SLUSC76C July 2015 – May 2018
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.2
Feature Description
- 9.2.1 Device Power-On-Reset (POR)
- 9.2.2 Device Power Up from Battery without Input Source
- 9.2.3 Device Power Up from Input Source
- 9.2.4 Input Current Optimizer (ICO)
- 9.2.5 Boost Mode Operation from Battery
- 9.2.6 Power Path Management
- 9.2.7 Battery Charging Management
- 9.2.8 Battery Monitor
- 9.2.9 Status Outputs (PG, STAT, and INT)
- 9.2.10 BATET (Q4) Control
- 9.2.11 Current Pulse Control Protocol
- 9.2.12 Input Current Limit on ILIM
- 9.2.13 Thermal Regulation and Thermal Shutdown
- 9.2.14 Voltage and Current Monitoring in Buck and Boost Mode
- 9.2.15 Battery Protection
- 9.2.16 Serial Interface
- 9.3 Device Functional Modes
- 9.4 Register Maps
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Orderable Information
9.2.12 Input Current Limit on ILIM
For safe operation, the device has an additional hardware pin on ILIM to limit maximum input current on ILIM pin. The input maximum current is set by a resistor from ILIM pin to ground as:
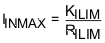
The actual input current limit is the lower value between ILIM setting and register setting (IINLIM). For example, if the register setting is 111111 for 3.25 A, and ILIM has a 260-Ω resistor (KILIM = 390 max.) to ground for 1.5 A, the input current limit is 1.5 A. ILIM pin can be used to set the input current limit rather than the register settings when EN_ILIM bit is set. The device regulates ILIM pin at 0.8 V. If ILIM voltage exceeds 0.8 V, the device enters input current regulation (Refer to Dynamic Power Management section).
The ILIM pin can also be used to monitor input current when EN_ILIM is enabled. The voltage on ILIM pin is proportional to the input current. ILIM pin can be used to monitor the input current following Equation 4:
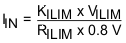
For example, if ILIM pin is set with 260-Ω resistor, and the ILIM voltage is 0.4 V, the actual input current 0.615 A - 0.75 A (based on KILM specified). If ILIM pin is open, the input current is limited to zero since ILIM voltage floats above 0.8 V. If ILIM pin is short, the input current limit is set by the register.
The ILIM pin function can be disabled by setting EN_ILIM bit to 0. When the pin is disabled, both input current limit function and monitoring function are not available.