SSZTAW4 september 2016 CC2640
For many of us using an encyclopedia has become as distant of a relic as listening to an 8-track tape. From researching information to streaming music, smartphones have enhanced our lives, making it easier to run a business, keep in touch with friends and even improve our health. Let’s take a look at one of the latest health benefits: Leveraging a smartphone to monitor glucose levels.
Glucose monitoring has evolved in the last decade from the size of the meter to the type of the meter. Historically slow and bulky meters were used numerous times a day to monitor the amount of glucose in a person’s blood. This progressed to continuous glucose monitoring which provides patients with constant glucose readings from disposable wearable sensors that output data to a hand-held receiver. As technology advanced, near field communication (NFC) was used inside the receiver so when it was placed in close contact with the sensor it would output the glucose reading. Now there is an even better solution that utilizes Bluetooth® low energy.
With Bluetooth low energy technology, glucose sensors can wirelessly send data to a user’s smart phone or tablet making it even easier to constantly monitor glucose levels (Figure 1). This increases patients awareness and with a cellphone in hand, patients can be quickly alerted when their glucose levels are becoming too low or too high (Figure 2). Imagine how proactively you can manage your blood sugar with a cell phone app. Not only can you share your glucose data with your family or spouse to aid with food preparation but you can be alerted around the clock to reduce the amount of stressful emergencies like your blood sugar dropping in the middle of the night.
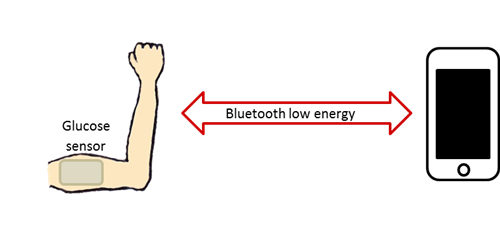 Figure 1 Glucose Monitoring
System
Figure 1 Glucose Monitoring
System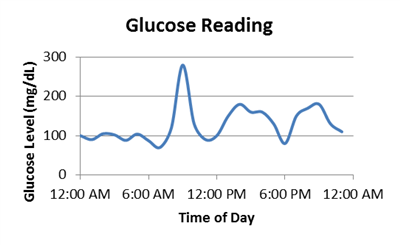 Figure 2 Sample Glucose Tracking
Chart
Figure 2 Sample Glucose Tracking
ChartAs more advancements are made in medical applications like continuous glucose monitors, the goal is to create products that are faster, smaller and less inhibiting to users. Similarly, TI’s latest Bluetooth low energy wireless microcontroller (MCU), the SimpleLink™ CC2640 device, is highly integrated to facilitate the design of smaller and smaller products. The CC2640 wireless MCU is optimized for low current consumption to extend the battery life of sensors and it makes it easy to add Bluetooth low energy functionality to any existing product. TI’s software stack, BLE-Stack2.2, also provides enhanced security and privacy which is critical for health applications. The medical use cases for wireless connectivity are endless from patient monitoring to pulse oximetry even prosthetics.
Next time you’re holding your smartphone try to envision where else Bluetooth low energy can impact your life.
Many medical applications seek to enhance our quality of life and TI is a valued supplier who focuses on quality as well, striving to manufacture devices with longevity. Take a minute to read about TI’s effort to not obsolete products.
Additional Resources:
- Learn more about SimpleLink CC2640 wireless MCU: TI’s latest Bluetooth low energy wireless MCU
- Start development with the SimpleLink™ Bluetooth low energy LaunchPad™ kit
- Download TI’s latest Bluetooth low energy software stack supporting BT4.2