SLUU381B September 2009 – February 2022 TPS51220A
8 EVM Assembly Drawing and PCB Layout
The following figures (Figure 8-1 through Figure 8-6) show the design of the TPS51220A EVM-476 printed circuit board. The PCB is 0.062” thick. It uses four layers of copper. The two internal layers are 2-oz copper while the external layers are 1-oz copper.
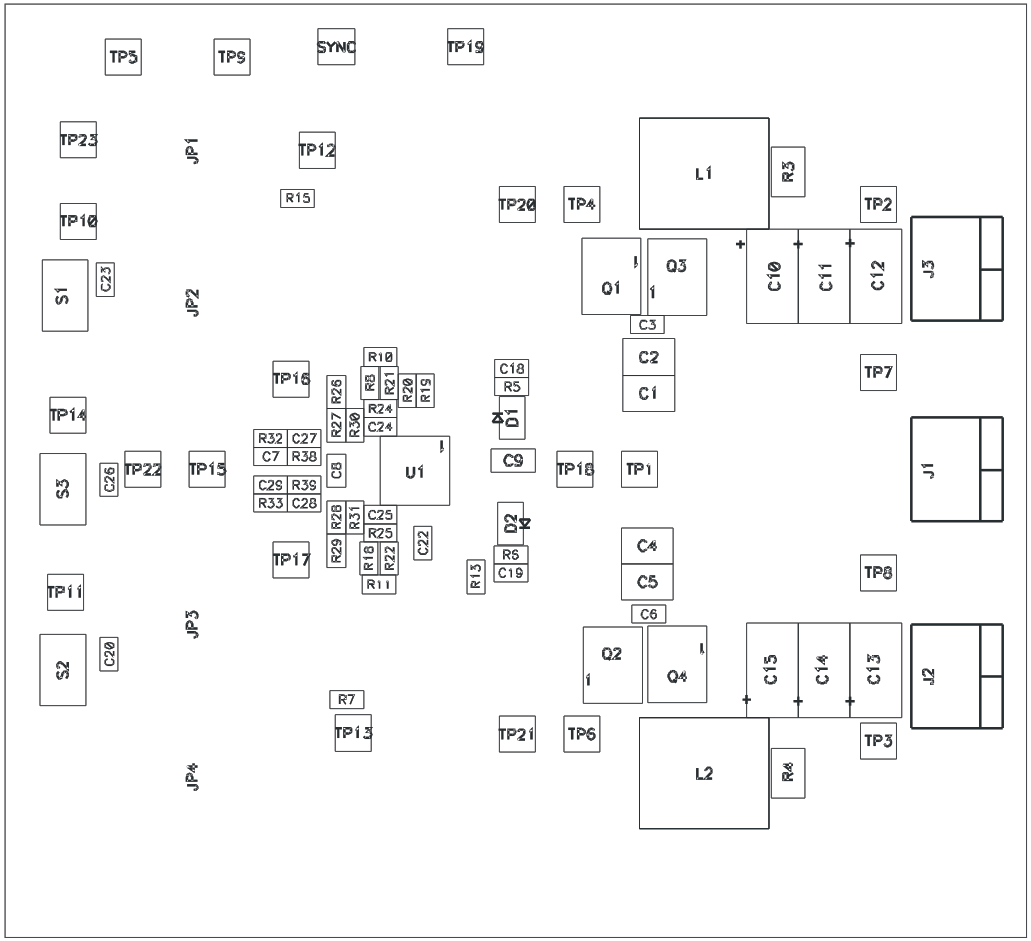 Figure 8-1 Top Layer Assembly
Drawing (Top View)
Figure 8-1 Top Layer Assembly
