only RESET needs to be released for the device to boot properly. TRST may be asserted indefinitely for normal operation, keeping the JTAG port interface and device's emulation logic in the reset state.
TRST only needs to be released when it is necessary to use a JTAG controller to debug the device or exercise the device's boundary scan functionality. Note: TRST is synchronous and must be clocked by TCK; otherwise, the boundary scan logic may not respond as expected after TRST is asserted.
RESET must be released only in order for boundary-scan JTAG to read the variant field of IDCODE correctly. Other boundary-scan instructions work correctly independent of current state of RESET. For maximum reliability, the device includes an internal pulldown on the TRST pin to ensure that TRST will always be asserted upon power up and the device's internal emulation logic will always be properly initialized.
JTAG controllers from Texas Instruments actively drive TRST high. However, some third-party JTAG controllers may not drive TRST high but expect the use of a pullup resistor on TRST. When using this type of JTAG controller, assert TRST to intialize the device after powerup and externally drive TRST high before attempting any emulation or boundary scan operations.
A summary of the effects of Power-On Reset is given below:
- All internal logic (including emulation logic and the PLL logic) is reset to its default state
- Internal memory is not maintained through a POR
- RESETOUT goes active
- All device pins go to a high-impedance state
- The RTC peripheral is not reset during a POR. A software sequence is required to reset the RTC
CAUTION: A watchdog reset triggers a POR.
5.8.2 Warm Reset
A warm reset provides a limited reset to the device. Warm Reset is initiated by bringing only RESET low (TRST is maintained high through a warm reset). Warm reset sets certain portions of the device to their default state while leaving others unaltered. All pins are tri-stated with the exception of RESETOUT which remains active through the reset sequence, and RTCK/GP8[0]. During reset, GP8[0] is configured as a reserved function, and its behavior is not deterministic; the user should be aware that this pin will drive a level, and fact may toggle, during reset. RESETOUT is an output for use by other controllers in the system that indicates the device is currently in reset.
During an emulation, the emulator will maintain TRST high and hence only warm reset (not POR) is available during emulation debug and development.
A summary of the effects of Warm Reset is given below:
- All internal logic (except for the emulation logic and the PLL logic) is reset to its default state
- Internal memory is maintained through a warm reset
- RESETOUT goes active
- All device pins go to a high-impedance state
- The RTC peripheral is not reset during a warm reset. A software sequence is required to reset the RTC
5.9 Interrupts
The device has a large number of interrupts to service the needs of its many peripherals and subsystems.
5.9.1 DSP Interrupts
The C674x DSP interrupt controller combines device events into 12 prioritized interrupts. The source for each of the 12 CPU interrupts is user programmable and is listed in Table 5-6. Also, the interrupt controller controls the generation of the CPU exceptions, NMI, and emulation interrupts. Table 5-7 summarizes the C674x interrupt controller registers and memory locations.
Refer to the C674x DSP MegaModule Reference Guide (SPRUFK5) and the TMS320C674x DSP CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (SPRUFE8) for details of the C674x interrupts.
Table 5-6 C6748 DSP Interrupts
