SPRAB89A September 2011 – March 2014
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Data Representation
- 3 Calling Conventions
- 4 Data Allocation and Addressing
- 5 Code Allocation and Addressing
- 6 Addressing Model for Dynamic Linking
-
7 Thread-Local Storage Allocation and Addressing
- 7.1 About Multi-Threading and Thread-Local Storage
- 7.2 Terms and Concepts
- 7.3 User Interface
- 7.4 ELF Object File Representation
- 7.5
TLS Access Models
- 7.5.1 C6x Linux TLS Models
- 7.5.2 Static Executable TLS Model
- 7.5.3 Bare-Metal Dynamic Linking TLS Model
- 7.6 Thread-Local Symbol Resolution and Weak References
- 8 Helper Function API
-
9 Standard C Library API
- 9.1 Reserved Symbols
- 9.2 <assert.h> Implementation
- 9.3 <complex.h> Implementation
- 9.4 <ctype.h> Implementation
- 9.5 <errno.h> Implementation
- 9.6 <float.h> Implementation
- 9.7 <inttypes.h> Implementation
- 9.8 <iso646.h> Implementation
- 9.9 <limits.h> Implementation
- 9.10 <locale.h> Implementation
- 9.11 <math.h> Implementation
- 9.12 <setjmp.h> Implementation
- 9.13 <signal.h> Implementation
- 9.14 <stdarg.h> Implementation
- 9.15 <stdbool.h> Implementation
- 9.16 <stddef.h> Implementation
- 9.17 <stdint.h> Implementation
- 9.18 <stdio.h> Implementation
- 9.19 <stdlib.h> Implementation
- 9.20 <string.h> Implementation
- 9.21 <tgmath.h> Implementation
- 9.22 <time.h> Implementation
- 9.23 <wchar.h> Implementation
- 9.24 <wctype.h> Implementation
-
10C++ ABI
- 10.1 Limits (GC++ABI 1.2)
- 10.2 Export Template (GC++ABI 1.4.2)
- 10.3 Data Layout (GC++ABI Chapter 2)
- 10.4 Initialization Guard Variables (GC++ABI 2.8)
- 10.5 Constructor Return Value (GC++ABI 3.1.5)
- 10.6 One-Time Construction API (GC++ABI 3.3.2)
- 10.7 Controlling Object Construction Order (GC++ ABI 3.3.4)
- 10.8 Demangler API (GC++ABI 3.4)
- 10.9 Static Data (GC++ ABI 5.2.2)
- 10.10 Virtual Tables and the Key function (GC++ABI 5.2.3)
- 10.11 Unwind Table Location (GC++ABI 5.3)
-
11Exception Handling
- 11.1 Overview
- 11.2 PREL31 Encoding
- 11.3 The Exception Index Table (EXIDX)
- 11.4 The Exception Handling Instruction Table (EXTAB)
- 11.5 Unwinding Instructions
- 11.6 Descriptors
- 11.7 Special Sections
- 11.8 Interaction With Non-C++ Code
- 11.9 Interaction With System Features
- 11.10 Assembly Language Operators in the TI Toolchain
- 12DWARF
- 13ELF Object Files (Processor Supplement)
- 14ELF Program Loading and Dynamic Linking (Processor Supplement)
-
15Linux ABI
- 15.1 File Types
- 15.2 ELF Identification
- 15.3 Program Headers and Segments
- 15.4 Data Addressing
- 15.5 Code Addressing
- 15.6 Lazy Binding
- 15.7 Visibility
- 15.8 Preemption
- 15.9 Import-as-Own Preemption
- 15.10 Program Loading
- 15.11 Dynamic Information
- 15.12 Initialization and Termination Functions
- 15.13 Summary of the Linux Model
- 16Symbol Versioning
- 17Build Attributes
- 18Copy Tables and Variable Initialization
- 19Extended Program Header Attributes
- 20Revision History
4.1 Data Sections and Segments
In a relocatable object file output by the compiler or assembler, variables are allocated into sections using default rules and compiler directives. A section is an indivisible unit of allocation in a relocatable file. Sections often contain objects with similar properties. Various sections are designated for data, depending on whether the section is initialized, whether it is writable or read-only, how it will be addressed, and what kind of data it contains.
