SBAA401A July 2019 – January 2024 TLV320ADC3140 , TLV320ADC5140 , TLV320ADC6140
2.2 AGC Parameters
Table 2-3 shows the parameters of the AGC algorithm. The first two parameters (AGC Target Level and Maximum Gain) are controlled by writing to the device registers. The other parameters reside in the 32-bit wide coefficient memory (Book 0, Page 5, Page 6, and Page 7) of the device.
| AGC PARAMETER | Function/Description |
|---|---|
| AGC Target Level (dB) | The AGC target level represents the nominal level at which the AGC attempts to maintain its output signal. |
| Maximum Gain (dB) | Upper limit of gain in dB applied by the AGC for signals below target level. |
| Noise Threshold (dB) | The threshold level the AGC utilizes to distinguish noise from weak signals. Signals lower than this threshold are classified as noise and not amplified by the AGC. |
| Release Time Constant (seconds) | How fast the AGC circuitry responds with a PGA gain increase when the input signal falls below the target level. |
| Attack Time Constant (seconds) | How fast the AGC circuitry responds with a PGA gain decrease when input signal rises above the target level. |
| Release Hysteresis (dB) | Amount of signal level decrease in dB past the Target Level that forces the AGC to increase gain and start a release. |
| Attack Hysteresis (dB) | Amount of signal level increase in dB past the Target Level that forces the AGC to decrease gain and start an attack. |
| Noise Hysteresis (dB) | Amount of signal level change past the Noise Threshold that causes the AGC to decide between noise or signal. |
| Release Debounce (samples) | The number of consecutive input samples that falls below Target Level after an attack event before the AGC starts releasing and increasing PGA gain. |
| Attack Debounce (samples) | The number of consecutive input samples that rises above Target Level after a release event before the AGC starts attacking and decreasing PGA gain. |
| Noise Debounce (samples) | The number of consecutive samples for the input to fall below Noise Threshold for the signal to be considered as noise. |
AGC Target Level: The AGC target level represents the nominal level at which the AGC attempts to maintain the output signal. The target level is expressed relative to full scale (dBFS) of the ADC output. Table 2-4 lists the AGC Target Level configuration settings. The default is -34 dB. Setting a high target level increases the converted output level. However, large target level settings can lead to clipping the input signal with a sudden increase in the signal level. Therefore, set the target level with enough margin so as to prevent clipping when loud sounds occur.
| P0_R112_D[7:4] : AGC_LVL[3:0] | AGC TARGET LEVEL FOR OUTPUT |
|---|---|
| 0000 | The AGC target level is the –6 dB output signal level |
| 0001 | The AGC target level is the –8 dB output signal level |
| 0010 | The AGC target level is the –10 dB output signal level |
| … | … |
| 1110 (default) | The AGC target level is the –34 dB output signal level |
| 1111 | The AGC target level is the –36 dB output signal level |
Maximum Gain: The maximum gain represents the upper limit of gain applied by the AGC for signals below the target level. Table 2-5 lists the Maximum Gain configuration settings. The default value is 24 dB. It can be programmed from 3 dB to 42 dB with steps of 3 dB.
| P0_R112_D[3:0] : AGC_MAXGAIN[3:0] | AGC MAXIMUM GAIN ALLOWED |
|---|---|
| 0000 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 3 dB |
| 0001 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 6 dB |
| 0010 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 9 dB |
| … | … |
| 0111 (default) | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 24 dB |
| … | … |
| 1110 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 39 dB |
| 1111 | The AGC maximum gain allowed is 42 dB |
Noise Threshold: The threshold level used by the AGC to distinguish noise from weak signals. Signals lower than this threshold are classified as noise and not amplified by the AGC. Noise Threshold is set by writing to the AGC_NOISE coefficient. Equation 5 shows the computation of the AGC_NOISE parameter.
