SLUSFD7 April 2024 BQ25308
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Description (continued)
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Revision History
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
9.2.1.2.3 Inductor Selection
The 1.2-MHz switching frequency allows the use of small inductor and capacitor values. The inductance value is selected based on the maximum input voltage VVBUS_MAX in the application. A 1-µH inductor is recommended if VVBUS_MAX < 6.2V and a 2.2-µH inductor is recommended if VVBUS_MAX > 6.2V. Inductor saturation current ISAT should be higher than the charging current ICHG plus half the ripple current IRIPPLE:
The inductor ripple current IRIPPLE depends on the input voltage (VVBUS), the duty cycle (D = VBAT/VVBUS), the switching frequency (fS), and the inductance (L).
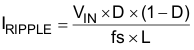
The maximum inductor ripple current occurs when the duty cycle (D) is 0.5 or approximately 0.5.