| EVT# | Interrupt Name | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | EVT0 | C674x Int Ctl 0 |
| 1 | EVT1 | C674x Int Ctl 1 |
| 2 | EVT2 | C674x Int Ctl 2 |
| 3 | EVT3 | C674x Int Ctl 3 |
| 4 | T64P0_TINT12 | Timer64P0 - TINT12 |
| 5 | SYSCFG_CHIPINT2 | SYSCFG CHIPSIG Register |
| 6 | PRU_EVTOUT0 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 7 | EHRPWM0 | HiResTimer/PWM0 Interrupt |
| 8 | EDMA3_0_CC0_INT1 | EDMA3_0 Channel Controller 0 Shadow Region 1 Transfer Completion Interrupt |
| 9 | EMU_DTDMA | C674x-ECM |
| 10 | EHRPWM0TZ | HiResTimer/PWM0 Trip Zone Interrupt |
| 11 | EMU_RTDXRX | C674x-RTDX |
| 12 | EMU_RTDXTX | C674x-RTDX |
| 13 | IDMAINT0 | C674x-EMC |
| 14 | IDMAINT1 | C674x-EMC |
| 15 | MMCSD0_INT0 | MMCSD0 MMC/SD Interrupt |
| 16 | MMCSD0_INT1 | MMCSD0 SDIO Interrupt |
| 17 | PRU_EVTOUT1 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 18 | EHRPWM1 | HiResTimer/PWM1 Interrupt |
| 19 | USB0_INT | USB0 Interrupt |
| 20 | USB1_HCINT | USB1 OHCI Host Controller Interrupt |
| 21 | USB1_RWAKEUP | USB1 Remote Wakeup Interrupt |
| 22 | PRU_EVTOUT2 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 23 | EHRPWM1TZ | HiResTimer/PWM1 Trip Zone Interrupt |
| 24 | SATA_INT | SATA Controller |
| 25 | T64P2_TINTALL | Timer64P2 Combined TINT12 and TINT 34 Interrupt |
| 26 | EMAC_C0RXTHRESH | EMAC - Core 0 Receive Threshold Interrupt |
| 27 | EMAC_C0RX | EMAC - Core 0 Receive Interrupt |
| 28 | EMAC_C0TX | EMAC - Core 0 Transmit Interrupt |
| 29 | EMAC_C0MISC | EMAC - Core 0 Miscellaneous Interrupt |
| 30 | EMAC_C1RXTHRESH | EMAC - Core 1 Receive Threshold Interrupt |
| 31 | EMAC_C1RX | EMAC - Core 1 Receive Interrupt |
| 32 | EMAC_C1TX | EMAC - Core 1 Transmit Interrupt |
| 33 | EMAC_C1MISC | EMAC - Core 1 Miscellaneous Interrupt |
| 34 | UHPI_DSPINT | UHPI DSP Interrupt |
| 35 | PRU_EVTOUT3 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 36 | IIC0_INT | I2C0 |
| 37 | SP0_INT | SPI0 |
| 38 | UART0_INT | UART0 |
| 39 | PRU_EVTOUT5 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 40 | T64P1_TINT12 | Timer64P1 Interrupt 12 |
| 41 | GPIO_B1INT | GPIO Bank 1 Interrupt |
| 42 | IIC1_INT | I2C1 |
| 43 | SPI1_INT | SPI1 |
| 44 | PRU_EVTOUT6 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 45 | ECAP0 | ECAP0 |
| 46 | UART_INT1 | UART1 |
| 47 | ECAP1 | ECAP1 |
| 48 | T64P1_TINT34 | Timer64P1 Interrupt 34 |
| 49 | GPIO_B2INT | GPIO Bank 2 Interrupt |
| 50 | PRU_EVTOUT7 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 51 | ECAP2 | ECAP2 |
| 52 | GPIO_B3INT | GPIO Bank 3 Interrupt |
| 53 | MMCSD1_INT1 | MMCSD1 SDIO Interrupt |
| 54 | GPIO_B4INT | GPIO Bank 4 Interrupt |
| 55 | EMIFA_INT | EMIFA |
| 56 | EDMA3_0_CC0_ERRINT | EDMA3_0 Channel Controller 0 Error Interrupt |
| 57 | EDMA3_0_TC0_ERRINT | EDMA3_0 Transfer Controller 0 Error Interrupt |
| 58 | EDMA3_0_TC1_ERRINT | EDMA3_0 Transfer Controller 1 Error Interrupt |
| 59 | GPIO_B5INT | GPIO Bank 5 Interrupt |
| 60 | DDR2_MEMERR | DDR2 Memory Error Interrupt |
| 61 | MCASP0_INT | McASP0 Combined RX/TX Interrupts |
| 62 | GPIO_B6INT | GPIO Bank 6 Interrupt |
| 63 | RTC_IRQS | RTC Combined |
| 64 | T64P0_TINT34 | Timer64P0 Interrupt 34 |
| 65 | GPIO_B0INT | GPIO Bank 0 Interrupt |
| 66 | PRU_EVTOUT4 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 67 | SYSCFG_CHIPINT3 | SYSCFG_CHIPSIG Register |
| 68 | MMCSD1_INT0 | MMCSD1 MMC/SD Interrupt |
| 69 | UART2_INT | UART2 |
| 70 | PSC0_ALLINT | PSC0 |
| 71 | PSC1_ALLINT | PSC1 |
| 72 | GPIO_B7INT | GPIO Bank 7 Interrupt |
| 73 | LCDC_INT | LDC Controller |
| 74 | PROTERR | SYSCFG Protection Shared Interrupt |
| 75 | GPIO_B8INT | GPIO Bank 8 Interrupt |