The ABI designates static data sections as near or far. Near sections can be addressed using efficient near DP-relative addressing, but their size and placement is constrained. Conventions for placement of static variables into sections and for how they are addressed are covered in Section 4.3.2.
The linker combines sections from object files to form segments in an ELF load module (executable or shared library). A segment is a continuous range of memory allocated to a load module, representing part of the execution image of the program.
A load module may contain one or more data segments, into which the linker allocates stack, heap, and static variables. Items may be grouped into a single segment or multiple segments, subject only to these restrictions:
- All sections accessed with near DP-relative addressing must be grouped such that they fall within the unsigned 15-bit addressing range of the static base address as defined by _ _C6000_DSBT_BASE.
- All data within a given segment is subject to the same segment attributes (see Chapter 19)
- Within a segment, initialized data must precede uninitialized data. This is a structural constraint of ELF.
- Any additional restrictions imposed by the platform-specific conventions.
A segment is designated as DP-relative if it is accessed using DP-relative addressing. A single DP-relative segment may contain a mixture of near and far addressing, provided it meets the constraints listed previously.
The run-time environment can dynamically allocate or resize uninitialized data segments, to allocate space for items such as the stack and heap.
Figure 4-1 shows the data sections defined by the ABI, and an abstract mapping of sections into segments. The mapping is only representative; the specific configuration may vary by platform or system. Initialized sections are shaded blue; uninitialized sections are shaded gray.
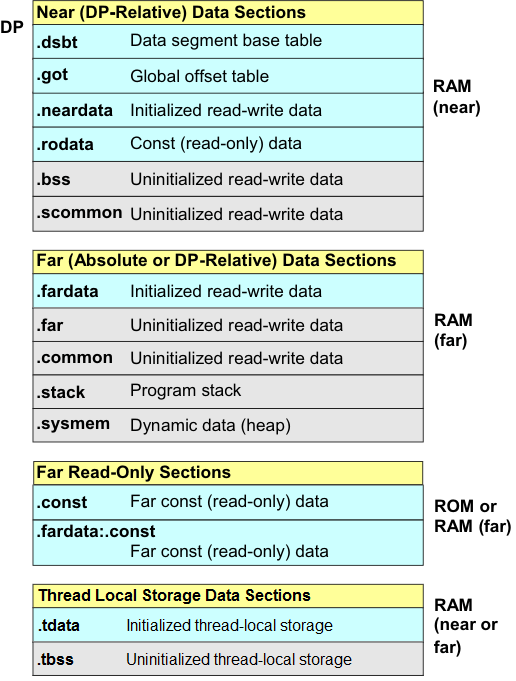 Figure 4-1 Data Sections and Segments (Typical)
Figure 4-1 Data Sections and Segments (Typical)The .const and .fardata:.const sections contain read-only constants. The .const section contains position-independent constants. Depending on the platform, the .const section may be in read-only memory, and may be addressed using absolute addressing, or in position-independent models, relative to code via PC-relative addressing. On some platforms such as Linux that share read-only segments, const objects whose initializers contain address constants cannot be shared. Accordingly, they are placed into a distinct section called .fardata:.const, so named because it can be considered part of .fardata, in the data segment.
The .rodata section contains read-only constants addressable with near DP-relative addressing.
The .neardata and .fardata sections contain initialized read-write variables. These sections correspond to the .data section commonly found on other architectures.
The .bss and .far sections contain uninitialized variables.
The .common and .scommon sections contain common-block symbols allocated by the linker. These are not actual sections in the object files. Instead, the section names are a convention in the linker command file for placing variables. These sections should not be used for other purposes.
The .got and .dsbt sections contain data structures related to dynamic linking. See Chapter 6.
Additional special sections that can be placed by the linker command file are listed in Section 13.4.5.