SLUSBB8A December 2012 – June 2016
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Tables
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Qi Wireless Power System and bq51010B Power Transfer Flow Diagrams
- 8.3.2 Dynamic Rectifier Control
- 8.3.3 Dynamic Efficiency Scaling
- 8.3.4 RILIM Calculations
- 8.3.5 Input Overvoltage
- 8.3.6 Adapter Enable Functionality and EN1 or EN2 Control
- 8.3.7 End Power Transfer Packet (WPC Header 0x02)
- 8.3.8 Status Outputs
- 8.3.9 WPC Communication Scheme
- 8.3.10 Communication Modulator
- 8.3.11 Adaptive Communication Limit
- 8.3.12 Synchronous Rectification
- 8.3.13 Temperature Sense Resistor Network (TS)
- 8.3.14 3-State Driver Recommendations For the TS-CTRL Pin
- 8.3.15 Thermal Protection
- 8.3.16 WPC 1.1 Compliance - Foreign Object Detection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFP|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltage | AC1, AC2 | –0.8 | 20 | V |
| RECT, COM1, COM2, OUT, WPG, CLAMP1, CLAMP2 | –0.3 | 20 | ||
| AD, AD-EN | –0.3 | 30 | ||
| BOOT1, BOOT2 | –0.3 | 26 | ||
| EN1, EN2, TERM, FOD, TS-CTRL, ILIM | –0.3 | 7 | ||
| Input current | AC1, AC2 | 1.5 | A(RMS) | |
| Output current | OUT | 750 | mA | |
| Output sink current | WPG | 15 | mA | |
| COM1, COM2 | 1 | A | ||
| Junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages are with respect to the VSS terminal, unless otherwise noted.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 (1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101 (2) | ±500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRECT | Voltage range | RECT | 4 | 10 | V |
| IRECT | Current through internal rectifier | RECT | 1 | A | |
| IOUT | Output current | OUT | 750 | mA | |
| IAD-EN | Sink current | AD-EN | 1 | mA | |
| ICOMM | COMM sink current | COMM | 400 | mA | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | 0 | 125 | °C | |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC (1) | bq51010B | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| YFP (DSBGA) | |||
| 28 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 58.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 0.2 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 9.1 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 1.4 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 8.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range, 0°C to 125°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UVLO | Undervoltage lockout | VRECT = 0 V to 3 V | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.8 | V | |
| VHYS | Hysteresis on UVLO | VRECT = 3 V to 2 V | 250 | mV | |||
| Hysteresis on OVP | VRECT = 16 V to 5 V | 150 | |||||
| VRECT | Input overvoltage threshold | VRECT = 5 V to 16 V | 14.5 | 15 | 15.5 | V | |
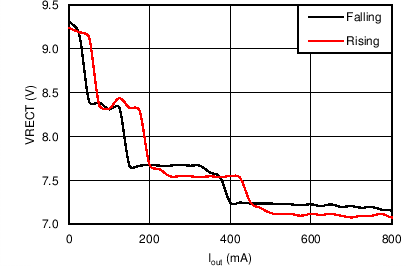
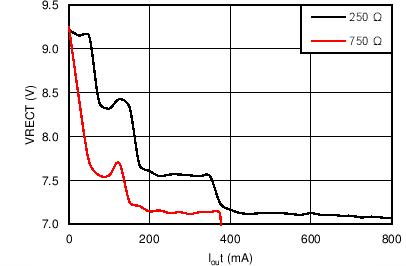
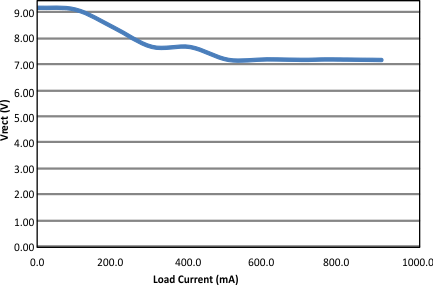
