SBAA590 june 2023 ADC12DJ5200RF , ADC32RF52 , ADC32RF54 , ADC32RF55 , ADC34RF52 , ADC34RF55
3.3 Background Calibration
Background calibration is a continuous process taking place during the operation of the ADC. Background calibration involves the continual use of an out-of-calibration spare ADC core. Once this spare ADC core is calibrated, the ADC core is swapped with (one of) the active ADC cores. As a result, background calibration maintains the accuracy of the ADC across various environments, such as rapidly changing temperatures, in real-time. However, background calibration consumes more power than other calibration modes since the spare ADC core is always powered on and undergoing a continuous swapping with an active ADC core.
In the case of the ADC32RF55, the background calibration function is referred to as continuous calibration in the data sheet. During the continuous calibration, one of the five internal ADC cores (per channel) is swapped out approximately every 27 ms, equating to approximately every 81 million samples if the device is operating at 3 GSPS. Figure 3-4 shows a comparison of the internal ADC core swap during foreground calibration (the first two GPIO1 pulses indicate two separate foreground calibrations) versus how the ADC cores swap during a continuous calibration (the longer GPIO1 pulse is used to represent a continuous calibration).
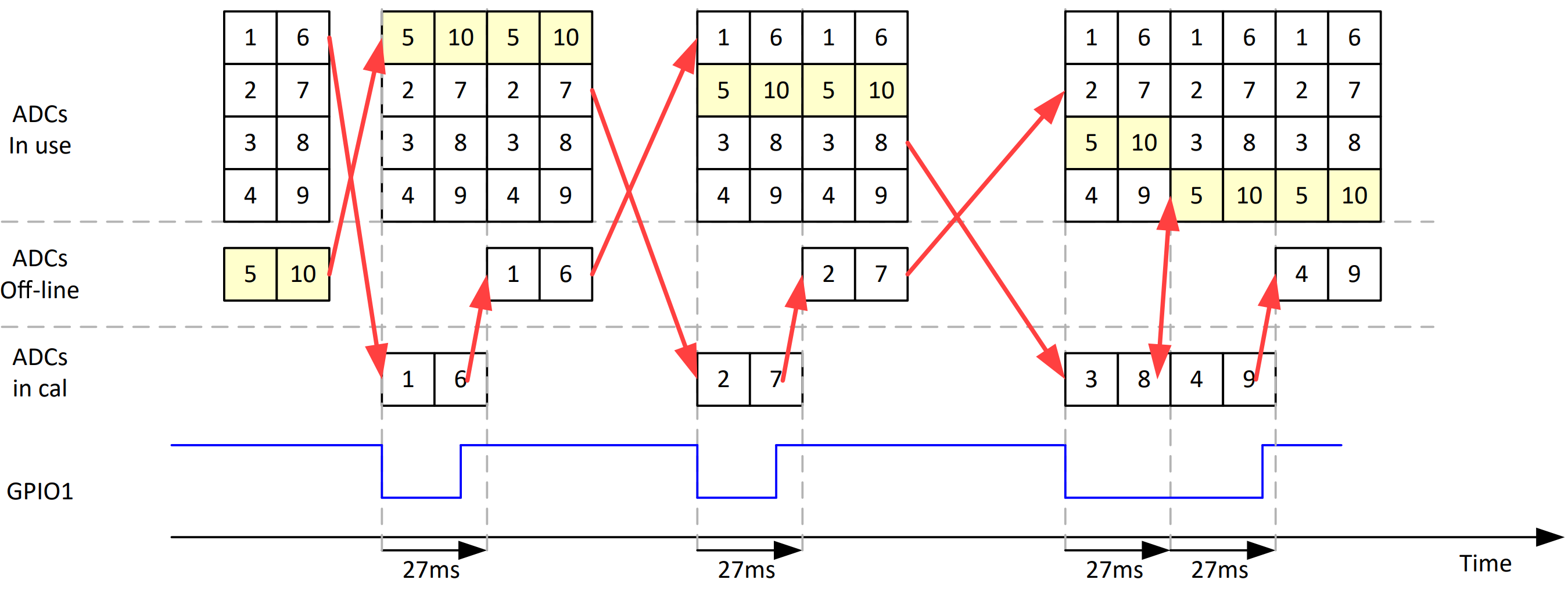 Figure 3-4 ADC32RF55 Core Swap During
Background Calibration
Figure 3-4 ADC32RF55 Core Swap During
Background CalibrationBackground calibration must be configured using SPI by a register field. Some devices, such as the ADC12DJ5200RF support a low-power background calibration (LPBG) mode (as shown previously in Figure 2-1) reducing the overall power used during background calibration, but can increase the transient requirements of the device power supply. In the instance of the ADC32RF55, a GPIO can be configured to temporarily freeze the background calibration, reducing power dissipation during periods of low activity.