Drawing (Top View)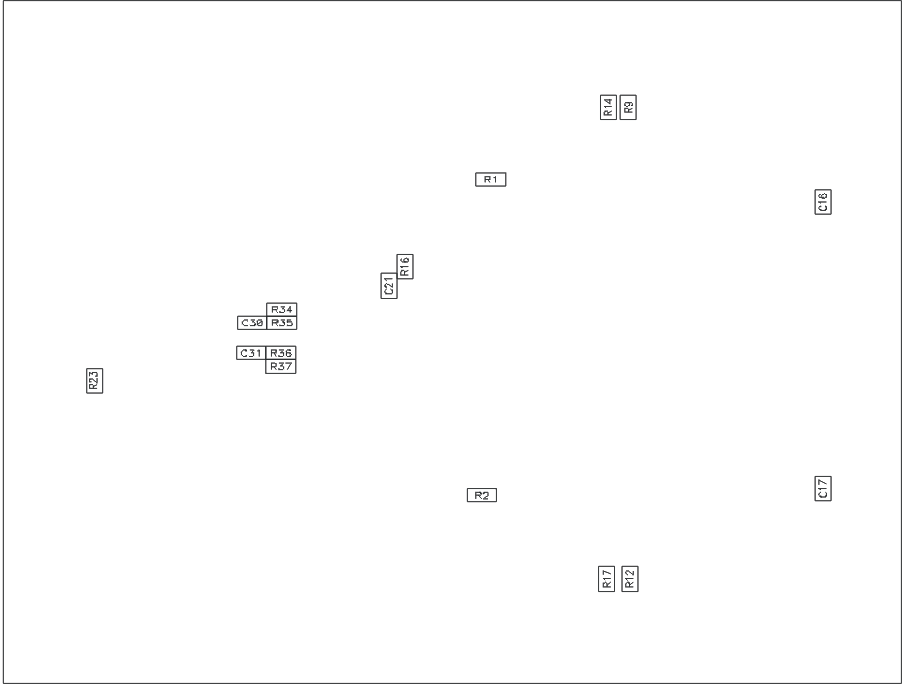 Figure 8-2 Bottom Assembly Drawing
(Top View)
Figure 8-2 Bottom Assembly Drawing
(Top View)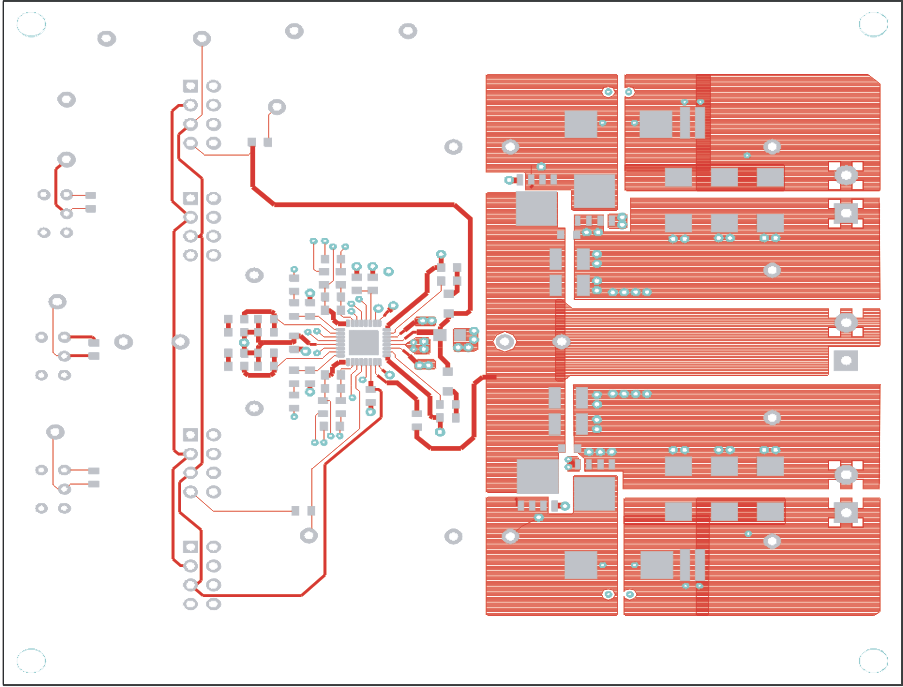 Figure 8-3 Top Copper (Top View)
Figure 8-3 Top Copper (Top View)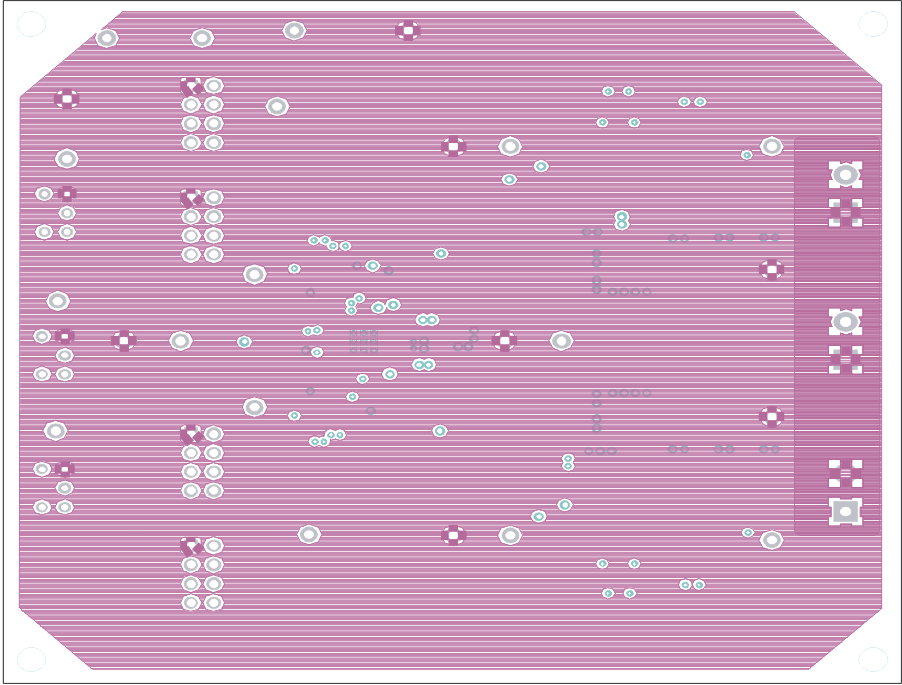 Figure 8-4 Internal Layer 1 (Top View)
Figure 8-4 Internal Layer 1 (Top View) Figure 8-5 Internal Layer 2 (Top View)
Figure 8-5 Internal Layer 2 (Top View) Figure 8-6 Bottom Copper (Top View)
Figure 8-6 Bottom Copper (Top View)