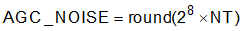
where
- NT is the Noise Threshold in dB
The default value (0xFFFFA600) corresponds to -90 dB. Table 2-6 shows the registers that control the AGC_NOISE parameter.
| COEFFICIENT | PAGE | REGISTER | RESET VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC_NOISE | 0x06 | 0x20 | 0xFF | AGC_NOISE Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x21 | 0xFF | AGC_NOISE Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x22 | 0xA6 | AGC_NOISE Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x23 | 0x00 | AGC_NOISE Byte[7:0]\ |
Release Time Constant: How fast the AGC circuitry responds with a PGA gain increase when the input signal falls below the target level. The Release Time Constant is controlled by two coefficients: AGC_REL_ALPHA and AGC_REL_BETA. Equation 6 and Equation 7 show how to compute the AGC_REL_ALPHA and AGC_REL_BETA parameters from the following time constant:
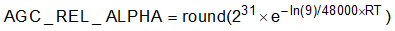
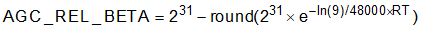
where
- RT is the Release Time Constant in seconds
Table 2-7 shows the registers that control AGC_REL_ALPHA and AGC_REL_BETA parameters. These parameters are written in 2s-complement representation. The default values for AGC_REL_ALPHA and AGC_REL_BETA corresponds to a time constant of 20 milliseconds.
| COEFFICIENT | PAGE | REGISTER | RESET VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC_REL_ALPHA | 0x05 | 0x7C | 0x7F | AGC_REL_ALPHA Byte[31:24] |
| 0x05 | 0x7D | 0xB5 | AGC_REL_ALPHA Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x05 | 0x7E | 0x16 | AGC_REL_ALPHA Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x05 | 0x7F | 0x50 | AGC_REL_ALPHA Byte[7:0] | |
| AGC_REL_BETA | 0x06 | 0x08 | 0x00 | AGC_REL_BETA Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x09 | 0x4A | AGC_REL_BETA Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x0A | 0xE9 | AGC_REL_BETA Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x0B | 0xB0 | AGC_REL_BETA Byte[7:0] |
Attack Time Constant: How fast the AGC circuitry responds with a PGA gain decrease when the input signal rises above the target level. Equation 8 and Equation 9 show the computation of the Attack Time Constant Parameters AGC_ATT_ALPHA and AGC_ATT_BETA.
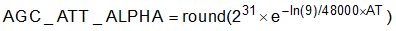

where
- AT is the Attack Time Constant in seconds
AGC_ATT_ALPHA and AGC_ATT_BETA parameters are each 32-bit wide, 2s-complement representations, and are controlled by registers shown in Table 2-8. The default values for AGC_ATT_ALPHA and AGC_ATT_BETA corresponds to a time constant of 0.1 milliseconds.
| COEFFICIENT | PAGE | REGISTER | RESET VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC_ATT_ALPHA | 0x06 | 0x0C | 0x50 | AGC_ATT_ALPHA Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x0D | 0xFC | AGC_ATT_ALPHA Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x0E | 0x64 | AGC_ATT_ALPHA Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x0F | 0x5C | AGC_ATT_ALPHA Byte[7:0] | |
| AGC_ATT_BETA | 0x06 | 0x10 | 0x2F | AGC_ATT_BETA Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x11 | 0x03 | AGC_ATT_BETA Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x12 | 0x9B | AGC_ATT_BETA Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x13 | 0xA4 | AGC_ATT_BETA Byte[7:0] |
Release Hysteresis: Amount of signal level decrease past Target Level that forces the AGC to increase gain and start a release. Release Hysteresis is specified in dB. Equation 10 shows the computation of the AGC_REL_HYST parameter.
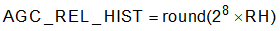
where
- RH (>= 0) is the Release Hysteresis in dB
The default value of AGC_REL_HYST is 0x00000300, which corresponds to a hysteresis of 3 dB. Table 2-9 list the registers corresponding to AGC_REL_HYST.
| COEFFICIENT | PAGE | REGISTER | RESET VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC_REL_HYST | 0x06 | 0x34 | 0x00 | AGC_REL_HYST Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x35 | 0x00 | AGC_REL_HYST Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x36 | 0x03 | AGC_REL_HYST Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x37 | 0x00 | AGC_REL_HYST Byte[7:0] |
Attack Hysteresis: Amount of signal level increase past Target Level that forces the AGC to decrease the gina and start an attack. Attack Hysteresis is specified in dB. Equation 11 shows the computation of the AGC_ATT_HYST parameter.