| VRECT-REG | Dynamic VRECT threshold 1 | ILOAD < 0.1 × IIMAX (ILOAD rising) | 9.08 | V | |||
| Dynamic VRECT threshold 2 | 0.1 × IIMAX < ILOAD < 0.2 × IIMAX
(ILOAD rising) |
8.28 | |||||
| Dynamic VRECT threshold 3 | 0.2 × IIMAX < ILOAD < 0.4 × IIMAX
(ILOAD rising) |
7.53 | |||||
| Dynamic VRECT threshold 4 | ILOAD > 0.4 × IIMAX (ILOAD rising) | 7.11 | |||||
| VRECT tracking | In current limit voltage above VOUT | VO + 0.25 | |||||
| ILOAD | ILOAD hysteresis for dynamic VRECT thresholds as a percentage of IILIM | ILOAD falling | 4% | ||||
| VRECT-DPM | Rectifier undervoltage protection, restricts IOUT at VRECT-DPM | 3 | 3.1 | 3.2 | V | ||
| VRECT-REV | Rectifier reverse voltage protection at the output | VRECT-REV = VOUT – VRECT, VOUT = 10 V |
8 | 9 | V | ||
| QUIESCENT CURRENT | |||||||
| IRECT | Active chip quiescent current consumption from RECT | ILOAD = 0 mA, 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C | 8 | 10 | mA | ||
| ILOAD = 300 mA, 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C |
2 | 3 | |||||
| IOUT | Quiescent current at the output when wireless power is disabled (standby) | VOUT = 7 V, 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C | 28 | 40 | µA | ||
| ILIM SHORT CIRCUIT | |||||||
| RILIM | Highest value of ILIM resistor considered a fault (short). Monitored for IOUT > 100 mA | RILIM = 200 Ω to 50 Ω. IOUT latches off, cycle power to reset | 120 | Ω | |||
| tDGL | Deglitch time transition from ILIM short to IOUT disable | 1 | ms | ||||
| ILIM_SC | ILIM-SHORT,OK enables the ILIM short comparator when IOUT is greater than this value | ILOAD = 0 mA to 200 mA | 110 | 145 | 165 | mA | |
| Hysteresis for ILIM-SHORT,OK comparator | ILOAD = 0 mA to 200 mA | 30 | |||||
| IOUT | Maximum output current limit, CL | Maximum ILOAD that is delivered for 1 ms when ILIM is shorted | 2.45 | A | |||
| OUTPUT | |||||||
| VOUT-REG | Regulated output voltage | ILOAD = 750 mA | 6.9 | 6.96 | 7.02 | V | |
| ILOAD = 10 mA | 6.9 | 6.95 | 7.05 | ||||
| KILIM | Current programming factor for hardware protection | RLIM = KILIM / IILIM, where IILIM is the hardware current limit. IOUT = 750 mA |
303 | 314 | 322 | AΩ | |
| KIMAX | Current programming factor for the nominal operating current | IIMAX = KIMAX / RLIM, where IMAX is the maximum normal operating current. IOUT = 750 mA | 262 | AΩ | |||
| IOUT | Current limit programming range | 1.5 | A | ||||
| ICOMM | Current limit during WPC communication | IOUT > 300 mA | IOUT + 50 | mA | |||
| IOUT < 300 mA | 343 | 378 | 425 | ||||
| tHOLD | Hold off time for the communication current limit during start-up | 1 | s | ||||
| TS / CTRL | |||||||
| VTS | Internal TS bias voltage | ITS-Bias < 100 µA (periodically driven see tTS-CTRL) | 2 | 2.2 | 2.4 | V | |
| VCOLD | Rising threshold | VTS = 50% to 60% | 56.5% | 58.7% | 60.8% | VTS-Bias | |
