SLVSCF2A January 2014 – December 2014 TPS61097A-33
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
As for all switching power supplies, the layout is an important step in the design, especially at high peak currents and high switching frequencies. If the layout is not carefully done, the regulator could show stability problems as well as EMI problems. Therefore, use wide and short traces for the main current path and for the power ground tracks. The input and output capacitor, as well as the inductor should be placed as close as possible to the IC. Use a common ground node for power ground and a different one for control ground to minimize the effects of ground noise. Connect these ground nodes at any place close to one of the ground pins of the IC.
The feedback divider should be placed as close as possible to the control ground pin of the IC. To lay out the control ground, it is recommended to use short traces as well, separated from the power ground traces. This avoids ground shift problems, which can occur due to superimposition of power ground current and control ground current.
11.2 Layout Example
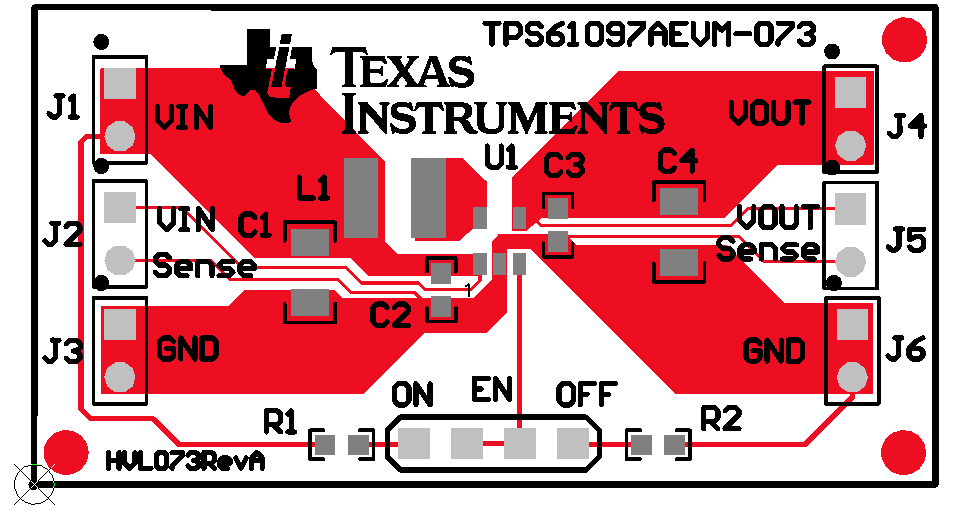 Figure 22. Layout Example
Figure 22. Layout Example