| 76 - 77 | - | Reserved |
| 78 | T64P2_CMPINT0 | Timer64P2 - Compare Interrupt 0 |
| 79 | T64P2_CMPINT1 | Timer64P2 - Compare Interrupt 1 |
| 80 | T64P2_CMPINT2 | Timer64P2 - Compare Interrupt 2 |
| 81 | T64P2_CMPINT3 | Timer64P2 - Compare Interrupt 3 |
| 82 | T64P2_CMPINT4 | Timer64P2 - Compare Interrupt 4 |
| 83 | T64P2_CMPINT5 | Timer64P2 - Compare Interrupt 5 |
| 84 | T64P2_CMPINT6 | Timer64P2 - Compare Interrupt 6 |
| 85 | T64P2_CMPINT7 | Timer64P2 - Compare Interrupt 7 |
| 86 | T64P3_TINTALL | Timer64P3 Combined TINT12 and TINT 34 Interrupt |
| 87 | MCBSP0_RINT | McBSP0 Receive Interrupt |
| 88 | MCBSP0_XINT | McBSP0 Transmit Interrupt |
| 89 | MCBSP1_RINT | McBSP1 Receive Interrupt |
| 90 | MCBSP1_XINT | McBSP1 Transmit Interrupt |
| 91 | EDMA3_1_CC0_INT1 | EDMA3_1 Channel Controller 0 Shadow Region 1 Transfer Completion Interrupt |
| 92 | EDMA3_1_CC0_ERRINT | EDMA3_1 Channel Controller 0 Error Interrupt |
| 93 | EDMA3_1_TC0_ERRINT | EDMA3_1 Transfer Controller 0 Error Interrupt |
| 94 | UPP_INT | uPP Combined Interrupt |
| 95 | VPIF_INT | VPIF Combined Interrupt |
| 96 | INTERR | C674x-Int Ctl |
| 97 | EMC_IDMAERR | C674x-EMC |
| 98 - 112 | - | Reserved |
| 113 | PMC_ED | C674x-PMC |
| 114 - 115 | - | Reserved |
| 116 | UMC_ED1 | C674x-UMC |
| 117 | UMC_ED2 | C674x-UMC |
| 118 | PDC_INT | C674x-PDC |
| 119 | SYS_CMPA | C674x-SYS |
| 120 | PMC_CMPA | C674x-PMC |
| 121 | PMC_CMPA | C674x-PMC |
| 122 | DMC_CMPA | C674x-DMC |
| 123 | DMC_CMPA | C674x-DMC |
| 124 | UMC_CMPA | C674x-UMC |
| 125 | UMC_CMPA | C674x-UMC |
| 126 | EMC_CMPA | C674x-EMC |
| 127 | EMC_BUSERR | C674x-EMC |
Table 5-7 C674x DSP Interrupt Controller Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0180 0000 | EVTFLAG0 | Event flag register 0 |
| 0x0180 0004 | EVTFLAG1 | Event flag register 1 |
| 0x0180 0008 | EVTFLAG2 | Event flag register 2 |
| 0x0180 000C | EVTFLAG3 | Event flag register 3 |
| 0x0180 0020 | EVTSET0 | Event set register 0 |
| 0x0180 0024 | EVTSET1 | Event set register 1 |
| 0x0180 0028 | EVTSET2 | Event set register 2 |
| 0x0180 002C | EVTSET3 | Event set register 3 |
| 0x0180 0040 | EVTCLR0 | Event clear register 0 |
| 0x0180 0044 | EVTCLR1 | Event clear register 1 |
| 0x0180 0048 | EVTCLR2 | Event clear register 2 |
| 0x0180 004C | EVTCLR3 | Event clear register 3 |
| 0x0180 0080 | EVTMASK0 | Event mask register 0 |
| 0x0180 0084 | EVTMASK1 | Event mask register 1 |
| 0x0180 0088 | EVTMASK2 | Event mask register 2 |
| 0x0180 008C | EVTMASK3 | Event mask register 3 |
| 0x0180 00A0 | MEVTFLAG0 | Masked event flag register 0 |
| 0x0180 00A4 | MEVTFLAG1 | Masked event flag register 1 |
| 0x0180 00A8 | MEVTFLAG2 | Masked event flag register 2 |
| 0x0180 00AC | MEVTFLAG3 | Masked event flag register 3 |
| 0x0180 00C0 | EXPMASK0 | Exception mask register 0 |
| 0x0180 00C4 | EXPMASK1 | Exception mask register 1 |
| 0x0180 00C8 | EXPMASK2 | Exception mask register 2 |
| 0x0180 00CC | EXPMASK3 | Exception mask register 3 |
| 0x0180 00E0 | MEXPFLAG0 | Masked exception flag register 0 |
| 0x0180 00E4 | MEXPFLAG1 | Masked exception flag register 1 |
| 0x0180 00E8 | MEXPFLAG2 | Masked exception flag register 2 |
| 0x0180 00EC | MEXPFLAG3 | Masked exception flag register 3 |
| 0x0180 0104 | INTMUX1 | Interrupt mux register 1 |
| 0x0180 0108 | INTMUX2 | Interrupt mux register 2 |
| 0x0180 010C | INTMUX3 | Interrupt mux register 3 |
| 0x0180 0140 - 0x0180 0144 | - | Reserved |
| 0x0180 0180 | INTXSTAT | Interrupt exception status |
| 0x0180 0184 | INTXCLR | Interrupt exception clear |
| 0x0180 0188 | INTDMASK | Dropped interrupt mask register |
| 0x0180 01C0 | EVTASRT | Event assert register |