| Falling hysteresis | VTS = 60% to 50% | 2% | |||||
| VHOT | Falling threshold | VTS = 20% to 15% | 18.5% | 19.6% | 20.7% | VTS-Bias | |
| Rising hysteresis | VTS = 15% to 20% | 3% | |||||
| VCTRL | CTRL pin threshold for a high | VTS/CTRL = 50 mV to 150 mV | 80 | 100 | 130 | mV | |
| CTRL pin threshold for a low | VTS/CTRL = 150 mV to 50 mV | 50 | 80 | 100 | |||
| tTS-CTRL | Time VTS-Bias is active when TS measurements occur | Synchronous to the communication period | 24 | ms | |||
| tTS | Deglitch time for all TS comparators | 10 | ms | ||||
| RTS | Pullup resistor for the NTC network. Pulled up to the voltage bias | 18 | 20 | 22 | kΩ | ||
| THERMAL PROTECTION | |||||||
| TJ | Thermal shutdown temperature | 155 | °C | ||||
| Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 20 | ||||||
| OUTPUT LOGIC LEVELS ON WPG | |||||||
| VOL | Open drain WPG pin | ISINK = 5 mA | 500 | mV | |||
| IOFF | WPG leakage current when disabled | V WPG = 20 V | 1 | µA | |||
| COMM PIN | |||||||
| RDS(ON) | COM1 and COM2 | VRECT = 2.6 V | 1.5 | Ω | |||
| fCOMM | Signaling frequency on COMM pin | 2 | Kb/s | ||||
| IOFF | Comm pin leakage current | VCOM1 = 20 V, VCOM2 = 20 V | 1 | µA | |||
| CLAMP PIN | |||||||
| RDS(ON) | Clamp1 and Clamp2 | 0.8 | Ω | ||||
| ADAPTER ENABLE | |||||||
| V AD-EN | VAD rising threshold voltage. EN-UVLO | VAD = 0 V to 5 V | 3.5 | 3.6 | 3.8 | V | |
| V AD-EN hysteresis, EN-HYS | VAD = 5 V to 0 V | 400 | mV | ||||
| IAD | Input leakage current | VRECT = 0 V, VAD = 5 V | 60 | μA | |||
| RAD | Pullup resistance from AD-EN to OUT when adapter mode is disabled and VOUT > VAD, EN-OUT | VAD = 0 V, VOUT = 5 V | 200 | 350 | Ω | ||
| VAD | Voltage difference between VAD and V AD-EN when adapter mode is enabled, EN-ON | VAD = 5 V, 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 85°C | 3 | 4.5 | 5 | V | |
| SYNCHRONOUS RECTIFIER | |||||||
| IOUT | IOUT at which the synchronous rectifier enters half-synchronous mode, SYNC_EN | ILOAD = 200 mA to 0 mA | 80 | 100 | 130 | mA | |
| Hysteresis for IOUT,RECT-EN (full-synchronous mode enabled) | ILOAD = 0 mA to 200 mA | 25 | |||||
| VHS-DIODE | High-side diode drop when the rectifier is in half-synchronous mode | IAC-VRECT = 250 mA and TJ = 25°C |
0.7 | V | |||
| EN1 AND EN2 | |||||||
| VIL | Input low threshold for EN1 and EN2 | 0.4 | V | ||||
| VIH | Input high threshold for EN1 and EN2 | 1.3 | V | ||||
| RPD | EN1 and EN2 pull down resistance | 200 | kΩ | ||||
| ADC (WPC RELATED MEASUREMENTS AND COEFFICIENTS) | |||||||
| IOUT SENSE | Accuracy of the current sense over the load range | IOUT = 0 mA to 750 mA | –1.5% | 0% | 0.9% | ||
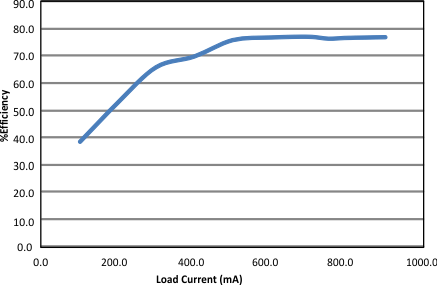
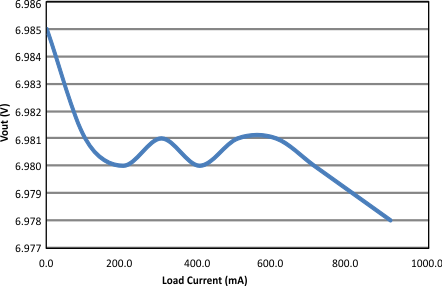
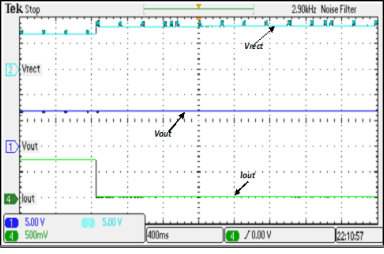
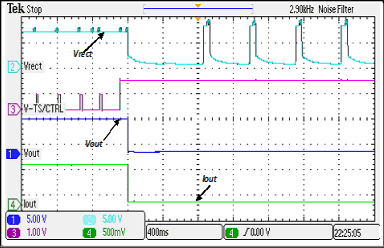
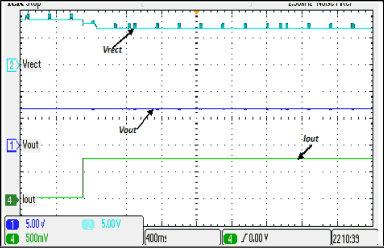
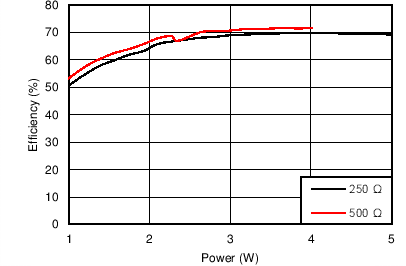
7.6 Typical Characteristics