SWRA662A January 2020 – September 2022 AWR1243 , AWR1443 , AWR1642 , AWR1843 , AWR1843AOP , AWR2243 , AWR6843 , AWR6843AOP , IWR1443 , IWR1642 , IWR1843 , IWR6443 , IWR6843 , IWR6843AOP
2.1 FMCW Radar
In FMCW radar a chirp, a signal with a linearly ramping frequency, is generated and transmitted (see Figure 2-1).
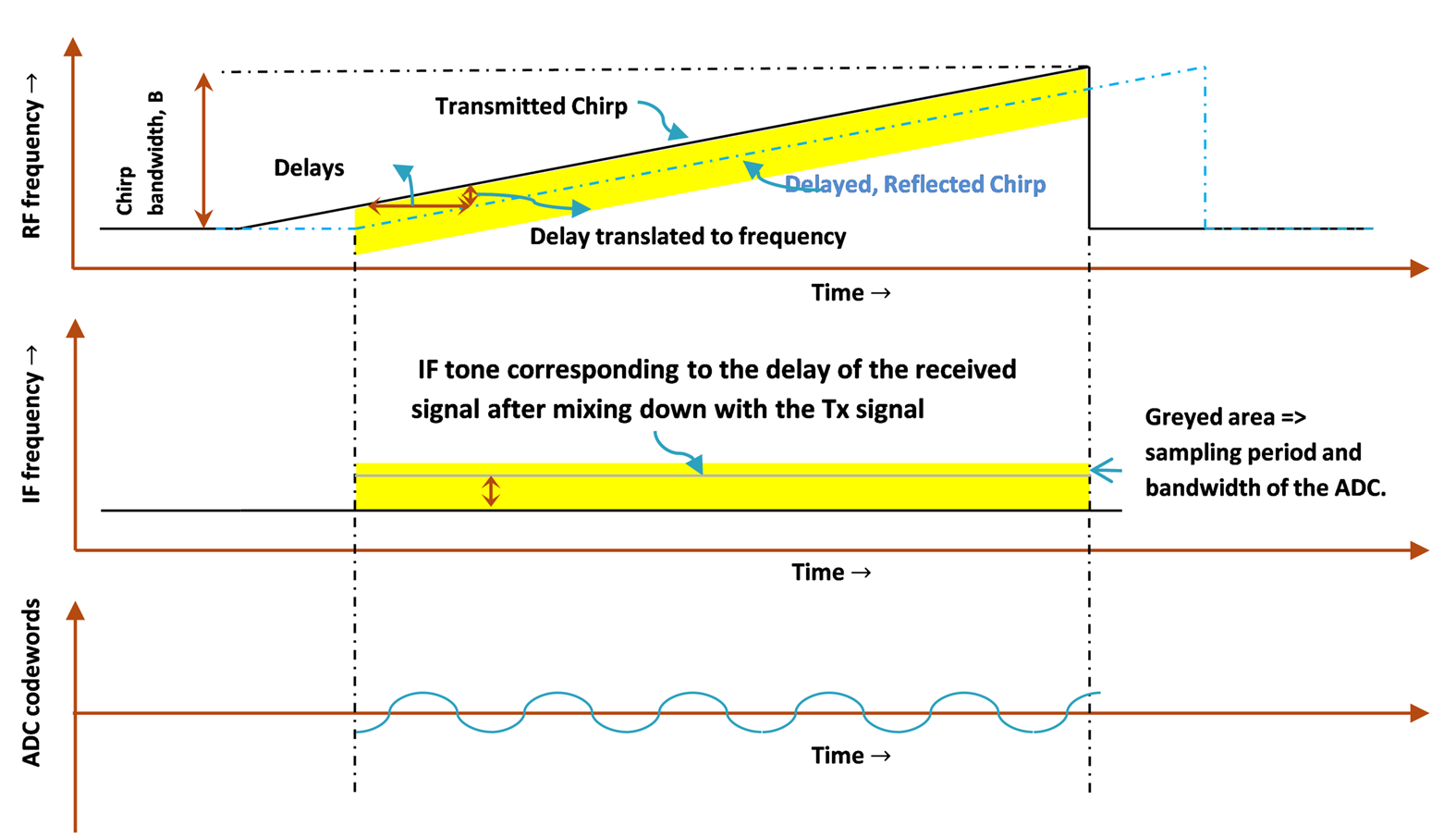 Figure 2-1 FMCW Radar Functionality in Different Domains, RF, IF, and ADC Codewords
Figure 2-1 FMCW Radar Functionality in Different Domains, RF, IF, and ADC CodewordsThis transmitted signal is reflected from targets in its field of view and received at the receiver. The received signal is a delayed copy of the transmitted signal. The signal received is mixed down, using the transmitted signal, and then digitized to create ADC data. Because the reflected signal is a delayed version of the transmitted signal, the mixed down signal corresponds to a sinusoid whose frequency is proportional to this delay. The delay is itself proportional to the distance of the target.
Delays can never be negative. Thus, given a positive slope, all valid objects correspond to positive frequencies. With the tone frequency estimated by a Fourier transform, the delay can be estimated. Using the delay and light speed, the distance to the target can be estimated. Thus, the maximum distance that the receiver can detect is limited by the IF bandwidth. If the target’s frequency exceeds the IF bandwidth, it is filtered out.