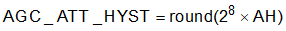
where
- AH (>= 0) is the Attack Hysteresis in dB
The default value of Attack Hysteresis is 1 dB. Table 2-10 shows the registers that control the AGC_ATT_HYST parameter.
| COEFFICIENT | PAGE | REGISTER | RESET VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC_ATT_HYST | 0x06 | 0x3C | 0x00 | AGC_ATT_HYST Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x3D | 0x00 | AGC_ATT_HYST Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x3E | 0x01 | AGC_ATT_HYST Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x3F | 0x00 | AGC_ATT_HYST Byte[7:0] |
Noise Hysteresis: (AGC_NOISE_HYST): Amount of signal level change around the Noise Threshold that causes the AGC to decide between noise and signal. A rising signal has to rise above the Noise Hysteresis level to be amplified to the Target Level. A decreasing signal has to fall below the Noise Hysteresis level to be considered as noise. Noise Hysteresis is specified in dB. Equation 12 shows the computation of the AGC_NOISE_HYST parameters.

where
- NH (>= 0) is the Noise Hysteresis in dB
The default value of AGC_NOISE_HYST is 0x00000600, which corresponds to a hysteresis of 6 dB. Table 2-10 shows the registers controlling the AGC_NOISE_HYST parameter.
| COEFFICIENT | PAGE | REGISTER | RESET VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC_NOISE_HYST | 0x06 | 0x54 | 0x00 | AGC_NOISE_HYST Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x55 | 0x00 | AGC_NOISE_HYST Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x56 | 0x06 | AGC_NOISE_HYST Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x57 | 0x00 | AGC_NOISE_HYST Byte[7:0] |
Attack Debounce: The number of consecutive input samples that rises above the target level after a release event before the AGC starts attack and decreases the PGA. Equation 13 shows the computation of the AGC_ATT_CNT parameter.
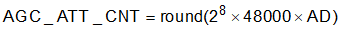
where
- AD (>= 0) is specified in seconds
Table 2-12 shows the registers controlling the AGC_ATT_CNT parameter.
| COEFFICIENT | PAGE | REGISTER | RESET VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC_ATT_CNT | 0x06 | 0x18 | 0x00 | AGC_ATT_CNT Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x19 | 0x00 | AGC_ATT_CNT Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x1A | 0x02 | AGC_ATT_CNT Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x1B | 0x00 | AGC_ATT_CNT Byte[7:0] |
Release Debounce: The number of consecutive input samples that falls below Target Level after an attack event before the AGC starts releasing and increasing the PGA gain. The default value of Release Debounce is 25 milliseconds at 48 kHz. Equation 14 shows the computation of the AGC_REL_CNT parameter.
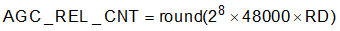
where
- RD (>= 0) is the Release Debounce specified in seconds
Table 2-13 shows the registers controlling the AGC_REL_CNT parameter.
| COEFFICIENT | PAGE | REGISTER | RESET VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC_REL_CNT | 0x06 | 0x1C | 0x00 | AGC_REL_CNT Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x1D | 0x04 | AGC_REL_CNT Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x1E | 0xB0 | AGC_REL_CNT Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x1F | 0x00 | AGC_REL_CNT Byte[7:0] |
Noise Debounce: The number of consecutive samples for the input to fall below Noise Threshold for the signal to be considered noise. Equation 15 shows the computation of the AGC_NOISE_CNT parameter.
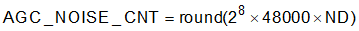
where
- ND (>= 0) is the Noise Debounce time specified in seconds
The default value of AGC_NOISE_CNT is 0x0004B000, which corresponds to a debounce time of 25 milliseconds at 48 kHz. Table 2-14 shows the registers controlling the AGC_NOISE_CNT parameter.
| COEFFICIENT | PAGE | REGISTER | RESET VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGC_NOISE_CNT | 0x06 | 0x44 | 0x00 | AGC_NOISE_CNT Byte[31:24] |
| 0x06 | 0x45 | 0x04 | AGC_NOISE_CNT Byte[23:16] | |
| 0x06 | 0x46 | 0xB0 | AGC_NOISE_CNT Byte[15:8] | |
| 0x06 | 0x47 | 0x00 | AGC_NOISE_CNT Byte[7:0] |