SLVAEX9B April 2022 – August 2022 ESD122 , ESD1LIN24-Q1 , ESD204 , ESD224 , ESD2CAN24-Q1 , ESD2CANFD24 , ESD2CANXL24-Q1 , ESD321 , ESD341 , ESD351 , ESD401 , ESD451 , ESD751 , ESD751-Q1 , ESD752 , ESD761 , ESD761-Q1 , ESD762 , ESDS302 , ESDS304 , ESDS312 , ESDS314 , SN65220 , SN65240 , TPD1E01B04 , TPD1E01B04-Q1 , TPD1E04U04 , TPD1E05U06 , TPD1E05U06-Q1 , TPD1E0B04 , TPD1E10B06 , TPD1E10B09-Q1 , TPD1E1B04 , TPD1E6B06 , TPD2E001 , TPD2E001-Q1 , TPD2E007 , TPD2E009 , TPD2E1B06 , TPD2E2U06 , TPD2EUSB30 , TPD2EUSB30A , TPD2S017 , TPD3E001 , TPD3F303 , TPD4E001 , TPD4E001-Q1 , TPD4E002 , TPD4E004 , TPD4E02B04 , TPD4E02B04-Q1 , TPD4E05U06-Q1 , TPD4E101 , TPD4E110 , TPD4E1B06 , TPD4E1U06 , TPD4E6B06 , TPD4F003 , TPD4S009 , TPD4S012 , TPD5E003 , TPD6E001 , TPD6E004 , TPD6E05U06 , TPD8S009 , TSD05 , TSD05C , TSM24A-Q1 , TSM24CA-Q1 , TSM36A , TVS0500 , TVS0701 , TVS1400 , TVS1401 , TVS2200 , TVS2701 , TVS3301 , UC1611-SP , UC2610 , UC3610 , UC3611 , UC3611M
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Definitions of ESD Device Specifications
- 2ESD Layout Tips
-
3ESD Solutions by Package Types
- 3.1 0201 2-pin SON (TI: DPL) | 0.6 mm x 0.3 mm
- 3.2 0402 2-pin SON (TI: DPY) | 1.0 mm × 0.6 mm
- 3.3 2-pin SOD-523 (TI: DYA) | 1.2 mm x 0.8 mm
- 3.4 3-pin SOT-9X3 (TI: DRT) | 1 mm × 1 mm
- 3.5 3-pin SC70 (TI: DCK) | 2 mm × 1.25 mm
- 3.6 3-pin SOT23 (TI:DBZ) | 3.04 mm × 2.64 mm
- 3.7 4-pin SON (TI: DPW) | 0.8 mm × 0.8 mm
- 3.8 5-pin SOT-5X3 (TI: DRL) | 1.6 mm × 1.2 mm
- 3.9 5-pin SOT-23 (TI: DBV) | 2.9 mm × 1.6 mm
- 3.10 6-pin SON (TI: DRY) | 1.45 mm × 1 mm
- 3.11 6-pin SOT-5X3 (TI: DRL) | 1.6 mm × 1.2 mm
- 3.12 6-pin SOT-23 (TI: DBV) | 1.6 mm × 2.9 mm
- 3.13 6-pin SC70 (TI: DCK) | 2.15 mm × 1.4 mm
- 3.14 8-pin SON (TI: DQD) | 1.35 mm × 1.7 mm
- 3.15 10-pin SON (TI: DQA) | 1 mm × 2.5 mm
- 4References
- 5Revision History
2.3 Routing With VIAs
It is strongly recommended to route traces on the PCB from the ESD source to TVS without switching layers by VIA. Figure 2-3 shows three cases of routing with VIAs.
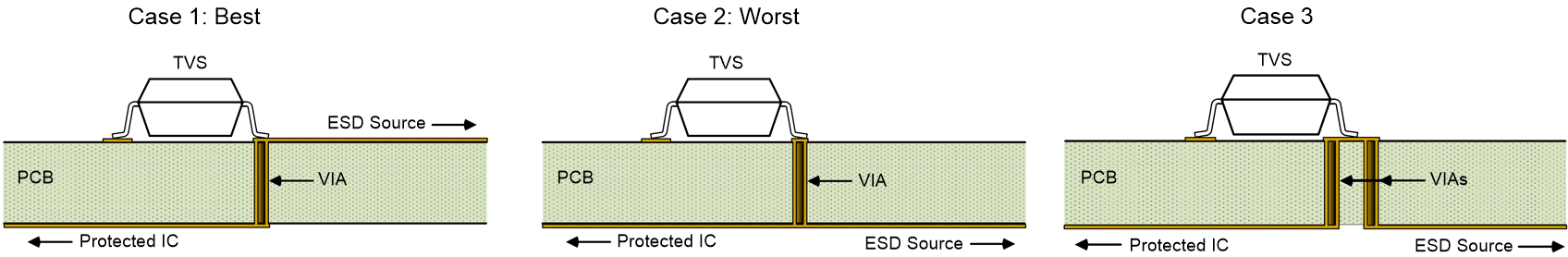 Figure 2-3 Routing With VIAs
Figure 2-3 Routing With VIAsIf VIA is required between the ESD source and the protected IC, Case 1 is the preferred method, Case 2 should be avoided, and Case 3 is acceptable if there is no alternative. In Case 1, IESD is forced to the TVS protection pin before passing through VIA to the protected IC. The VIA correlates to L4 in Figure 2-1. In Case 2, IESD branches between the protected IC and VIA to the TVS protection pin. The VIA correlates to L2 in Figure 2-1. This practice should be avoided as the protected IC can take the brunt of the current during an ESD event. In Case 3, IESD is forced to the protection pin of the TVS before passing to the protected IC. Use these 2 tips when routing with VIAs:
- Avoid VIAs between the ESD source and TVS
- If VIA is required between the ESD source and the protected IC, route directly from the ESD Source to the TVS before using the VIA