SBASA78A March 2021 – October 2021 ADS7067
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 ADS7067 Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YBH|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.8.1 Bit-Walk Test Mode
To enable write access to the configuration registers for diagnostics, write 0x96 in the DIAGNOSTICS_KEY register. To enable bit-walk test mode, configure BITWALK_EN = 1b. In the bit-walk test mode (see Figure 7-1), the sampling switch (SW) remains open and the test voltage is applied on the sampling capacitor (CSH) during the acquisition phase of the ADC. In diagnostic mode, the conversion process of the ADC remains the same as normal device operation. The ADC starts the conversion phase on the rising edge of CS and outputs the code corresponding to the sampled test voltage. The output code of the ADC is expected to be proportional to the test voltage, as shown in Equation 2, after adjusting for DC errors (such as INL, gain error, offset error, and thermal drift of offset and gain errors).
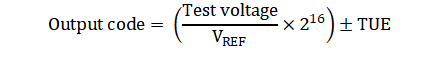
where
- TUE = Total unadjusted error, given by the root sum square of the offset error, gain error, and INL
The test voltage is generated by a DAC configured by the BIT_SAMPLE_MSB and BIT_SAMPLE_LSB registers. Because the test voltage is derived from the ADC reference, as given by Equation 3, this diagnostic mode is not sensitive to variations in reference voltage.
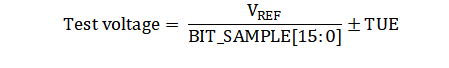
To resume conversion of the ADC input signal, configure BITWALK_EN = 0b.