TIDT308 October 2022
3.3 Load Transients
The output voltage variation, during load transients, was measured by supplying the converter at 24 VDC and by switching the load current between 1.25 A and 2 A. For all waveforms, the bandwidth limit of the oscilloscope was set to 20 MHz
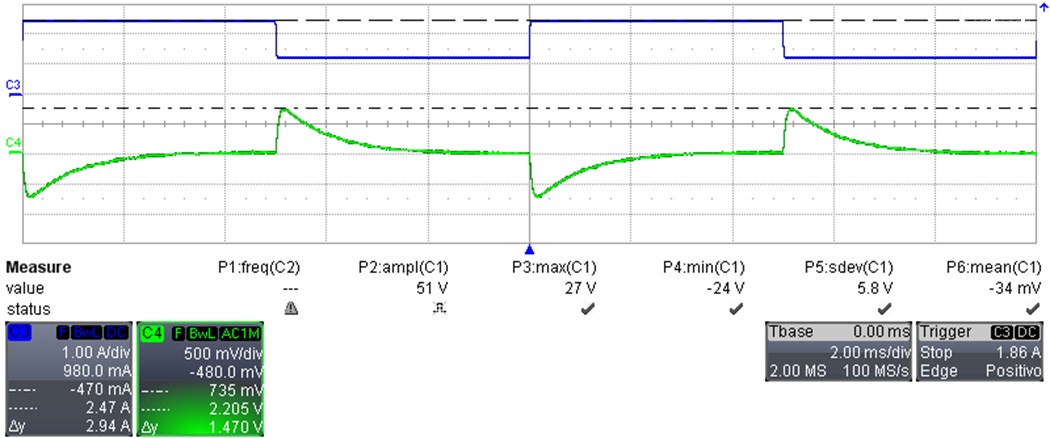 Figure 3-6 Load Transients 1.25 A to 2 A
Figure 3-6 Load Transients 1.25 A to 2 A- Channel C4: Output voltage (500 mV / div, 2 ms / div, AC coupling)
- Channel C3: Output current (1 A / div, DC coupling)