SLUSCK6C May 2017 – September 2021 BQ25606
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Device Power Up from Battery without Input Source
- 9.3.2 Power Up from Input Source
- 9.3.3 Boost Mode Operation From Battery
- 9.3.4 Power Path Management
- 9.3.5 Battery Charging Management
- 9.3.6 Status Outputs ( PG, STAT)
- 9.3.7 Protections
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
7 Pin Configuration and Functions
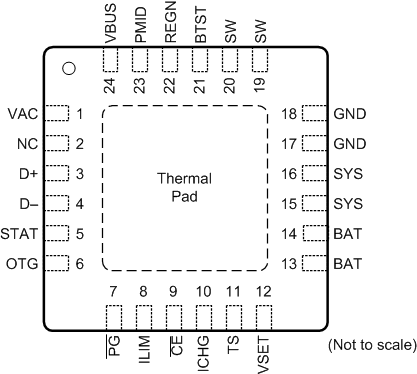 Figure 7-1 BQ25606 RGE Package24-Pin VQFNTop View
Figure 7-1 BQ25606 RGE Package24-Pin VQFNTop ViewTable 7-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| NC | 2 | No connection. This pin must be floating. | |
| BAT | 13 | P | Battery connection point to the positive terminal of the battery pack. The internal current sensing resistor is connected between SYS and BAT. Connect a 10-µF capacitor closely to the BAT pin. |
| 14 | |||
| BTST | 21 | P | PWM high side driver positive supply. internally, the BTST is connected to the cathode of the boost-strap diode. Connect a 0.047-μF bootstrap capacitor from SW to BTST. |
| CE | 9 | DI | Charge enable pin. When this pin is driven low, battery charging is enabled. |
| D+ | 3 | AIO | Positive line of the USB data line pair. D+/D– based USB host/charging port detection. The detection includes data contact detection (DCD), primary and secondary detection in BC1.2 and nonstandard adaptors. |
| D– | 4 | AIO | Negative line of the USB data line pair. D+/D– based USB host/charging port detection. The detection includes data contact detection (DCD), primary and secondary detection in BC1.2 and nonstandard adaptors. |
| GND | 17 | P | Power ground and signal ground. |
| 18 | |||
| ICHG | 10 | AI | ICHG pin sets the charge current limit. A resistor is connected from ICHG pin to ground to set charge current limit as ICHG = KICHG/RICHG. The acceptable range for charge current is 300 mA to 3000 mA. |
| ILIM | 8 | AI | ILIM sets the
input current limit. A resistor is connected from ILIM pin to ground to
set the input current limit as IINDPM =
KILIM/RILIM. The acceptable range for ILIM
current is 500 mA to 3200 mA. The resistor based input current limit is effective only when the input adapter is detected as unknown. Otherwise, the input current limit is determined by D+/D– detection outcome. |
| OTG | 6 | DI | Boost mode enable pin. When this pin is pulled HIGH, OTG is enabled. OTG cannot be floating. |
| PG | 7 | DO | Open drain active low power good indicator. Connect to the pull up rail through a 10-kΩ resistor. LOW indicates a good input if the input voltage is between UVLO and ACOV, above SLEEP mode threshold, and input current limit is above 30 mA. |
| PMID | 23 | P | Connected to the drain of the reverse blocking MOSFET (RBFET) and the drain of HSFET. Connect a 10-μF ceramic capacitor between PMID and GND. |
| REGN | 22 | P | PWM low side driver positive supply output. Internally, REGN is connected to the anode of the boost-strap diode. Connect a 4.7-μF (10-V rating) ceramic capacitor from REGN to analog GND. The capacitor should be placed close to the IC. |
| STAT | 5 | DO | Open-drain
interrupt output. Connect the STAT pin to a logic rail via 10-kΩ
resistor. The STAT pin indicates charger status. Charge in progress: LOW Charge complete or charger in SLEEP mode: HIGH Charge suspend (fault response): Blink at 1 Hz. |
| SW | 19 | P | Switching node connecting to output inductor. Internally SW is connected to the source of the n-channel HSFET and the drain of the n-channel LSFET. Connect a 0.047-μF bootstrap capacitor from SW to BTST. |
| 20 | |||
| SYS | 15 | P | Converter output connection point. The internal current sensing resistor is connected between SYS and BAT. Connect a 20-µF capacitor close to the SYS pin. |
| 16 | |||
| TS | 11 | AI | Temperature qualification voltage input to support JEITA profile. Connect a negative temperature coefficient thermistor. Program temperature window with a resistor divider from REGN to TS to GND. Charge suspends when TS pin voltage is out of range. Recommend 103AT-2 thermistor. |
| VAC | 1 | AI | Input voltage sensing. This pin must be shorted to the VBUS pin. |
| VBUS | 24 | P | Charger input voltage. The internal n-channel reverse block MOSFET (RBFET) is connected between VBUS and PMID with VBUS on source. Place a 1-uF ceramic capacitor from VBUS to GND and place it as close as possible to the IC. |
| VSET | 12 | AI | VSET pin sets
default battery charge voltage in the BQ25606. Program battery
regulation voltage with a resistor pull-down from VSET to GND. RPD > 50 kΩ (float pin) = 4.208 V RPD < 500 Ω (short to GND) = 4.352 V 5 kΩ < RPD < 25 kΩ = 4.400 V |
| Thermal Pad | P | Ground reference for the device that is also the thermal pad used to conduct heat from the device. This connection serves two purposes. The first purpose is to provide an electrical ground connection for the device. The second purpose is to provide a low thermal-impedance path from the device die to the PCB. This pad should be tied externally to a ground plane. | |