SLUS696C June 2006 – February 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5
Programming
- 7.5.1 Communicating with the bq26100 Device
- 7.5.2 Memory Descriptions
- 7.5.3 SHA-1 Description
- 7.5.4 Key Programming Description
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRP|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRP|6
Orderable Information
7.5.2.1.1 General Use – Memory Function Commands 0xF0 (Read) and 0x0F (Write)
The general use space is erased to read 0x00. Data written to the general space is ORed with data already present at the address to be written. A bit can only be flipped from 0 to 1.
Table 2. General Memory Space Addressing
| ADDRESSES | FUNCTION |
|---|---|
| 0x007F – 0x0060 | Page 3 – 32 bytes general use |
| 0x005F – 0x0040 | Page 2 – 32 bytes general use |
| 0x003F – 0x0020 | Page 1 – 32 bytes general use |
| 0x001F – 0x0000 | Page 0 – 32 bytes general use |
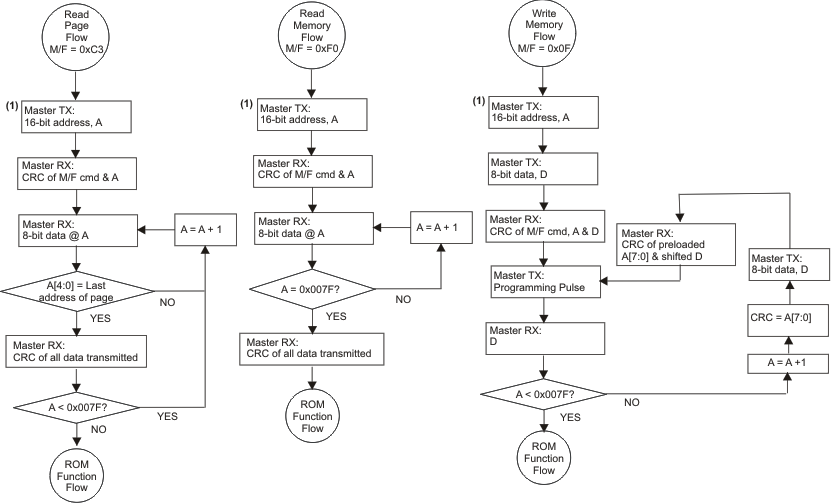
1. 16-Bit address is sent with lower 8-bit address followed by higher 8-bit address with least significant bit first.
Figure 12. General Memory OTP Write/Read Flows