SLPS574B February 2016 – April 2018 CSD87335Q3D
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- 4Revision History
- 5Specifications
- 6Applications and Implementation
- 7Recommended PCB Design Overview
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DQZ|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
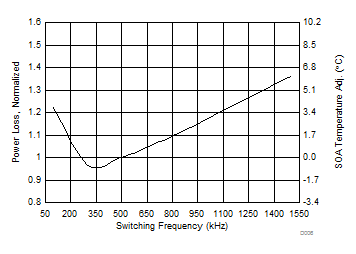
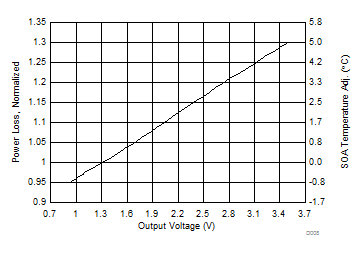
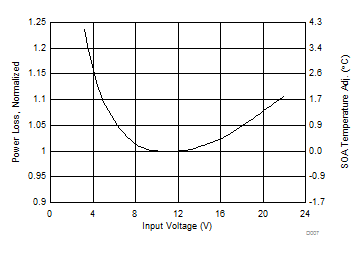
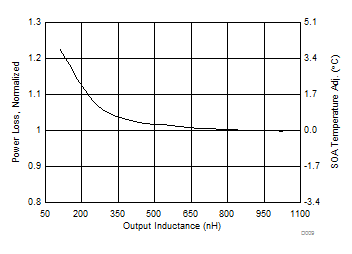
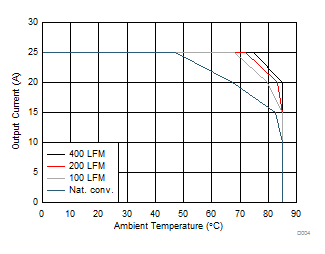
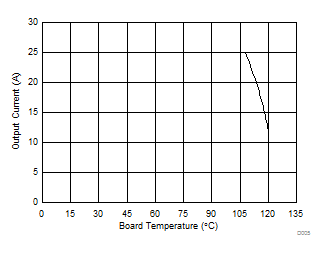
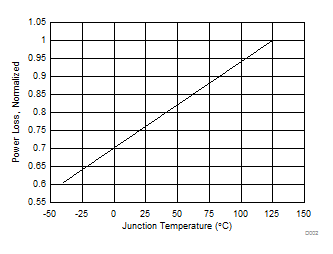
5.6 Typical Power Block Device Characteristics
Test conditions: VIN = 12 V, VDD = 5 V, ƒSW = 500 kHz, VOUT = 1.3 V, LOUT = 950 nH, IOUT = 25 A, TJ = 125°C, unless stated otherwise.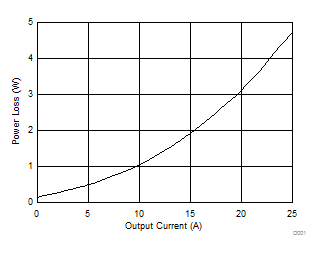
1. The Typical Power Block System Characteristic curves are based on measurements made on a PCB design with dimensions of 4 in (W) × 3.5 in (L) × 0.062 in (H) and 6 copper layers of 1-oz copper thickness. See Applications and Implementation section for detailed explanation.